Abstract
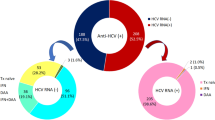
To assess the prevalence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and to investigate their mutual influences on infection status among human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-seropositive injection drug users (IDUs). A cross-sectional study was conducted among HIV infected IDUs in Dali, China. The participants were tested for serological markers of HBV and HCV infection, alanine transaminase (ALT) activity and CD4+ T cell count. HCV genotype was determined by sequencing. Of 529 patients, 498 (94.1 %) HIV infected IDUs agreed to participate. The overall prevalence of HCV infection (anti-HCV antibody positive) and spontaneous HCV clearance were 90.8 % (452/498) and 21.5 % (97/452), respectively. Of 411 subjects who had not received HBV vaccine, 296 (72.0 %) were positive for antibody against HBV core antigen (HBcAb), while 274 (66.7 %) were positive for both HCV antibody and HBcAb. HBV antigens were detected in 52 of the HBV-infected subjects (17.6 %). HCV clearance was associated with HBV antigenemia (p = 0.0002) and higher CD4+ T cell count (p = 0.0294). Resolved HBV infection was associated with HCV genotype 3 (p = 0.0365). HBV and HCV infection are highly prevalent and mutually influence infection status in HIV-1 infected IDUs in Dali, China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson KB, Guest JL, Rimland D (2004) Hepatitis C virus coinfection increases mortality in HIV-infected patients in the highly active antiretroviral therapy era: data from the HIV Atlanta VA Cohort Study. Clin Infect Dis 39:1507–1513
Chen SY, Kao CF, Chen CM, Shih CM, Hsu MJ, Chao CH, Wang SH, You LR, Lee YH (2003) Mechanisms for inhibition of hepatitis B virus gene expression and replication by hepatitis C virus core protein. J Biol Chem 278:591–607
Gebo KA, Diener-West M, Moore RD (2003) Hospitalization rates differ by hepatitis C status in an urban HIV cohort. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 34:165–173
Gerlach JT, Diepolder HM, Jung MC, Gruener NH, Schraut WW, Zachoval R, Hoffmann R, Schirren CA, Santantonio T, Pape GR (1999) Recurrence of hepatitis C virus after loss of virus-specific CD4(+) T-cell response in acute hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 117:933–941
Graham CS, Baden LR, Yu E, Mrus JM, Carnie J, Heeren T, Koziel MJ (2001) Influence of human immunodeficiency virus infection on the course of hepatitis C virus infection: a meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis 33:562–569
Greub G, Ledergerber B, Battegay M, Grob P, Perrin L, Furrer H, Burgisser P, Erb P, Boggian K, Piffaretti JC, Hirschel B, Janin P, Francioli P, Flepp M, Telenti A (2000) Clinical progression, survival, and immune recovery during antiretroviral therapy in patients with HIV-1 and hepatitis C virus coinfection: the Swiss HIV Cohort Study. Lancet 356:1800–1805
Guidotti LG, Chisari FV (2001) Noncytolytic control of viral infections by the innate and adaptive immune response. Annu Rev Immunol 19:65–91
Hoffmann CJ, Thio CL (2007) Clinical implications of HIV and hepatitis B co-infection in Asia and Africa. Lancet Infect Dis 7:402–409
Kobayashi Y, Kawaguchi Y, Mizuta T, Kuwashiro T, Oeda S, Oza N, Takahashi H, Iwane S, Eguchi Y, Anzai K, Ozaki I, Fujimoto K (2011) Metabolic factors are associated with serum alanine aminotransferase levels in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol 46:529–535
Liaw YF (1995) Role of hepatitis C virus in dual and triple hepatitis virus infection. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 22:1101–1108
Lu L, Nakano T, He Y, Fu Y, Hagedorn CH, Robertson BH (2005) Hepatitis C virus genotype distribution in China: predominance of closely related subtype 1b isolates and existence of new genotype 6 variants. J Med Virol 75:538–549
Maio G, d’Argenio P, Stroffolini T, Bozza A, Sacco L, Tosti ME, Intorcia M, Fossi E, d’Alessio G, Kondili LA, Rapicetta M, Mele A (2000) Hepatitis C virus infection and alanine transaminase levels in the general population: a survey in a southern Italian town. J Hepatol 33:116–120
Morsica G, Bagaglio S, Cicconi P, Capobianchi MR, Pellizzer G, Caramello P, Orani A, Moioli C, Rizzardini G, Uberti-Foppa C, Puoti M, Monforte AD (2009) Viral interference between hepatitis B, C, and D viruses in dual and triple infections in HIV-positive patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 51:574–581
Nelson PK, Mathers BM, Cowie B, Hagan H, Des Jarlais D, Horyniak D, Degenhardt L (2011) Global epidemiology of hepatitis B and hepatitis C in people who inject drugs: results of systematic reviews. Lancet 378:571–583
Pontisso P, Ruvoletto MG, Fattovich G, Chemello L, Gallorini A, Ruol A, Alberti A (1993) Clinical and virological profiles in patients with multiple hepatitis virus infections. Gastroenterology 105:1529–1533
Pratt DS, Kaplan MM (2000) Evaluation of abnormal liver-enzyme results in asymptomatic patients. N Engl J Med 342:1266–1271
Ruan YH, Hong KX, Liu SZ, He YX, Zhou F, Qin GM, Chen KL, Xing H, Chen JP, Shao YM (2004) Community-based survey of HCV and HIV coinfection in injection drug abusers in Sichuan Province of China. World J Gastroenterol 10:1589–1593
