Abstract
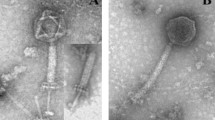
P59, a virulent phage of Bacillus oceanisediminis, was isolated from the sediment of Weiming Lake at Peking University (Beijing, China). P59 showed the typical morphology of myovirids. The complete genome sequence of P59 is 159,363 bp in length with a G+C content of 42.34%. The genome sequence has very low similarity to the other phage genome sequences in the GenBank database, suggesting that P59 is a new phage. A total of 261 open reading frames and 15 tRNA genes were predicted. Based on its morphological and genetic traits, we propose phage P59 to be a new member of the family Herelleviridae.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dion MB, Oechslin F, Moineau S (2020) Phage diversity, genomics and phylogeny. Nat Rev Microbiol 18(3):125–138. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-019-0311-5
Salmond GP, Fineran PC (2015) A century of the phage: past, present and future. Nat Rev Microbiol 13(12):777–786. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3564
Hernandez-Gonzalez IL, Moreno-Hagelsieb G, Olmedo-Alvarez G (2018) Environmentally-driven gene content convergence and the Bacillus phylogeny. BMC Evol Biol 18(1):148. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-018-1261-7
Saxena AK, Kumar M, Chakdar H, Anuroopa N, Bagyaraj DJ (2020) Bacillus species in soil as a natural resource for plant health and nutrition. J Appl Microbiol 128(6):1583–1594. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14506
Dunne M, Hupfeld M, Klumpp J, Loessner MJ (2018) Molecular basis of bacterial host interactions by gram-positive targeting bacteriophages. Viruses 10(8):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080397
Krasowska A, Biegalska A, Augustyniak D, Los M, Richert M, Lukaszewicz M (2015) Isolation and characterization of phages infecting Bacillus subtilis. Biomed Res Int 2015:179597. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/179597
Fu Y, Deng S, Liang L, Wu Y, Gao M (2019) Complete genome sequence of the novel phage vB_BthS-HD29phi infecting Bacillus thuringiensis. Arch Virol 164(12):3089–3093. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04416-5
Kong L, Ding Y, Wu Q, Wang J, Zhang J, Li H, Yu S, Yu P, Gao T, Zeng H, Yang M, Liang Y, Wang Z, Xie Z, Wang Q (2019) Genome sequencing and characterization of three Bacillus cereus-specific phages, DK1, DK2, and DK3. Arch Virol 164(7):1927–1929. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04258-1
Zhang J, Wang J, Fang C, Song F, Xin Y, Qu L, Ding K (2010) Bacillus oceanisediminis sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60(12):2924–2929. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.019851-0
Lee YJ, Lee SJ, Jeong H, Kim HJ, Ryu N, Kim BC, Lee HS, Lee DW, Lee SJ (2012) Draft genome sequence of Bacillus oceanisediminis 2691. J Bacteriol 194(22):6351–6352. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01643-12
Peng F, Mi Z, Huang Y, Yuan X, Niu W, Wang Y, Hua Y, Fan H, Bai C, Tong Y (2014) Characterization, sequencing and comparative genomic analysis of vB_AbaM-IME-AB2, a novel lytic bacteriophage that infects multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. BMC Microbiol 14:181. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-14-181
Wang R, Xing S, Zhao F, Li P, Mi Z, Shi T, Liu H, Tong Y (2018) Characterization and genome analysis of novel phage vB_EfaP_IME195 infecting Enterococcus faecalis. Virus Genes 54(6):804–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-018-1608-6
Zhang W, Mi Z, Yin X, Fan H, An X, Zhang Z, Chen J, Tong Y (2013) Characterization of Enterococcus faecalis phage IME-EF1 and its endolysin. PLoS ONE 8(11):e80435. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080435
Wang H, Guo Z, Feng H, Chen Y, Chen X, Li Z, Hernandez-Ascencio W, Dai X, Zhang Z, Zheng X, Mora-Lopez M, Fu Y, Zhang C, Zhu P, Huang L (2018) Novel Sulfolobus virus with an exceptional capsid architecture. J Virol 92(5):e01727–e1817. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01727-17
Coil D, Jospin G, Darling AE (2015) A5-miseq: an updated pipeline to assemble microbial genomes from Illumina MiSeq data. Bioinformatics 31(4):587–589. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu661
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19(5):455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Besemer J, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M (2001) GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucleic Acids Res 29(12):2607–2618. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.12.2607
Lowe TM, Chan PP (2016) tRNAscan-SE On-line: integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 44(W1):W54–57. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw413
Barylski J, Enault F, Dutilh BE, Schuller MB, Edwards RA, Gillis A, Klumpp J, Knezevic P, Krupovic M, Kuhn JH, Lavigne R, Oksanen HM, Sullivan MB, Jang HB, Simmonds P, Aiewsakun P, Wittmann J, Tolstoy I, Brister JR, Kropinski AM, Adriaenssens EM (2020) Analysis of spounaviruses as a case study for the overdue reclassification of tailed phages. Syst Biol 69(1):110–123. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syz036
