Abstract
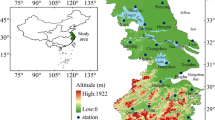
Based on daily precipitation records at 46 meteorological stations in Inner Mongolia, northern China, the space and time changes in precipitation characteristics are analyzed by defining 15 precipitation indices. The Mann–Kendall trend test is used to detect trends in the precipitation indices series. Results indicate that: (1) Inner Mongolia is dominated by decreasing precipitation, and precipitation deficit may further deteriorate the shortage of water resources; (2) precipitation extremes are not dominant in this province, and most extreme precipitation indices are generally decreasing; (3) wet spells with short duration are prevalent in this province and the occurrence and fractional contribution of short-duration wet spells are increasing; (4) daily precipitation events with light and moderate intensity are dominant in this province and the occurrence and fractional contribution of moderate precipitation are increasing; (5) a higher risk of droughts can be expected in summer and precipitation in winter and spring is increasing, which imply evident seasonality and seasonal shifts of precipitation changes within this province.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander LV, Zhang X, Peterson TC et al (2006) Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation. J Geophys Res 111:D05109. doi:10.1029/2005JD006290
Bai Y, Wu J, Xing Q et al (2008) Primary production and rain use efficiency across a precipitation gradient on the Mongolia plateau. Ecology 89(8):2140–2153
Bao Y, Li XB, Huang LM, Zhang YX, Wang H (2011) Spatial–temporal distribution characteristics of precipitation in Inner Mongolia from 1961-2007. Arid Land Geogr 34(1):52–61 (in Chinese)
Bewket W, Conway D (2007) A note on the temporal and spatial variability of rainfall in the drought-prone Amhara region of Ethiopia. Int J Climatol 27(11):1467–1477
Cannarozzo M, Noto LV, Viola F (2006) Spatial distribution of rainfall trends in Sicily (1921–2000). Phys Chem Earth 31:1201–1211
Coscarelli R, Caloiero T (2012) Analysis of daily and monthly rainfall concentration in Southern Italy (Calabria region). J Hydrol 416:145–150
De Luis M, González-Hidalgo JC, Brunetti M, Longares LA (2011) Precipitation concentration changes in Spain 1946-2005. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 11(5):1259–1265
Deni SM, Jemain AA (2009) Fitting the distribution of dry and wet spells with alternative probability models. Meteorol Atmos Phys 104(1–2):13–27
Deni SM, Suhaila J, Zin WZW, Jemain AA (2010) Spatial trends of dry spells over Peninsular Malaysia during monsoon seasons. Theoret Appl Climatol 99(3–4):357–371
Gao T, Xiao SJ, Wu L (2009) Temporal–spatial characteristics of precipitation and temperature in Inner Mongolia for the last 47 years (1961–2007). Inn Mong Meteorol 1:3–7 (in Chinese)
Gong DY, Wang JA, Han H (2005) Trends of summer dry spells in China during the late twentieth century. Meteorol Atmos Phys 88(3–4):203–214
Huang J, Sun SL, Zhang JC (2013) Detection of trends in precipitation during 1960–2008 in Jiangxi province, southeast China. Theor Appl Climatol 14:237–251
Karl TR, Easterling DR (1999) Climate extremes: selected review and future research directions. Clim Change 42(1):309–325
Liang L, Li L, Liu Q (2011) Precipitation variability in northeast China from 1961 to 2008. J Hydrol 404(1):67–76
Liu L (2012) Xu ZX, Huang JX (2012) Spatio-temporal variation and abrupt changes for major climate variables in the Taihu Basin, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 26:777–791
Oliver JE (1980) Monthly precipitation distribution: a comparative index. Geographer 32:300–309
Pei H, Hao l, Han JW (2011) Pentad precipitation changes during recent 40 years in Inner Mongolia. J Appl Meteorol Sci 23(5):543–570 (in Chinese)
Qian WH, Qin A (2008) Precipitation division and climate shift in China from 1960 to 2000. Theoret Appl Climatol 93(1–2):1–17
