Abstract
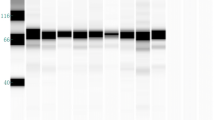
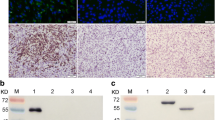
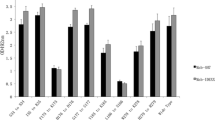
The E protein of flaviviruses is the primary antigen that induces protective immunity, but a monoclonal antibody (mAb) against the E protein of duck Tembusu virus (DTMUV) has never been characterized. Six hybridoma cell lines secreting DTMUV anti-E mAbs were prepared and designated 2A5, 1F3, 1G2, 1B11, 3B6, and 4F9, respectively. An immunofluorescence assay indicated that the mAbs could specifically bind to duck embryo fibroblast (DEF) cells infected with DTMUV and that the E protein was distributed in the cytoplasm of the infected cells. Immunoglobulin isotyping differentiated the mAbs as IgG1 (1G2, 1B11, 4F9, 1F3, and 2A5) and IgG2b (3B6). The mAbs were used to identify three epitopes, A (2A5, 1F3, and 1G2), B (1B11 and 4F9), and C (3B6) on the E protein on the basis of a competitive binding assay. By using mAbs 1F3 and 3B6, we developed an antigen-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (AC-ELISA) to detect E antigen from clinical samples. The AC-ELISA did not react with other known pathogens, indicating that the mAbs are specific for DTMUV. Compared to RT-PCR, the specificity and sensitivity of the AC-ELISA was 94.1 % and 98.0 %, respectively. This AC-ELISA thus represents a sensitive and rapid method for detecting DTMUV infection in birds.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao ZZ, Zhang C, Liu Y, Liu Y, Ye W, Han J, Ma G, Zhang D, Xu F, Gao X, Tang Y, Shi S, Wan C, Zhang C, He B, Yang M, Lu X, Huang Y, Diao Y, Ma X, Zhang D (2011) Tembusu virus in ducks, China. Emerg Infect Dis 17:1873–1875
Chen SY, Chen S, Wang S, Li Z, Lin F, Cheng X, Zhu X, Wang J, Chen S, Huang M, Zheng M (2014) Isolation and characterization of a Chinese strain of Tembusu virus from Hy-Line Brown layers with acute egg-drop syndrome in Fujian, China. Structural, antigenic, and evolutionary characterizations of the envelope protein of newly emerging Duck Tembusu Virus. Arch Virol 159:1099–10107
Crill WD, Chang GJ (2004) Localization and characterization of flavivirus envelope glycoprotein cross-reactive epitopes. J Virol 78:13975–13986
Crill WD, Roehrig JT (2001) Monoclonal antibodies that bind to domain III of dengue virus E glycoprotein are the most efficient blockers of virus adsorption to Vero cells. J Virol 75:7769–7773
Goncalvez AP, Purcell RH, Lai CJ (2004) Epitope determinants of a chimpanzee Fab antibody that efficiently cross-neutralizes Dengue type 1 and type 2 viruses map to inside and in close proximity to fusion loop of the Dengue type 2 virus envelope glycoprotein. J Virol 78:12919–12928
Guo DC, Qiu N, Shaozhou WL, Bai XF, He YL, Zhang QS, Zhao J, Liu M, Zhang Y (2014) Muscovy duck reovirus p10.8 protein localizes to the nucleus via a nonconventional nuclear localization signal. Virol J 11:37
Kuhn RJ, Zhang W, Rossmann MG, Pletnev SV, Corver J, Lenches E, Jones CT, Mukhopadhyay S, Chipman PR, Strauss EG, Baker TS, Strauss JH (2002) Structure of dengue virus: implications for flavivirus organization, maturation, and fusion. Cell 108:717–725
Li XS, Li GX, Teng QY, Yu L, Wu XG, Li ZJ (2012) Development of a blocking ELISA for detection of serum neutralizing antibodies against newly emerged duck tembusu virus. PLoS ONE 7:e53026
Lindenbach BD, Thiel HJ, Rice CM (2007) Flaviviridae: the viruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE (eds) Fields virology, 5th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 1101–1152
Liu M, Liu CG, Li G, Li XJ, Yin XC, Chen YH, Zhang Y (2012) Complete genomic sequence of duck flavivirus from China. J Virol 86:3398
Liu M, Chen SY, Chen YH, Liu CG, Chen SL, Yin X, Li G, Zhang Y (2012) Adapted tembusu-like virus in chickens and geese in China. J Clin Microbiol 50:2807–2809