Barylski J, Kropinski AM, Alikhan NF, Adriaenssens EM, Consortium IR (2020) ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Herelleviridae. J Gen Virol 101(4):362–363. https://doi.org/10.1099/jgv.0.001392
Zhao X, Shen M, Jiang X, Shen W, Zhong Q, Yang Y, Tan Y, Agnello M, He X, Hu F, Le S (2017) Transcriptomic and metabolomics profiling of phage-host interactions between phage PaP1 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front Microbiol 8:548. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00548
Gao EB, Huang Y, Ning D (2016) Metabolic genes within cyanophage genomes: implications for diversity and evolution. Genes (Basel) 7(10):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7100080
Dwivedi B, Xue B, Lundin D, Edwards RA, Breitbart M (2013) A bioinformatic analysis of ribonucleotide reductase genes in phage genomes and metagenomes. BMC Evol Biol 13:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-13-33
Morgado S, Vicente AC (2019) Global in-silico scenario of tRNA genes and their organization in virus genomes. Viruses 11(2):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020180
Bailly-Bechet M, Vergassola M, Rocha E (2007) Causes for the intriguing presence of tRNAs in phages. Genome Res 17(10):1486–1495. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.6649807
Delesalle VA, Tanke NT, Vill AC, Krukonis GP (2016) Testing hypotheses for the presence of tRNA genes in mycobacteriophage genomes. Bacteriophage 6(3):e1219441. https://doi.org/10.1080/21597081.2016.1219441
Xu YL, Zhang R, Wang NN, Cai LL, Tong YG, Sun Q, Chen F, Jiao NZ (2018) Novel phage-host interactions and evolution as revealed by a cyanomyovirus isolated from an estuarine environment. Environ Microbiol 20(8):2974–2989. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.14326
Lancaster JC, Hodde MK, Hernandez AC, Kuty Everett GF (2015) Complete genome sequence of Bacillus megaterium myophage mater. Genome Announc 3(1):e01424–e1514. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01424-14
Miller SY, Colquhoun JM, Perl AL, Chamakura KR, Kuty Everett GF (2013) Complete genome of Bacillus subtilis myophage grass. Genome Announc 1(6):e00857–e913. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00857-13
Cadungog JN, Khatemi BE, Hernandez AC, Kuty Everett GF (2015) Complete genome sequence of Bacillus megaterium myophage moonbeam. Genome Announc 3(1):e01428–e1514. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01428-14
Burton BM, Marquis KA, Sullivan NL, Rapoport TA, Rudner DZ (2007) The ATPase SpoIIIE transports DNA across fused septal membranes during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Cell 131(7):1301–1312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.009
Sullivan MJ, Petty NK, Beatson SA (2011) Easyfig: a genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 27(7):1009–1010. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr039
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Liu GY, Lin X, Xu SY, Liu G, Liu F, Mu W (2020) Screening, identification and application of soil bacteria with nematicidal activity against root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) on tomato. Pest Manag Sci 76(6):2217–2224. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5759
Boucherba N, Gagaoua M, Bouanane-Darenfed A, Bouiche C, Bouacem K, Kerbous MY, Maafa Y, Benallaoua S (2017) Biochemical properties of a new thermo- and solvent-stable xylanase recovered using three phase partitioning from the extract of Bacillus oceanisediminis strain SJ3. Bioresour Bioprocess 4(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-017-0161-9
Jung J, Jeong H, Kim HJ, Lee DW, Lee SJ (2016) Complete genome sequence of Bacillus oceanisediminis 2691, a reservoir of heavy-metal resistance genes. Mar Genom 30:73–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2016.07.002
Acknowledgements
The authors want to express their many thanks to Prof. Yigang Tong from Beijing University of Chemical Technology and Prof. Xiangyu Fan from Jinan University for valuable discussions. This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0902100 and 2018YFA0902103) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31761133006 to XLW).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0902100 and 2018YFA0902103) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31761133006 to XLW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Availability of data and material
The nucleotide sequence data reported here are available in the GenBank database under the accession number MT151604.
Additional information
Handling Editor: T. K. Frey.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Z., Liu, X., Liu, W. et al. Complete genome sequence of a novel Bacillus phage, P59, that infects Bacillus oceanisediminis. Arch Virol 165, 2679–2683 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04761-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04761-w