Abstract
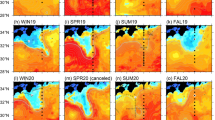
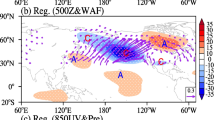
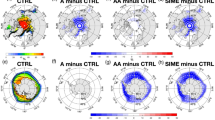
The present study aims to characterize the synoptic atmospheric circulations and precursors of the extreme rainfall events (ERE) over the South Indian Peninsula (SIP). The ERE is identified using a standardized precipitation index (SPI) from the daily TRMM 3B42 rainfall data. The composite maps of various diagnostic atmospheric variables are analyzed to understand the large-scale environmental conditions responsible for the ERE. During Indian Summer Monsoon, the presence of meridional lower troposphere dipole pressure gradient pattern might influence the ERE. The presence of anomalous low (high) over the SIP (northern Bay of Bengal) at the lower troposphere supports the occurrence of ERE. Most of the top ERE are associated with cyclonic circulation over the SIP during the post-monsoon. During the pre-monsoon, localized severe mesoscale convective events are responsible for the occurrence of ERE. In addition, the northward propagation of convection from the Indian Ocean and an upper-level atmosphere trough influence the occurrences of ERE. Further, the synoptic-scale circulations are investigated during the El Niño-Southern Oscillation and Madden Julian Oscillation (MJO) phases. Findings suggest that during La Niña and the active phases of the MJO, enhancement of convection is evident. The Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) model was employed to understand the remote moisture sources and pathways during ERE. Results confirm remote moisture sources for the top ERE across the seasons.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Agnihotri G, Dimri AP (2015) Simulation study of heavy rainfall episodes over the southern Indian peninsula. Meteorol Appl 22:223–235. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1446
Akter N, Tsuboki K (2017) Climatology of the pre-monsoon Indian dryline. Int J Climatol 37:3991–3998. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4968
Anandh PC, Vissa NK (2020) On the linkage between extreme rainfall and the Madden–Julian Oscillation over the Indian region. Meteorol Appl. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1901
Anandh PC, Vissa NK, Broderick C (2018) Role of MJO in modulating rainfall characteristics observed over India in all seasons utilizing TRMM. Int J Climatol 38:2352–2373. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5339
Baisya H, Pattnaik S (2019) Orographic effect and multiscale interactions during an extreme rainfall event. Environ Res Commun 1:051002. https://doi.org/10.1088/2515-7017620/ab2417
Bhate J, Kesarkar AP, Karipot A et al (2016) A sea breeze induced thunderstorm over an inland station over Indian South Peninsula—a case study. J Atmos Solar-Terr Phys 148:96–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2016.09.002
Boers N, Goswami B, Rheinwalt A et al (2019) Complex networks reveal global pattern of extreme-rainfall teleconnections. Nature 566:373–377. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0872-x
Boyaj A, Ashok K, Ghosh S, Devanand A, Dandu G (2018) The Chennai extreme rainfall event in 2015: The Bay of Bengal connection. Clim Dyn 50(7):2867–2879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3778-7
Dee DP, Uppala SM, Simmons AJ et al (2011) The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137:553–597. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.828
Edwards DC, McKee TB (1997) Characteristics of 20th century drought in the United States at multiple time scales. Climatology Rep. 97–2, Colorado State University, Dept. of Atmospheric Science, Fort Collins, Colorado, p 155
Francis PA, Gadgil S (2006) Intense rainfall events over the west coast of India. Meteorol Atmos Phys 94:27–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-005-0167-2
Fuhrmann CM, Konrad CE (2013) A trajectory approach to analyzing the ingredients associated with heavy winter storms in Central North Carolina. Weather Forecast 28:647–667. https://doi.org/10.1175/WAF-D-12-00079.1
Gimeno L, Stohl A, Trigo RM et al (2012) Oceanic and terrestrial sources of continental precipitation. Rev Geophys 50:RG4003. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012RG000389
Guhathakurta P, Menon P, Inkane PM et al (2017) Trends and variability of meteorological drought over the districts of India using standardized precipitation index. J Earth Syst Sci 126:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-017-0896-x
Huffman GJ, Bolvin DT, Nelkin EJ et al (2007) The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J Hydrometeorol 8:38–55. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM560.1
Hunt KMR, Turner AG, Shaffrey LC (2018) Extreme daily rainfall in Pakistan and North India: scale interactions, mechanisms, and precursors. Mon Weather Rev 146:1005–1022. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-17-0258.1
Ibebuchi CC (2021a) Circulation pattern controls of wet days and dry days in Free State, South Africa. Meteorol Atmos Phys 133:1469–1480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-021-00822-0
Ibebuchi CC (2021b) Revisiting the 1992 severe drought episode in South Africa: the role of El Niño in the anomalies of atmospheric circulation types in Africa south of the equator. Theor Appl Climatol 146:723–740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03741-7
