Abstract
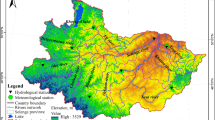
Knowledge of the historical changes in streamflow is essential for operating and planning water structures. Hence, the monthly mean streamflow trends of 20 streamflow gauge stations in Turkey’s Mediterranean basins, which are sensitive to climate change, are examined using the Mann–Kendall test, and trend slopes are calculated using Sen’s slope method. Furthermore, the innovative trend significance test (ITST) and recently proposed innovative polygon trend analysis (IPTA) method are used to analyse the historical changes in streamflow values at the stations. The trend analysis results of a total of 240-time series between 1977 and 2015 are evaluated and compared with three different trend methods. As a result of the study, the MK method determined significant trends in only 24% (3 increasing, 55 decreasing), ITST in 83% (41 increasing, 158 decreasing), and IPTA in 82% (38 increasing, 158 decreasing) of the 240-time series. The IPTA and ITST methods are more sensitive to determining significant monthly streamflow trends than the MK method. In addition, there is a more significant decrease in the streamflow values of the stations located east of the basin, and the trend slope value reaches − 26%/decade. Therefore, the results of the streamflow trend in the Mediterranean basins will benefit decision-makers in planning the efficient use of water resources in the region.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on a reasonable request.
References
Achite M, Ceribasi G, Ceyhunlu AI, Wałęga A, Caloiero T (2021) The innovative polygon trend analysis (IPTA) as a simple qualitative method to detect changes in environment—example detecting trends of the total monthly precipitation in semiarid area. Sustainability 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132212674
Ahmed N, Wang G, Booij MJ, Ceribasi G, Bhat MS, Ceyhunlu AI, Ahmed A (2021) Changes in monthly streamflow in the Hindukush–Karakoram–Himalaya region of Pakistan using innovative polygon trend analysis. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 36:811–830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-021-02067-0
Akçay F, Kankal M, Şan M (2022) Innovative approaches to the trend assessment of streamflows in the Eastern Black Sea basin, Turkey. Hydrol Sci J 67:222–247. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2021.1998509
Arab Amiri M, Gocić M (2021) Innovative trend analysis of annual precipitation in Serbia during 1946–2019. Environmental Earth Sciences 80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10095-w
Caloiero T, Coscarelli R, Ferrari E (2020) Assessment of seasonal and annual rainfall trend in Calabria (southern Italy) with the ITA method. J Hydroinf 22:738–748. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2019.138
Ceribasi G, Ceyhunlu AI (2021) Analysis of total monthly precipitation of Susurluk Basin in Turkey using innovative polygon trend analysis method. Journal of Water and Climate Change 12:1532–1543. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2020.253
DSI (2016) Strategic action plan for 2017–2021. Ankara, Turkey
Gadedjisso-Tossou A, Adjegan K, II, Kablan AKM (2021) Rainfall and temperature trend analysis by Mann–Kendall test and significance for rainfed cereal yields in Northern Togo. Sci 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci3010017
Genta J, Perez-Iribarren G, Mechoso CR (1998) A recent increasing trend in the streamflow of rivers in southeastern South America. J Clim 11:2858–2862. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1998)011%3c2858:Aritit%3e2.0.Co;2
Gocic M, Trajkovic S (2013) Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia. Global Planet Change 100:172–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.10.014
Gul S, Ren J (2022) Application of non-parametric innovative trend analysis of different time scale precipitation during (1951–2016) in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Acta Geophys 70:485–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-021-00703-5
Gumus V (2019) Spatio-temporal precipitation and temperature trend analysis of the Seyhan-Ceyhan river basins, Turkey. Meteorol Appl 26:369–384. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1768
Gumus V, Avsaroglu Y, Simsek O (2022) Streamflow trends in the Tigris river basin using Mann–Kendall and innovative trend analysis methods. Journal of Earth System Science 131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-021-01770-4
Hadi SJ, Tombul M (2018) Long-term spatiotemporal trend analysis of precipitation and temperature over Turkey. Meteorol Appl 25:445–455. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1712
Hırca T, Eryılmaz Türkkan G, Niazkar M (2022) Applications of innovative polygonal trend analyses to precipitation series of Eastern Black Sea Basin, Turkey. Theoret Appl Climatol 147:651–667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03837-0
IPCC (2021) Climate change 2021 the physical science basis. In: I WG (ed), The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Geneva. p 3949
Kahya E, Kalaycı S (2004) Trend analysis of streamflow in Turkey. J Hydrol 289:128–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2003.11.006
Kendall MG (1948) Rank correlation methods. Griffin, London
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica: Journal of the econometric society:245–259.
