Abstract
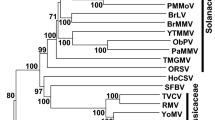
Aglaonema bacilliform virus (ABV), a member of the genus Badnavirus in the family Caulimoviridae, is associated with leaf deformation and chlorosis in Aglaonema modestum. The complete genome sequence of a Minnesota isolate of ABV was determined. The ABV genome is 7,178 bp in length and similar in size and organization to those of the members of the genus Badnavirus, containing three open reading frames (ORFs) with the potential to encode three proteins of 14.92, 13.33 and 207.95 kDa, respectively. The last ORF (ORF3) encodes a putative polyprotein with conserved domains, including zinc finger, aspartic protease, reverse transcriptase (RT) and RNase H domains, in that order. Phylogenetic analysis using the amino acid sequence of the ORF3 polyprotein showed that ABV clusters with several isolates of taro bacilliform CH virus (TaBCHV). Pairwise alignment using the highly conserved RT/RNase H region reveals that ABV has the highest level of identity (71%) at the nucleotide level to a Hawaiian isolate of TaBCHV.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lockhart B (1996) Association of a Badnavirus with Premature Leaf Senescence in Aglaonema [abstract], in: abstracts of papers presented at the ninth international symposium on virus diseases of ornamental plants. Phytoparasitica 24:333–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02981414
Lockhart BEL (1990) Evidence for a double-stranded circular DNA genome in a second group of plant viruses. Phytopathology 80:127–131. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-80-127
Lockhart BEL, Kiratiya-Angul K, Jones P et al (1997) Identification of Piper yellow mottle virus, a mealybug-transmitted badnavirus infecting Piper spp. in Southeast Asia. Eur J Plant Pathol 103:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008699414536
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A et al (2012) Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28:1647–1649. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199
Miller MA, Pfeiffer W, Schwartz T (2010) Creating the CIPRES science gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In: Gateway computing environments workshop (GCE). New Orleans, LA, pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/gce.2010.5676129
Funding
University of Minnesota, Twin Cities. Alvarez-Quinto R.A is supported by the Republic of Ecuador through the Ecuadorean Science and Technology Secretariat (SENESCYT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Jesus Navas-Castillo.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alvarez-Quinto, R.A., Lockhart, B.E.L., Moreno-Martinez, J.M. et al. Complete genome sequence of aglaonema bacilliform virus (ABV). Arch Virol 165, 237–239 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04445-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04445-0