Abstract
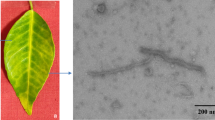
Through sequencing and assembly of small RNAs, an orthotospovirus was identified from a celtuce plant (Lactuca sativa var. augustana) showing vein clearing and chlorotic spots in the Zhejiang province of China. The S, M, and L RNAs of this orthotospovirus were determined to be 3146, 4734, and 8934 nt, respectively, and shared 30.4-72.5%, 43.4-80.8%, and 29.84-82.9% nucleotide sequence identities with that of known orthotospoviruses. The full length nucleoprotein (N) of this orthotospovirus shared highest amino acid sequence identity (90.25%) with that of calla lily chlorotic spot virus isolated from calla lily (CCSV-calla) [China: Taiwan: 2001] and tobacco (CCSV-LJ1) [China: Lijiang: 2014]. Phylogenetic analyses showed that this orthotospovirus is phylogenetically associated with CCSV isolates and clustered with CCSV, tomato zonate spot virus (TZSV), and tomato necrotic spot-associated virus (TNSaV) in a separate sub-branch. These results suggest that this orthotospovirus is a divergent isolate of CCSV and was thus named CCSV-Cel [China: Zhejiang: 2017].

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MJ, Lefkowitz EJ, King AMQ et al (2017) Changes to taxonomy and the international code of virus classification and nomenclature ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2017). Arch Virol 162:2505–2538
Amroun A, Priet S, de Lamballerie X, Quérat G (2017) Bunyaviridae RdRps: structure, motifs, and RNA synthesis machinery. Crit Rev Microbiol 43:753–778
Chen CC, Chen TC, Lin YH, Yeh SD, Hsu HT (2005) A chlorotic spot disease on calla lilies (Zantedeschia spp.) is caused by a tospovirus serologically but distantly related to Watermelon silver mottle virus. Plant Dis 89:440–445
Lin YH, Chen TC, Hsu HT, Liu FL, Chu FH, Chen CC, Lin YZ, Yeh SD (2005) Serological comparison and molecular characterization for verification of Calla lily chlorotic spot virus as a new tospovirus species belonging to Watermelon silver mottle virus serogroup. Phytopathology 95:1482–1488
Liu Y, Lu X, Zhi L, Zheng Y, Chen X, Xu Y, Wu F, Li Y (2012) Calla lily chlorotic spot virus from spider lily (Hymenocallis litteralis) and tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) in the Southwest of China. J Phytopathol 160:201–205
Plyusnin A, Beaty BJ, Elliott RM, Goldbach R, Kormelink R, Lundkvist A, Schmaljohn CS, Tesh RB (2012) Family—Bunyaviridae. Virus Taxonomy. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 725–741
Scholthof K-BG, Adkins S, Czosnek H, Palukaitis P, Jacquot E, Hohn T, Hohn B, Saunders K, Candresse T, Ahlquist P, Hemenway C, Foster GD (2011) Top 10 plant viruses in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 12:938–954
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Turina M, Kormelink R, Resende R (2016) Resistance to tospoviruses in vegetable crops: epidemiological and molecular aspects. Ann Rev Phytopathol 54:347–371
Wang Y, Cheng X, Wu X, Wang A, Wu X (2014) Characterization of complete genome and small RNA profile of Pagoda yellow mosaic associated virus, a novel badnavirus in China. Virus Res 188:103–108
Wu Q, Ding S-W, Zhang Y, Zhu S (2015) Identification of viruses and viroids by next-generation sequencing and homology-dependent and homology-independent algorithms. Ann Rev Phytopathol 53:425–444
Xu Y, Wang SB, Li YZ, Tao HZ, Huang YN, Wu BW, Dong YM, Hu J, Liu YT (2016) Complete genome sequence of a distinct Calla lily chlorotic spot virus isolated in mainland China. Arch Virol 161:219–222
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Zhongkai Zhang and Dr. Jiahong Dong from the Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences for their valuable suggestions to this manuscript.
Funding
This study was financial funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no: 31671998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Ralf Georg Dietzgen.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Wu, X., Li, W. et al. Molecular characterization of a divergent strain of calla lily chlorotic spot virus infecting celtuce (Lactuca sativa var. augustana) in China. Arch Virol 163, 1375–1378 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-3743-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-3743-8