Abstract
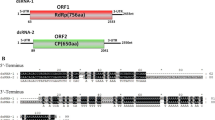
To our knowledge, no mycoviruses have been reported in Fusarium cerealis. Here, we describe a novel double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) virus, Fusarium cerealis partitivirus 1 (FcPV1), isolated from F. cerealis strain HN30 from Henan Province, China. The FcPV1 genome consists of two dsRNA segments, 1732 bp (dsRNA1) and 1361 bp (dsRNA2) in length, each containing a single open reading frame potentially encoding a 61.0-kDa protein and a 42.0-kDa protein, respectively. dsRNA1 encodes a putative RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), while the dsRNA2 product has no significant similarity to any other capsid proteins (CPs) in the GenBank databases other than limited similarity to hypothetical “capsid” proteins of a few partitiviruses. Sequence alignments and phylogenetic analysis showed that FcPV1 is related to members of the newly proposed genus “Zetapartitivirus” in the family Partitiviridae.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmagid A, Hafez M, Lawley Y, Adam LR, Daayf F (2018) First report of Fusarium cerealis causing root rot on soybean. Plant Dis 102:2638
Amarasinghe CC, Tittlemier SA, Fernando WGD (2014) Nivalenol producing Fusarium cerealis associated with Fusarium head blight in winter wheat in Manitoba, Canada. Plant Pathol 64:988–995
Chiba S, Salaipeth L, Lin Y-H, Sasaki A, Kanematsu S, Suzuki N (2009) A novel bipartite double-stranded RNA mycovirus from the white root rot fungus Rosellinia necatrix: molecular and biological characterization, taxonomic considerations, and potential for biological control. J Virol 83:12801–12812
Gachango E, Hanson LE, Rojas A, Hao JJ, Kirk WW (2012) Fusarium spp. causing dry rot of seed potato tubers in Michigan and their sensitivity to fungicides. Plant Dis 96:1767–1774
Gao J, Wang Y, Guan Y, Chen C (2014) Fusarium cerealis, a new pathogen causing ginseng (Panax ginseng) root rot in China. Plant Dis 98:1433
Ghabrial SA, Castón JR, Jiang D, Nibert ML, Suzuki N (2015) 50-plus years of fungal viruses. Virology 479:356–368
Jiang Y, Wang J, Yang B, Wang Q, Yu W (2019) Molecular characterization of a debilitation-associated partitivirus infecting the pathogenic fungus Aspergillus flavus. Front Microbiol 10:626
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Nerva L, Silvestri A, Ciuffo M, Palmano S, Varese GC, Turina M (2017) Transmission of Penicillium aurantiogriseum partiti-like virus 1 to a new fungal host (Cryphonectria parasitica) confers higher resistance to salinity and reveals adaptive genomic changes. Environ Microbiol 19:4480–4492
Nibert ML, Ghabrial SA, Maiss E, Lesker T, Vainio EJ, Jiang D, Suzuki N (2014) Taxonomic reorganization of family Partitiviridae and other recent progress in partitivirus research. Virus Res 188:128–141
Schiwek S, Beule L, Vinas M, Pfordt A, von Tiedemann A, Karlovsky P (2020) High-resolution melting (HRM) curve assay for the identification of eight Fusarium species causing ear rot in maize. Pathogens 9:270
Tangni EK (2015) Fusarium cerealis, a single phylogenetic species recovered annually from maize in Belgium and producing a wide range of mycotoxins. In: European Fusarium Selminar
Vainio EJ, Chiba S, Ghabrial SA, Maiss E, Roossinck M, Sabanadzovic S, Suzuki N, Xie J, Nibert M (2018) ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Partitiviridae. J Gen Virol 99:17–18
Wang S, Kondo H, Liu L, Guo L, Qiu D (2013) A novel virus in the family Hypoviridae from the plant pathogenic fungus Fusarium graminearum. Virus Res 174:69–77
Wang L, Zhang J, Zhang H, Qiu D, Guo L (2016) Two novel relative double-stranded RNA mycoviruses infecting Fusarium poae strain SX63. Int J Mol Sci 17:641
Xie J, Jiang D (2014) New insights into mycoviruses and exploration for the biological control of crop fungal diseases. Annu Rev Phytopathol 52:45–68
Zhang H, Chen W, Xu J, Xu J, Feng J (2011) First report of Fusarium cerealis causing Fusarium head blight on barley in China. Plant Dis 95:774
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0200500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies involving human participants or animals.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Ioly Kotta-Loizou.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1 (A)
Multiple alignment of the sequences of the conserved motifs in hypothetical proteins of FcPV1 and other homologous dsRNA viruses. Full names and accession numbers of selected viruses are as follows: AfPV1, Aspergillus flavus partitivirus 1 (QDE53635.1); BdV1, Botryosphaeria dothidea virus 1 (AIE47695.1); CaPV1, Colletotrichum acutatum partitivirus (AGL42313.1); CgRV1, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides RNA virus 1 (QED88096.1); PmPV1, Phoma matteucciicola partitivirus 1 (QDK65070.1); UvPV1, Ustilaginoidea virens partitivirus 1 (AGO04404.1). (B) Phylogenetic analysis based on protein sequences encoded by dsRNA2 of FcPV1 and other members of the family Partitiviridae. Bootstrap values higher than 60% are shown. The neighbor-joining (NJ) tree was constructed in MEGA 7.0 with 1000 bootstrap replicates. FcPV1 is indicated by a red circle (TIFF 7572 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, I., Li, P., Zhang, L. et al. First report of a novel partitivirus from the phytopathogenic fungus Fusarium cerealis in China. Arch Virol 165, 2979–2983 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04802-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04802-4