Abstract
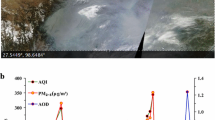
The present survey addresses the comprehensive description of geographic locations, transport ways, size, and vertical aerosol distribution during four large dust events which occurred in the Northwest China. Based on the data from 35 ground-based air quality monitoring stations and the satellite data, emission flows for dust events within the period of 2014 to 2017 have been estimated. The data show that maximum peak daily average PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations exceeded 380 and 150 μg/m3, respectively, and the PM2.5/PM10 ratio was ranging within 0.12–0.66. Both satellite data and simulation data of the Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) coincide with location and extension of a dust cloud. The Cloud Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) found dust at 0 to 10 km altitude which remained at this level during the most part of its trajectory. The vertical aerosol distribution at a wave of 532 nm total attenuated backscatter coefficient range of 0.0025–0.003 km−1 × sr−1. Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) (Terra) Collection 6 Level-3 aerosol products data show that aerosol optical depth (AOD) at pollution epicenters exceeds 1. A comprehensive data survey thus demonstrated that the main sources of high aerosol pollutions in the territory were deserted areas of North and Northwest China as well as the most part of the Republic of Mongolia, where one of the largest deserts, Gobi, extends.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assad NA, Balmes J, Mehta S, Cheema U, Sood A (2015) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease secondary to household air pollution. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 36(3):408–421. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1554846
Barea JM, Palenzuela J, Cornejo P, Sánchez-Castro I, Navarro-Fernández C, Lopéz-García A, Azcón-Aguilar C (2011) Ecological and functional roles of mycorrhizas in semi-arid ecosystems of Southeast Spain. J Arid Environ 75(12):1292–1301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2011.06.001
Bi J, Huang J, Fu Q, Wang X, Shi J, Zhang W, Zhang B (2011) Toward characterization of the aerosol optical properties over Loess Plateau of Northwestern China. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transfer 112(2):346–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2010.09.006
Blanco-Becerra LC, Gáfaro-Rojas AI, Rojas-Roa NY (2015) Influence of precipitation scavenging on the PM2.5/PM10 ratio at the Kennedy locality of Bogotá, Colombia. Rev Fac Ing-Univ Ant (76):58–65. https://doi.org/10.17533/udea.redin.n76a07
Chu HJ, Huang B, Lin CY (2015) Modeling the spatio-temporal heterogeneity in the PM10-PM2.5 relationship. Atmos Environ 102:176–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.11.062
Deng J, Wang T, Jiang Z, Xie M, Zhang R, Huang X, Zhu J (2011) Characterization of visibility and its affecting factors over Nanjing, China. Atmos Res 101(3):681–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2011.04.016
Ding R, Li J, Wang S, Ren F (2005) Decadal change of the spring dust storm in northwest china and the associated atmospheric circulation. Geophys Res Lett 32(2):341–356
Does MVD, Korte LF, Munday CI, Brummer GJA, Stuut JBW (2016) Particle size traces modern Saharan dust transport and deposition across the equatorial North Atlantic. Atmos Chem Phys 16(21):1–27
Engelstaedter S, Tegen I, Washington R (2006) North African dust emissions and transport. Earth-Sci Rev 79(1):73–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.06.004
Filonchyk M, Yan H, Yang S, Hurynovich V (2016) A study of PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations in the atmosphere of large cities in Gansu Province, China, in summer period. J Earth Sys Sci 125(6):1175–1187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-016-0722-x
Filonchyk M, Yan H, Hurynovich V (2017) Temporal-spatial variations of air pollutants in Lanzhou, Gansu Province, China, during the spring–summer periods, 2014–2016. Environ Qual Manag 26(4):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1002/tqem.21502