Santo FE, Ramos AM, de Lima MIP, Trigo RM (2013) Seasonal changes in daily precipitation extremes in mainland Portugal from 1941 to 2007. Reg Environ Change 1–24
Shi P, Qiao X, Chen X, Zhou M, Qu S, Ma X, Zhang Z (2014) Spatial distribution and temporal trends in daily and monthly precipitation concentration indices in the upper reaches of the Huai River, China. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 28(2):201–212
Sneyers R (1990) On statistical analysis of series of observations. WMO Tech Note, WMO: 14
Sun J, Ao J (2013) Changes in precipitation and extreme precipitation in a warming environment in China. Chin Sci Bull 58(12):1395–1401
Tank AMG, Können GP (2003) Trends in indices of daily temperature and precipitation extremes in Europe, 1946–99. J Clim 16(22):3665–3680
Wang HJ (2001) The weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970′s. Adv Atmos Sci 18:376–386
Wang YQ, Zhou L (2005) Observed trends in extreme precipitation events in China during 1961–2001 and the associated changes in large-scale circulation. Geophys Res Lett 32:L09707
Wang BJ, Huang YX, Tao JH, Li DL, Wang PX (2006) regional features and variations of water vapor in northwest China. J Glaciol Geocryol 28(1):15–21 (in Chinese)
Wang W, Shao Q, Peng S, Zhang Z, Xing W, An G, Yong B (2011) Spatial and temporal characteristics of changes in precipitation during 1957–2007 in the Haihe River basin, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 25(7):881–895
Wang W, Shao Q, Yang T, Peng S, Yu Z, Taylor J, Xing W, Zhao C, Sun F (2013) Changes in daily temperature and precipitation extremes in the Yellow River basin, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 27:401–421
Xu M et al (2006) Steady decline of east Asian monsoon winds, 1969–2000: evidence from direct ground measurements of wind speed. J Geophys Res Atmos 111:D24111
Yavuz H, Erdoğan S (2012) Spatial analysis of monthly and annual precipitation trends in Turkey. Water Resour Manage 26(3):609–621
Zhang X, Harvey DK, Hogg WD, Yuzyk TR (2001) Trends in Canadian streamflow. Water Resour Res 37(4):987–998
Zhang ZX, Zhang Q, Chen X, Zhang JC, Zhou JW (2011) Statistical properties of moisture transport in East Asia and their impacts on wetness/dryness variations in North China. Theor Appl Climatol 104(3):337–347
Zhang Q, Singh VP, Peng JT, Chen YD, Li JF (2012) Spatial–temporal changes of precipitation structure across the Pearl River basin, China. J Hydrol 440–441:113–122
Zhang Q, Peng J, Singh VP, Li J, Chen YD (2014) Spatio-temporal variations of precipitation in arid and semiarid regions of China: the Yellow River basin as a case study. Glob Planet Change 114:38–49
Zolina O, Simmer C, Gulev SK, Kollet S (2010) Changing structure of European precipitation: Longer wet periods leading to more abundant rainfalls. Geophys Res Lett 37(6)
Acknowledgments
This paper was financially supported by the Forestry Industry Research special funds for Public Welfare Projects ‘‘Study of water resource control function of typical forest vegetation in the region of Yangtze river delta’’ (No: 201104005-04) and fully supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 51109109, 41375006), National Basic Research Program of China (No: 31200534) and National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No: 2012BAC23B01, 2012BAD16B0305). We would like to thank the National Climate Centre (NCC) in Beijing for providing valuable climate datasets.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: J.-T. Fasullo.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Sun, S., Xue, Y. et al. Changing characteristics of precipitation during 1960–2012 in Inner Mongolia, northern China. Meteorol Atmos Phys 127, 257–271 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-014-0363-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-014-0363-z