Abstract
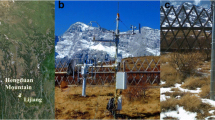
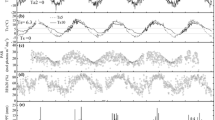
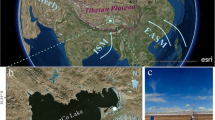
Based on eddy covariance flux data from July 15, 2014, to December 31, 2015, the water and CO2 fluxes were compared over a semiarid alpine steppe (Bange, Tibetan Plateau) and a humid alpine meadow (Lijiang, Yunnan) on the Tibetan Plateau and its surrounding region. During the wet season, the evaporative fraction (EF) was strongly and linearly correlated with the soil water content (SWC) at Bange because of its sparse green grass cover. In contrast, the correlation between the EF at Lijiang and the SWC and the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) was very low because the atmosphere was close to saturation and the EF was relatively constant. In the dry season, the EF at both sites decreased with the SWC. The net ecosystem exchange (NEE) at Bange was largely depressed at noon, while this phenomenon did not occur at Lijiang. The saturated NEE at Bange was 24% of that at Lijiang. The temperature sensitivity coefficient of ecosystem respiration at Bange (1.7) was also much lower than that at Lijiang (3.4). The annual total NEE in 2015 was 21.8 and −230.0 g C m−2 yr−1 at Bange and Lijiang, respectively, and the NEE was tightly controlled by the NDVI at the two sites. The distinct differences in the water and CO2 fluxes at Bange and Lijiang are attributed to the large SWC difference and its effect on vegetation growth.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aires LMI, Pio CA, Pereira JS (2008) Carbon dioxide exchange above a Mediterranean C3/C4 grassland during two climatologically contrasting years. Glob Chang Biol 14:539–555
Baldocchi D (2003) Assessing the eddy covariance technique for evaluating carbon dioxide exchange rates of ecosystems: past, present and future. Glob Chang Biol 9:479–492
Baldocchi D, Xu L, Kiang N (2004) How plant functional-type, weather, seasonal drought, and soil physical properties alter water and energy fluxes of an oak-grass savanna and an annual grassland. Agric For Meteorol 123:13–39
Ding MJ, Zhang YL, Sun XM, Liu LS, Wang ZF, Bai WQ (2013) Spatiotemporal variation in alpine grassland phenology in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from 1999 to 2009. Chinese Sci Bull 58:396–405
Falge E, Baldocchi D, Olson R (2001) Gap filling strategies for defensible annual sums of net ecosystem exchange. Agric For Meteorol 107:43–69
Fan ZX, Bräuning A, Thomas A, Li JB, Cao KF (2011) Spatial and temporal temperature trends on the Yunnan Plateau (southwest China) during 1961–2004. Int J Climatol 31:2078–2090
Findell K, Eltahir EAB (2003) Atmospheric controls on soil moisture–boundary layer interactions. Part I: framework development. J Hydrometeorol 4:552–569
Foken T, Wichura B (1996) Tools for quality assessment of surface-based flux measurements. Agric For Meteorol 78:83–105
Fu Y, Zheng Z, Yu G, Hu Z, Sun X, Shi P, Wang Y, Zhao X (2006) Depression of net ecosystem CO2 exchange in semi-arid Leymus chinensis steppe and alpine shrub. Agric For Meteorol 137:234–244
Fu YL, Yu GR, Sun XM, Li YN, Wen XF, Zhang LM, Li ZQ, Zhao L, Hao YB (2009) Environmental influences on carbon dioxide fluxes over three grassland ecosystems in China. Biogeosciences 6:2879–2893
Gentine P, Holtslag AAM, D’Andrea F, Ek M (2013) Surface and atmospheric controls on the onset of moist convection over land. J Hydrometeorol 14(5):1443–1462
Gu S, Tang YH, Cui XY, Kato T, Du MY, Li YN, Zhao XQ (2005) Energy exchange between the atmosphere and a meadow ecosystem on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric For Meteorol 129:175–185
Gu S, Tang YH, Cui XY, Du MY, Zhao L, Li YN, Xu SX, Zhou HK, Kato T, Qi PT, Zhao XQ (2008) Characterizing evapotranspiration over a meadow ecosystem on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res 113. doi:10.1029/2007JD009173
Kaimal JC, Finnigan JJ (1994) Atmospheric boundary layer flows: their structure and measurement. Oxford University Press, New York, p. 289
Kang SC, Xu YW, You QL, Flügel WA, Pepin N, Yao TD (2010) Review of climate and cryospheric change in the Tibetan Plateau. Environ Res Lett. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/5/1/015101
Kato T, Tang YH, Gu S, Cui XY, Hirota M, Du MY, Li YN, Zhao XQ, Oikawa T (2004) Seasonal patterns of gross primary production and ecosystem respiration in an alpine meadow ecosystem on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res 109. doi:10.1029/2003JD003951