Goudie AS (1978) Dust storms and their geomorphological implications. J Arid Environ 1:291–310
Guan Q, Yang J, Zhao S, Pan B, Liu C, Zhang D, Wu T (2015) Climatological analysis of dust storms in the area surrounding the Tengger Desert during 1960–2007. Clim Dyn 45(3–4):903–913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2321-3
Gurjar BR, Jain A, Sharma A, Agarwal A, Gupta P, Nagpure AS, Lelieveld J (2010) Human health risks in megacities due to air pollution. Atmos Environ 44(36):4606–4613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.08.011
Han YJ, Holsen TM, Hopke PK, Yi SM (2005) Comparison between back-trajectory based modeling and Lagrangian backward dispersion modeling for locating sources of reactive gaseous mercury. Environ Sci Technol 39(6):1715–1723. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0498540
Hogan TF, Brody LR (1993) Sensitivity studies of the Navy’s global forecast model parameterizations and evaluation of improvements to NOGAPS. Mon Weather Rev 121(8):2373–2395. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1993)121<2373:SSOTNG>2.0.CO;2
Hogan TF, Rosmond TE (1991) The description of the navy operational global atmospheric prediction system’s spectral forecast model. Mon Weather Rev 119(8):1786–1815. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1991)119<1786:TDOTNO>2.0.CO;2
Hsu NC, Tsay SC, King MD, Herman JR (2004) Aerosol properties over bright-reflecting source regions. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 42(3):557–569. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2004.824067
Hsu NC, Jeong MJ, Bettenhausen C, Sayer AM, Hansell R, Seftor CS, Huang J, Tsay SC (2013) Enhanced deep blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: the second generation. J Geophys Res Atmos 118(16):9296–9315. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50712
Huang J, Minnis P, Chen B, Huang Z, Liu Z, Zhao Q, Ayers JK (2008) Long-range transport and vertical structure of Asian dust from CALIPSO and surface measurements during PACDEX. J Geophys Res Atmos 113(D23):2036–2044
Huang J, Minnis P, Yan H, Yi Y, Chen B, Zhang L, Ayers JK (2010a) Dust aerosol effect on semi-arid climate over Northwest China detected from A-train satellite measurements. Atmos Chem Phys 10(14):6863–6872. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-6863-2010
Huang K, Zhuang G, Li J, Wang Q, Sun Y, Lin Y, Fu JS (2010b) Mixing of Asian dust with pollution aerosol and the transformation of aerosol components during the dust storm over China in spring 2007. J Geophys Res Atmos 115(D7):1307–1314
Kan H, Chen R, Tong S (2012) Ambient air pollution, climate change, and population health in China. Environ Int 42(1):10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2011.03.003
Kanakidou M, Seinfeld JH, Pandis SN, Barnes I, Dentener FJ, Facchini MC, Swietlicki E (2005) Organic aerosol and global climate modelling: a review. Atmos Chem Phys 5(4):1053–1123. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-5-1053-2005
Kapp P, Pullen A, Pelletier JD, Russell J, Goodman P, Cai F (2015) From dust to dust: quaternary wind erosion of the mu Us Desert and loess plateau, China. Geology 43(9):835–838. https://doi.org/10.1130/G36724.1
Kaskaoutis DG, Prasad AK, Kosmopoulos PG, Sinha PR, Kharol SK, Gupta P, El-Askary HM, Kafatos M (2012) Synergistic use of remote sensing and modeling for tracing dust storms in the Mediterranean. Adv Meteorol 2012(8):978–988
Kaskaoutis DG, Rashki A, Houssos EE, Goto D, Nastos PT (2014) Extremely high aerosol loading over Arabian Sea during June 2008: the specific role of the atmospheric dynamics and Sistan dust storms. Atmos Environ 94:374–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.05.012
Lee HJ, Chatfield RB, Strawa AW (2016) Enhancing the applicability of satellite remote sensing for PM2.5 estimation using MODIS deep blue AOD and land use regression in California, United States. Environ Sci Technol 50(12):6546–6555. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b01438
Levy RC, Mattoo S, Munchak LA, Remer LA, Sayer AM, Patadia F, Hsu NC (2013) The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos Meas Tech 6(11):2989–3034. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-6-2989-2013