Sagnelli E, Coppola N, Marrocco C, Onofrio M, Sagnelli C, Coviello G, Scolastico C, Filippini P (2006) Hepatitis C virus superinfection in hepatitis B virus chronic carriers: a reciprocal viral interaction and a variable clinical course. J Clin Virol 35:317–320
Sagnelli E, Coppola N, Pisaturo M, Masiello A, Tonziello G, Sagnelli C, Messina V, Filippini P (2009) HBV superinfection in HCV chronic carriers: a disease that is frequently severe but associated with the eradication of HCV. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 49:1090–1097
Schuttler CG, Fiedler N, Schmidt K, Repp R, Gerlich WH, Schaefer S (2002) Suppression of hepatitis B virus enhancer 1 and 2 by hepatitis C virus core protein. J Hepatol 37:855–862
Sheen IS, Liaw YF, Chu CM, Pao CC (1992) Role of hepatitis C virus infection in spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen clearance during chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Infect Dis 165:831–834
Shih CM, Lo SJ, Miyamura T, Chen SY, Lee YH (1993) Suppression of hepatitis B virus expression and replication by hepatitis C virus core protein in HuH-7 cells. J Virol 67:5823–5832
Simmonds P (1995) Variability of hepatitis C virus. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 21:570–583
Simmonds P (2001) The origin and evolution of hepatitis viruses in humans. J Gen Virol 82:693–712
Soriano V, Mocroft A, Rockstroh J, Ledergerber B, Knysz B, Chaplinskas S, Peters L, Karlsson A, Katlama C, Toro C, Kupfer B, Vogel M, Lundgren J (2008) Spontaneous viral clearance, viral load, and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus (HCV) in HIV-infected patients with anti-HCV antibodies in Europe. J Infect Dis 198:1337–1344
Squadrito G, Orlando ME, Pollicino T, Raffa G, Restuccia T, Cacciola I, Di Marco V, Picciotto A, Colucci G, Craxi A, Raimondo G (2002) Virological profiles in patients with chronic hepatitis C and overt or occult HBV infection. Am J Gastroenterol 97:1518–1523
Sterling RK, Sulkowski MS (2004) Hepatitis C virus in the setting of HIV or hepatitis B virus coinfection. Semin Liver Dis 24(Suppl 2):61–68
Strader DB, Wright T, Thomas DL, Seeff LB (2004) Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 39:1147–1171
Sulkowski MS, Moore RD, Mehta SH, Chaisson RE, Thomas DL (2002) Hepatitis C and progression of HIV disease. JAMA 288:199–206
Sulkowski MS, Thomas DL, Mehta SH, Chaisson RE, Moore RD (2002) Hepatotoxicity associated with nevirapine or efavirenz-containing antiretroviral therapy: role of hepatitis C and B infections. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 35:182–189
Thio CL, Seaberg EC, Skolasky R Jr, Phair J, Visscher B, Munoz A, Thomas DL (2002) HIV-1, hepatitis B virus, and risk of liver-related mortality in the Multicenter Cohort Study (MACS). Lancet 360:1921–1926
Thomson EC, Fleming VM, Main J, Klenerman P, Weber J, Eliahoo J, Smith J, McClure MO, Karayiannis P (2011) Predicting spontaneous clearance of acute hepatitis C virus in a large cohort of HIV-1-infected men. Gut 60:837–845
Verucchi G, Calza L, Manfredi R, Chiodo F (2004) Human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus coinfection: epidemiology, natural history, therapeutic options and clinical management. Infection 32:33–46
Weber R, Sabin CA, Friis-Moller N, Reiss P, El-Sadr WM, Kirk O, Dabis F, Law MG, Pradier C, De Wit S, Akerlund B, Calvo G, Monforte A, Rickenbach M, Ledergerber B, Phillips AN, Lundgren JD (2006) Liver-related deaths in persons infected with the human immunodeficiency virus: the D:A:D study. Arch Intern Med 166:1632–1641
Wietzke P, Schott P, Braun F, Mihm S, Ramadori G (1999) Clearance of HCV RNA in a chronic hepatitis C virus-infected patient during acute hepatitis B virus superinfection. Liver 19:348–353
Xia X, Lu L, Tee KK, Zhao W, Wu J, Yu J, Li X, Lin Y, Mukhtar MM, Hagedorn CH, Takebe Y (2008) The unique HCV genotype distribution and the discovery of a novel subtype 6u among IDUs co-infected with HIV-1 in Yunnan, China. J Med Virol 80:1142–1152
Zarski JP, Bohn B, Bastie A, Pawlotsky JM, Baud M, Bost-Bezeaux F, Tran van Nhieu J, Seigneurin JM, Buffet C, Dhumeaux D (1998) Characteristics of patients with dual infection by hepatitis B and C viruses. J Hepatol 28:27–33
Zhang C, Yang R, Xia X, Qin S, Dai J, Zhang Z, Peng Z, Wei T, Liu H, Pu D, Luo J, Takebe Y, Ben K (2002) High prevalence of HIV-1 and hepatitis C virus coinfection among injection drug users in the southeastern region of Yunnan, China. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 29:191–196
Zhou YH, Liu FL, Yao ZH, Duo L, Li H, Sun Y, Zheng YT (2011) Comparison of HIV-, HBV-, HCV- and co-infection prevalence between Chinese and Burmese intravenous drug users of the China-Myanmar border region. PLoS ONE 6:e16349
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Y. Dong, C. Qiu and X. Xia equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Y., Qiu, C., Xia, X. et al. Hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection among HIV-1-infected injection drug users in Dali, China: prevalence and infection status in a cross-sectional study. Arch Virol 160, 929–936 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2311-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2311-0