IPCC (2021) Summary for policymakers. In: Climate change 2021: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the sixth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [MassonDelmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press (in press)
Jana S, Rajagopalan B, Alexander MA, Ray AJ (2018) Understanding the dominant sources and tracks of moisture for summer rainfall in the Southwest United States. J Geophys Res Atmos 123:4850–4870. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017JD027652
Johari Chan KJB (2020) The intraseasonal variability of the Indian Summer Monsoon: dynamics, thermodynamics and. University of Reading, Department of Meteorology, Reading
Karmakar N, Krishnamurti TN (2019) Characteristics of northward propagating intraseasonal oscillation in the Indian Summer Monsoon. Clim Dyn 52:1903–1916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4268-2
Karmakar N, Chakraborty A, Nanjundiah RS (2015) Decreasing intensity of monsoon low-frequency intraseasonal variability over India. Environ Res Lett 10:54018. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/10/5/054018
Kishtawal CM, Niyogi D, Tewari M et al (2010) Urbanization signature in the observed heavy rainfall climatology over India. Int J Climatol 30:1908–1916. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2044
Konduru RT, Mrudula G (2021) Effect of offshore troughs on the South India erratic summer monsoon rainfall in June 2017. Dyn Atmos Ocean 93:101187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2020.101187
Krishnamurti TN, Krishnamurti R, Simon A et al (2016) A mechanism of the MJO invoking scale interactions. Meteorol Monogr 56:5.1-5.16. https://doi.org/10.1175/AMSMONOGRAPHS-D-15-0009.1
Krishnamurti TN, Dubey S, Kumar V et al (2017) Scale interaction during an extreme rain event over southeast India. Q J R Meteorol Soc 143:1442–1458. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3016
Lekshmy PR, Midhun M, Ramesh R, Jani RA (2015) 18O depletion in monsoon rain relates to large scale organized convection rather than the amount of rainfall. Sci Rep 4:5661. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05661
Liebmann B, Smith A (1996) Outgoing long-wave radiation. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:1275–1277
Murata F, Terao T, Fujinami H et al (2017) Dominant synoptic disturbance in the extreme rainfall at Cherrapunji, Northeast India, based on 104 years of rainfall data (1902–2005). J Clim 30:8237–8251. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0435.1
Ordóñez P, Ribera P, Gallego D, Peña-Ortiz C (2012) Major moisture sources for Western and Southern India and their role on synoptic-scale rainfall events. Hydrol Process 26(25):3886–3895. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8455.
Phadtare J (2018) Role of Eastern Ghats orography and cold pool in an extreme rainfall event over Chennai on 1 December 2015. Mon Weather Rev 146:943–965. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-16-0473.1
Prakash S, Mitra AK, Pai DS (2015) Comparing two high-resolution gauge-adjusted multisatellite rainfall products over India for the southwest monsoon period. Meteorol Appl 22(3):679–688. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1502
Prakash S, Mitra AK, Rajagopal EN, Pai DS (2016) Assessment of TRMM-based TMPA-3B42 and GSMaP precipitation products over India for the peak southwest monsoon season. Int J Climatol 36:1614–1631. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4446
Prathipati VK, Viswanadhapalli Y, Chennu VN, Dasari HP (2021) Study of active and break spell phenomena of Indian Summer Monsoon using WRF downscaled data. Pure Appl Geophys 178:4195–4219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-021-02837-5
Rai P, Dimri AP (2017) Effect of changing tropical easterly jet, low level jet and quasi-biennial oscillation phases on Indian summer monsoon. Atmos Sci Lett 18(2):52–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/asl.723
Rajeswari JR, Srinivas CV, Yesubabu V et al (2021) Impacts of urbanization, aerodynamic roughness, and land surface processes on the extreme heavy rainfall over Chennai, India. J Geophys Res Atmos 126:e2020JD034017. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JD034017
Reshmi Mohan P, Srinivas CV, Yesubabu V et al (2018) Simulation of a heavy rainfall event over Chennai in Southeast India using WRF: sensitivity to microphysics parameterization. Atmos Res 210:83–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.04.005
Romatschke U, Medina S, Houze RA (2010) Regional, seasonal, and diurnal variations of extreme convection in the South Asian Region. J Clim 23:419–439. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JCLI3140.1
Roxy MK, Ghosh S, Pathak A et al (2017) A threefold rise in widespread extreme rain events over central India. Nat Commun 8:708. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00744-9
Sahu RK, Dadich J, Tyagi B et al (2020) Evaluating the impact of climate change in threshold values of thermodynamic indices during pre-monsoon thunderstorm season over Eastern India. Nat Hazards 102:1541–1569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-03978-x
Saikrishna TS, Ramu DA, Osuri KK (2021) Inter-comparison of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over India during the summer monsoon season. Meteorol Atmos Phys 133(6):1675–1690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-021-00829-7