Li HJ, Li J, He Q (2008) Study on sandstorm trend and abrupt change in Xinjiang. J Desert Res 28(5):915–919 (in Chinese)
Liu D, Abuduwaili J, Lei J, Wu G, Gui D (2011) Wind erosion of saline playa sediments and its ecological effects in Ebinur Lake, Xinjiang, China. Environ Earth Sci 63(2):241–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0690-4
Lu Z, Streets DG, Zhang Q, Wang S (2012) A novel back-trajectory analysis of the origin of black carbon transported to the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau during 1996–2010. Geophys Res Lett 39(1):L01809
Luo Y, Zheng X, Zhao T, Chen J (2014) A climatology of aerosol optical depth over China from recent 10 years of MODIS remote sensing data. Int J Climatol 34(3):863–870. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3728
Maciszewska A, Markowicz K, Witek M (2010) A multiyear analysis of aerosol optical thickness over Europe and Central Poland using NAAPS model simulation. Acta Geophys 58(6):1147–1163
Middleton NJ, Goudie AS (2010) Saharan dust: sources and trajectories. Trans Ins Br Geogr 26(2):165–181
Miller RL, Tegen I, Perlwitz J (2004) Surface radiative forcing by soil dust aerosols and the hydrologic cycle. J Geophys Res 109:D04203
Oh HR, Ho CH, Kim J, Chen D, Lee S, Choi YS, Song CK (2015) Long-range transport of air pollutants originating in China: a possible major cause of multi-day high-PM 10 episodes during cold season in Seoul, Korea. Atmos Environ 109:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.03.005
Peterson MP, Hunt P, Weiß K (2017) Mapping air population. J Geovis Spat Anal 1(1–2):4
Qian G, Dong Z, Luo W, Zhang Z, Xiao S, Zhao A (2011) Grain size characteristics and spatial variation of surface sediments in the Badin Jaran Desert. J Desert Res 31(6):1357–1364 (in Chinese)
Ravi S, D’odorico P, Breshears DD, Field JP, Goudie AS, Huxman TE, Van Pelt S (2011) Aeolian processes and the biosphere. Rev Geophys 49(3):114–123
Ridley DA, Heald CL, Kok JF, Zhao C (2016) An observationally constrained estimate of global dust aerosol optical depth. Atmos Chem Phys 16(23):15097–15117. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-15097-2016
Rolph G, Stein A, Stunder B (2017) Real-time environmental applications and display sYstem: READY. Environ Model Softw 95:210–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2017.06.025
Seinfeld JH, Pandis SN (1998) Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to climate change. John Wiley, New York
Stein AF, Draxler RR, Rolph GD, Stunder BJB, Cohen MD, Ngan F (2016) NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull Amer Meteor Soc 96(12):150504130527006
Tegen I, Lacis AA, Fung I (1996) The influence of mineral aerosols from disturbed soils on the global aerosol radiation budget. Nature 380(6573):419–422. https://doi.org/10.1038/380419a0
Torres O, Tanskanen A, Veihelmann B, Ahn C, Braak R, Bhartia PK, Veefkind P, Levelt P (2007) Aerosols and surface UV products from Ozone Monitoring Instrument observations: An overview. J Geophys Res 112:D24S47. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD008809
Torres O, Ahn C, Chen Z (2013) Improvements to the OMI near-UV aerosol algorithm using A-train CALIOP and AIRS observations. Atmos Meas Tech 6(11):3257–3270. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-6-3257-2013
Vanos JK, Cakmak S, Kalkstein LS, Yagouti A (2015) Association of weather and air pollution interactions on daily mortality in 12 Canadian cities. Air Qual Atmos Health 8(3):307–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-014-0266-7
Von Schneidemesser E, Monks PS, Allan JD, Bruhwiler L, Forster P, Fowler D, Sindelarova K (2015) Chemistry and the linkages between air quality and climate change. Chem Rev 115(10):3856–3897. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00089
Wang X, Dong Z, Zhang J, Liu L (2004) Modern dust storms in China: an overview. J Arid Environ 58(4):559–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2003.11.009
Wang X, Xia D, Wang T, Xue X, Li J (2008) Dust sources in arid and semiarid China and southern Mongolia: impacts of geomorphological setting and surface materials. Geomorphology 97(3):583–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2007.09.006