Seenu PZ, Jayakumar KV (2021) Comparative study of innovative trend analysis technique with Mann-Kendall tests for extreme rainfall. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06906-w
Rahman MA, Yunsheng L, Sultana N (2016) Analysis and prediction of rainfall trends over Bangladesh using Mann-Kendall, Spearman’s rho tests and ARIMA model. Meteorol Atmos Phys 129:409–424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-016-0479-4
Salas JD, Delleur JW, Yevjevich VM, Lane WL (1980) Applied modeling of hydrologic time series. Water Resources Publications
Şan M, Akçay F, Linh NTT, Kankal M, Pham QB (2021) Innovative and polygonal trend analyses applications for rainfall data in Vietnam. Theoret Appl Climatol 144:809–822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03574-4
Sen PK (1968) Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J Am Stat Assoc 63:1379–1389
Şen Z (2012) Innovative trend analysis methodology. J Hydrol Eng 17:1042–1046
Şen Z (2017) Innovative trend significance test and applications. Theoret Appl Climatol 127:939–947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1681-x
Şen Z, Şişman E, Dabanli I (2019) Innovative polygon trend analysis (IPTA) and applications. J Hydrol 575:202–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.05.028
Simsek O (2021) Hydrological drought analysis of Mediterranean basins, Turkey. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08501-5
Singh RN, Sah S, Das B, Vishnoi L, Pathak H (2020) Spatio-temporal trends and variability of rainfall in Maharashtra, India: analysis of 118 years. Theoret Appl Climatol 143:883–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03452-5
Singh RN, Sah S, Das B, Potekar S, Chaudhary A, Pathak H (2021) Innovative trend analysis of spatio-temporal variations of rainfall in India during 1901–2019. Theoret Appl Climatol 145:821–838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03657-2
Singh RN, Sah S, Das B, Chaturvedi G, Kumar M, Rane J, Pathak H (2021a) Long-term spatiotemporal trends of temperature associated with sugarcane in west India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08315-5
Şişman E, Kizilöz B (2021) The application of piecewise ITA method in Oxford, 1870–2019. Theoret Appl Climatol 145:1451–1465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03703-z
von Storch H, Navarra A (1995) Analysis of climate variability: applications of statistical techniques: proceedings of an autumn school organized by the Commision of the European Community on Elba from October 30 to November 6, 1993. Springer
Topaloğlu F (2006) Trend detection of streamflow variables in Turkey. Fresenius Environ Bull 15:644–653
Wang Y, Xu Y, Tabari H, Wang J, Wang Q, Song S, Hu Z (2020) Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall in the Yangtze River Delta, eastern China. Atmospheric Research 231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104673
Wu S, Zhao W, Yao J, Jin J, Zhang M, Jiang G (2022) Precipitation variations in the Tai Lake Basin from 1971 to 2018 based on innovative trend analysis. Ecological Indicators 139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108868
Yu Y-S, Zou S, Whittemore D (1993) Non-parametric trend analysis of water quality data of rivers in Kansas. J Hydrol 150:61–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(93)90156-4
Yue S, Pilon P, Cavadias G (2002) Power of the Mann-Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J Hydrol 259:254–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-1694(01)00594-7
Yue S, Pilon P, Phinney BOB (2003) Canadian streamflow trend detection: impacts of serial and cross-correlation. Hydrol Sci J 48:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.48.1.51.43478
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the General Directorate of State Hydraulic Works in Turkey for providing the dataset.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VG: conceptualization, coding, performing analysis, and writing the manuscript; OS: preparing the graphics, interpreting results, and writing the manuscript; and YA: interpreting results and writing the discussion.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the co-authors are familiar and agree with the content of this paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gumus, V., Simsek, O. & Avsaroglu, Y. Evaluation of long-term monthly mean streamflow trend in the Mediterranean basins using different methods. Theor Appl Climatol 151, 1369–1382 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04293-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04293-0