Abstract
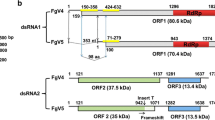
A novel double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) mycovirus, named Fusarium pseudograminearum megabirnavirus 1 (FpgMBV1), was found in a hypovirulent strain FC136-2A of Fusarium pseudograminearum, the causal agent of wheat crown rot. The complete genome of FpgMBV1 comprised two dsRNA segments, L1-dsRNA (8951 bp) and L2-dsRNA (5337 bp). Both dsRNAs carry two open reading frames on the positive strand. L1-dsRNA potentially encodes a 131.3-kDa coat protein (CP) and a 126.3-kDa RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), while L2-dsRNA encodes two putative proteins of 97.2 kDa and 30.6 kDa with unknown functions. As found in members of the family Megabirnaviridae, the 5’- and 3’-terminal sequences of L1-dsRNA and L2-dsRNA of FpgMBV1 are highly conserved. The identity between L1-dsRNA (1630 nt) and L2-dsRNA (1682 nt) is 88.95%, and the first 236 nt (nt 1-236) are exactly identical. The 3’ UTRs of L1-dsRNA (155 nt) and L2-dsRNA (109 nt) are 66.67% identical, with identical terminal hexamer sequences (5’-AAAAGC-3’). Phylogenetic analyses based on the amino acid sequences of the RdRps indicated that FpgMBV1 is a new member of the family Megabirnaviridae.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arjona-Lopez JT, Telengech P, Jamal A, Hisano S, Kondo H, Yelin MD, Arjona-Girona I, Kanematsu S, Lopez-Herrera CJ, Suzuki N (2018) Novel, diverse RNA viruses from Mediterranean isolates of the phytopathogenic fungus, Rosellinia necatrix: insights into evolutionary biology of fungal viruses. Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.14065
Chiba S, Salaipeth L, Lin YH, Sasaki A, Kanematsu S, Suzuki N (2009) A novel bipartite double-stranded RNA mycovirus from the white root rot fungus Rosellinia necatrix: molecular and biological characterization, taxonomic considerations, and potential for biological control. J Virol 83:12801–12812
Miyazaki N, Salaipeth L, Kanematsu S, Iwasaki K, Suzuki N (2015) Megabirnavirus structure reveals a putative 120-subunit capsid formed by asymmetrical dimers with distinctive large protrusions. J Gen Virol 96:2435–2441
Morris TJ, Dodds JA (1979) Isolation and analysis of double stranded RNA from virus infected plant and fungal tissue. Phytopathology 69:854–858
Sasaki A, Nakamura H, Suzuki N, Kanernatsu S (2016) Characterization of a new megabirnavirus that confers hypovirulence with the aid of a co-infecting partitivirus to the host fungus, Rosellinia necatrix. Virus Res 219:73–82
Wang MH, Wang Y, Sun XZ, Cheng JS, Fu YP, Liu HQ, Jiang DH, Ghabrial SA, Xie JT (2015) Characterization of a novel megabirnavirus from Sclerotinia sclerotiorum reveals horizontal gene transfer from single-stranded RNA virus to double-stranded RNA virus. J Virol 89:8567–8579
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Special Fund for Agro-Scientific Research in the Public Interest of China (201503112) and Henan Province Agricultural Science and Technology Research Project (182102110004). The authors would like to thank Prof. Jiatao Xie for advice during the preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Massimo Turina.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
705_2018_3970_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplemental Figure 2 Phylogenetic analysis of FpgMBV1 and selected members of the families Megabirnaviridae, Chrysoviridae, Quadriviridae, Totiviridae and Botybirnaviridae based on the aligned RdRp aa sequences of the viruses by the neighbor-joining method using the program MEGA 7.0. FpgMBV1 is highlighted in red with filled circle; other viruses in Megabirnaviridae are highlighted in black with filled circle; viruses in Chrysoviridae are highlighted in square; viruses in Quadriviririda are highlighted in diamond; viruses in Totiviridae are highlighted in simple circle and viruses in Botybirnaviridae are highlighted in triangle. Bootstrap values (1000 replicates) are shown at the nodes. The scale bar (0.1) corresponds to genetic distance. (PDF 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Gao, F., Zhang, F. et al. The complete genomic sequence of a novel megabirnavirus from Fusarium pseudograminearum, the causal agent of wheat crown rot. Arch Virol 163, 3173–3175 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-3970-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-3970-z