Sanap SD, Priya P, Sawaisarje GK, Hosalikar KS (2019) Heavy rainfall events over southeast peninsular India during northeast monsoon: role of El Niño and easterly wave activity. Int J Climatol 39:1954–1968. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5926
Shanmugasundaram J, Lee E, Srinivasan G (2018) Characterizing pentad rainfall variations during the North-East Indian monsoon season over the Southeastern Peninsular India. Int J Climatol 38:e1044–e1060. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5432
Singh KS, Bonthu S, Bhaskaran PK et al (2021) Impact of time step size on different cumulus parameterization schemes in the numerical simulation of a heavy rainfall event over Tamil Nadu, India. Pure Appl Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-021-02896-8
Sodemann H, Schwierz C, Wernli H (2008) Interannual variability of Greenland winter precipitation sources: Lagrangian moisture diagnostic and North Atlantic Oscillation influence. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD008503
Sreelekha PN, Babu CA (2019) Organized convection over southwest peninsular India during the pre-monsoon season. Theor Appl Climatol 135:1279–1293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2446-0
Srinivas CV, Yesubabu V, Hari Prasad D et al (2018a) Simulation of an extreme heavy rainfall event over Chennai, India using WRF: sensitivity to grid resolution and boundary layer physics. Atmos Res 210:66–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.04.014
Srinivas G, Chowdary JS, Kosaka Y et al (2018b) Influence of the Pacific-Japan pattern on Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall. J Clim 31:3943–3958. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0408.1
Tanoue M, Ichiyanagi K, Yoshimura K et al (2018) Seasonal variation in isotopic composition and the origin of precipitation over Bangladesh. Prog Earth Planet Sci 5:77. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40645-018-0231-4
van Oldenborgh GJ, Otto FEL, Haustein K, AchutaRao K (2016) The heavy precipitation event of December 2015 in Chennai, India. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 97:S87–S91. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-16-0129.1
Varikoden H, Revadekar JV (2020) On the extreme rainfall events during the southwest monsoon season in northeast regions of the Indian subcontinent. Meteorol Appl 27:e1822. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1822
Vissa NK, Satyanarayana ANV, Kumar BP (2013a) Impact of South China Sea cold surges and Typhoon Peipah on initiating cyclone Sidr in the Bay of Bengal. Pure Appl Geophys 170:2369–2381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-013-0671-0
Vissa NK, Satyanarayana ANV, Prasad Kumar B (2013b) Intensity of tropical cyclones during pre- and post-monsoon seasons in relation to accumulated tropical cyclone heat potential over Bay of Bengal. Nat Hazards 68:351–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0625-y
Viswanadhapalli Y, Srinivas CV, Basha G, Dasari HP, Langodan S, Venkat Ratnam M, Hoteit I (2019) A diagnostic study of extreme precipitation over Kerala during August 2018. Atmos Sci Lett 20(12):e941. https://doi.org/10.1002/asl.941
Wheeler MC, Hendon HH (2004) An all-season real-time multivariate MJO index: development of an index for monitoring and prediction. Mon Weather Rev 132:1917–1932. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132%3c1917:AARMMI%3e2.0.CO;2
Xavier P, Rahmat R, Cheong WK, Wallace E (2014) Influence of Madden–Julian oscillation on Southeast Asia rainfall extremes: observations and predictability. Geophys Res Lett 41(12):4406–4412. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0546.1
Xavier P, Lim SY, Ammar Bin Abdullah MF et al (2020) Seasonal dependence of cold surges and their interaction with the Madden–Julian oscillation over Southeast Asia. J Clim 33:2467–2482. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0048.1
Yadav RK (2013) Emerging role of Indian Ocean on Indian Northeast Monsoon. Clim Dyn 41:105–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1637-0
Yokoyama C, Tsuji H, Takayabu YN (2020) The effects of an upper-tropospheric trough on the heavy rainfall event in July 2018 over Japan. J Meteorol Soc Jpn Ser II 98:235–255. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.2020-013
Acknowledgements
NKV would like to acknowledge the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, for funding the research project (Grant Ref: ECR/2016/001896). Mr. P. C. Anandh would like to acknowledge the National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, for the financial support to carry out his research work.
Funding
The Department of Science and Technology, Government of India funded the research project (Grant Ref: ECR/2016/001896).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PCA: methodology, writing—original draft, editing, visualization, formal analysis. NKV: conceptualization, supervision, formal analysis, writing-review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that we do not have any known competing financial and personal interests that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: J.-F. Miao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anandh, P.C., Vissa, N.K. Role of synoptic-scale circulations, mechanisms, and precursors during extreme rainfall events over the Southern Indian Peninsula. Meteorol Atmos Phys 134, 27 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-022-00862-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-022-00862-0