Liu Z, Fu Y, Ji Y, Wei J, Cai X, Zhu Q (2013) Development and validation of one-step SYBR green real-time RT-PCR for the rapid detection of newly emerged duck Tembusu virus. Avian Dis 57:595–601
Lok SM, Kostyuchenko V, Nybakken GE, Holdaway HA, Battisti AJ, Sukupolvi-Petty S, Sedlak D, Fremont DH, Chipman PR, Roehrig JT, Diamond MS, Kuhn RJ, Rossmann MG (2008) Binding of a neutralizing antibody to dengue virus alters the arrangement of surface glycoproteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:312–317
Modis Y, Ogata S, Clements D, Harrison SC (2004) Structure of the dengue virus envelope protein after membrane fusion. Nature 427:313–319
Oliphant T, Engle M, Nybakken GE, Doane C, Johnson S, Huang L, Gorlatov S, Mehlhop E, Marri A, Chung KM, Ebel GD, Kramer LD, Fremont DH, Diamond MS (2005) Development of a humanized monoclonal antibody with therapeutic potential against West Nile virus. Nat Med 11:522–530
Rice CM, Strauss JH (1990) Production of flavivirus polypeptides by proteolytic processing. Semin Virol 1:357–367
Roehrig JT (2003) Antigenic structure of flavivirus proteins. Adv Virus Res 9:141–175
Stiasny K, Kiermayr S, Holzmann H, Heinz FX (2006) Cryptic properties of a cluster of dominant flavivirus cross-reactive antigenic sites. J Virol 80:9557–9568
Su J, Li S, Hu X, Yu X, Wang Y, Liu P, Lu X, Zhang G, Liu D, Li X, Su W, Lu H, Mok NS, Wang P, Wang M, Tian K, Gao GF (2011) Duck egg-drop syndrome caused by BYD virus, a new Tembusu-related flavivirus. PLoS ONE 6:e18106
Wang Y, Yuan X, Li Y, Yu K, Yang J, Xu H, Zhang Y, Yu K, Liao M, Qin Z (2011) Rapid detection of newly isolated Tembusu-related Flavivirus by reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. Virol J 8:553
Wilson MB, Nakane PK (1978) Recent developments in the periodate method of conjugating horseradish peroxidase (HRPO) to antibodies. Immunofluorescence and related staining techniques. Elsevier, North Holland, New York, pp 215–224
Yan LP, Yan PX, Zhou JW, Teng QY, Li ZJ (2011) Establishing a TaqMan-based real-time PCR assay for the rapid detection and quantification of the newly emerged duck tembusu virus. Virol J 8:464
Yin XC, Lv R, Chen XD, Liu M, Hua RH, Zhang Y (2013) Detection of Specific Antibodies against Tembusu Virus in Ducks by use of an E-ELISA. J Clin Microbiol 51:2400–2402
Yin XC, Zhang SM, Gao YL, Li JZ, Tan SY, Liu HY, Wu XY, Chen YH, Liu M, Zhang Y (2012) Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against waterfowl parvoviruses VP3 protein. Virol J 9:288
Yu KX, Sheng ZZ, Huang B, Ma XL, Li YF, Yuan XY, Qin ZM, Wang D, Chakravarty S, Li F, Song MX, Sun HC (2013) Structural, antigenic, and evolutionary characterizations of the envelope protein of newly emerging duck Tembusu virus. PLoS One 8:e71319
Egger D, Bienz K (1994) Protein (western) blotting. Mol Biotechnol 1(3):289–305
Li L, Giambrone JJ, Panangala VS, Hoerr FJ (1996) Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against avian reovirus strain S1133. Avian Dis 40:349–367
Liu M, Chen XD, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Li YF, Wang YF, Shen N, Chen HL (2010) Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Muscovy duck reovirus σB protein. Virol J 7:133
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-43-10), the Chinese Special Fund for Agro-Scientific Research in the Public Interest (201003012), and the Natural Science Foundation of China (31072132).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, X., Shaozhou, W., Zhang, Q. et al. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against duck Tembusu virus E protein: an antigen-capture ELISA for the detection of Tembusu virus infection. Arch Virol 160, 757–764 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2312-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2312-z