Wang GH, Zhou BH, Cheng CL, Cao JJ, Li JJ, Meng JJ, Fu PQ (2013) Impact of Gobi desert dust on aerosol chemistry of Xi’an, inland China during spring 2009: differences in composition and size distribution between the urban ground surface and the mountain atmosphere. Atmos Chem Phys 13(2):819–835. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-819-2013
Wang X, Pu W, Shi J, Bi J, Zhou T, Zhang X, Ren Y (2015) A comparison of the physical and optical properties of anthropogenic air pollutants and mineral dust over Northwest China. J Meteor Res 29(2):180–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-015-4092-0
Winker DM, Pelon J, Coakley JAJ, Ackerman SA, Charlson RJ, Colarco PR (2010) The CALIPSO mission: a global 3D view of aerosols and clouds. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 91(9):1211–1229. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010BAMS3009.1
Wu Y, Guo J, Zhang X, Tian X, Zhang J, Wang Y, Duan J, Li X (2012) Synergy of satellite and ground based observations in estimation of particulate matter in eastern China. Sci Total Environ 433:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.033
Xin J, Wang S, Wang Y, Yuan J, Zhang W, Sun Y (2005) Optical properties and size distribution of dust aerosols over the Tengger Desert in Northern China. Atmos Environ 39(32):5971–5978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.06.027
Xu G, Jiao L, Zhang B, Zhao S, Yuan M, Gu Y et al (2017) Spatial and temporal variability of the PM2.5/PM10 ratio in Wuhan, Central China. Aerosol Air Qual Res 17:741–751
Zhang J, Reid JS (2010) A decadal regional and global trend analysis of the aerosol optical depth using a data-assimilation grade over-water MODIS and level 2 MISR aerosol products. Atmos Chem Phys 10(22):10949–10963. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-10949-2010
Zhang XY, Arimoto R, Zhu GH, Chen T, Zhang GY (1998) Concentration, size-distribution and deposition of mineral aerosol over Chinese desert regions. Tellus B 50(4):317–330. https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusb.v50i4.16131
Zhang XY, Gong SL, Zhao TL, Arimoto R, Wang YQ, Zhou ZJ (2003) Sources of Asian dust and role of climate change versus desertification in Asian dust emission. Geophys Res Lett 30(24):5–8
Zhang H, Wang Y, Hu J, Ying Q, Hu XM (2015) Relationships between meteorological parameters and criteria air pollutants in three megacities in China. Environ Res 140:242–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.04.004
Zhang J, Xin J, Zhang W, Wang S, Wang L, Xie W, Kong L (2017) Validation of MODIS C6 AOD products retrieved by the dark target method in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration, China. Adv Atmos Sci 34(8):993–1002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-016-6217-5
Zhao H, Che H, Zhang X, Ma Y, Wang Y, Wang H, Wang Y (2013a) Characteristics of visibility and particulate matter (PM) in an urban area of Northeast China. Atmos Pollut Res 4(4):427–434. https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2013.049
Zhao Y, Huang A, Zhu X, Zhou Y, Huang Y (2013b) The impact of the winter North Atlantic Oscillation on the frequency of spring dust storms over Tarim Basin in northwest China in the past half-century. Environ Res Lett 8(2):024026. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/8/2/024026
Zhao S, Yin D, Qu J (2015) Identifying sources of dust based on CALIPSO, MODIS satellite data and backward trajectory model. Atmos Pollut Res 6(1):36–44. https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2015.005
Funding
The work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFB0504203 and 2017YFB0504201), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41371435), and the Talent Innovation Project of Lanzhou (No. 2015-RC-28).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Filonchyk, M., Yan, H., Shareef, T.M.E. et al. Aerosol contamination survey during dust storm process in Northwestern China using ground, satellite observations and atmospheric modeling data. Theor Appl Climatol 135, 119–133 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2362-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2362-8