Li SG, Asanuma J, Kotani A, Davaa G, Oyunbaatar D (2007) Evapotranspiration from a Mongolian steppe under grazing and its environmental constraints. J Hydrol 333:133–143
Li MS, Babel W, Chen XL, Zhang L, Sun FL, Wang BB, Ma YM, Hu ZY, Foken T (2015) A 3-year dataset of sensible and latent heat fluxes from the Tibetan Plateau, derived using eddy covariance measurements. Theor Appl Climatol 122:457–469
Liu XD, Chen BD (2000) Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Int J Climatol 20:1729–1742
Liu J, Zhang Y, Li Y, Wang D, Han G, Hou F (2008) Overview of grassland and its development in China. Multifunctional grasslands in a changing world volume (I). Guangdong People’s Publishing House, Guangzhou, pp. 3–5
Ma YM, Su Z, Koike T, Yao T, Ishikawa H, Ueno K, Menenti M (2003) On measuring and remote sensing surface energy partitioning over the Tibetan Plateau—from GAME/Tibet to CAMP/Tibet. Phys Chem Earth 28:63–74
Ma YM, Kang S, Zhu L, Xu B, Tian L, Yao T (2008) Tibetan observation and research platform—atmosphere–land interaction over a heterogeneous landscape. Bull Amer Meteor Soc 89:1487–1492
Ma N, Zhang YS, Guo YH, Gao HF, Zhang HB, Wang Y (2015) Environmental and biophysical controls on the evapotranspiration over the highest alpine steppe. J Hydrol 529:980–992
Meyers TP (2001) A comparison of summertime water and CO2 fluxes over rangeland for well watered and drought conditions. Agric For Meteorol 106:205–214
Moore CJ (1986) Frequency response corrections for eddy correlation systems. Bound Lay Meteorol 37:17–35
Moran MS, Scott RL, Keefer TO, Emmerich WE, Hernandez M, Nearing GS, Paige GB, Cosh MH, O’Neill PE (2009) Partitioning evapotranspiration in semiarid grassland and shrubland ecosystems using time series of soil surface temperature. Agric For Meteorol 149:59–72
Phillips TJ, Klein SA (2014) Land-atmosphere coupling manifested in warm-season observations on the U.S. Southern Great Plains. J Geophys Res 119:509–528
Schotanus P, Nieuwstadt FTM, Bruin HAR (1983) Temperature measurement with a sonic anemometer and its application to heat and moisture fluxes. Bound Lay Meteorol 26:81–93
Wang L, Liu HZ, Bernhofer C (2016a) Response of carbon dioxide exchange to grazing intensity over typical steppes in a semi-arid area of Inner Mongolia. Theor Appl Climatol. doi:10.1007/s00704-016-1736-7
Wang L, Liu HZ, Sun JH, Feng JW (2016b) Water and carbon dioxide fluxes over an alpine meadow in southwest China and the impact of a spring drought event. Int J Biometeorol 60:195–205
Wang L, Liu HZ, Bernhofer C (2016c) Grazing intensity effects on the partitioning of evapotranspiration in the semiarid typical steppe ecosystems in Inner Mongolia. Int J Climatol. doi:10.1002/joc.4622
Webb EK, Pearman GI, Leuning R (1980) Correction of flux measurements for density effects due to heat and water vapour transfer. Q J Roy Environ Soc 106:85–100
Wilczak JM, Oncley SP, Stage SA (2001) Sonic anemometer tilt correction algorithms. Bound Lay Meteorol 99:127–150
Williams IN, Torn MS (2015) Vegetation controls on surface heat flux partitioning, and land-atmosphere coupling. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1002/2015GL066305
Wilson K, Goldstein A, Falge E, Aubinet M, Baldocchi D, Berbigier P, Bernhofer C, Ceulemans R, Dolman H, Field C (2002) Energy balance closure at FLUXNET sites. Agric For Meteorol 113:223–243
Yang FL, Zhou GS, Hunt JE, Zhang F (2011) Biophysical regulation of net ecosystem carbon dioxide exchange over a temperate desert steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Agric For Meteorol 142:318–328
Zhang WL, Chen SP, Chen J, Wei L, Han XG, Lin GH (2007) Biophysical regulations of carbon fluxes of a steppe and a cultivated cropland in semiarid Inner Mongolia. Agric For Meteorol 146:216–229
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 91537212 and 41275023), the Third Tibetan Plateau Scientific Experiment: Observations for Boundary Layer and Troposphere (GYHY201406001), and the NSFC project (41305012). The staffs from Bange and Lijiang Meteorological Administration are also greatly appreciated for their helps in the maintenance of the measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Liu, H., Shao, Y. et al. Water and CO2 fluxes over semiarid alpine steppe and humid alpine meadow ecosystems on the Tibetan Plateau. Theor Appl Climatol 131, 547–556 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1997-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1997-1