Abstract
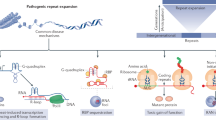
The most common neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s diseases, are characterized by synaptic dysfunction, neuronal loss and proteinaceous aggregates in central nervous system. The deposition of misfolded proteins constitutes neuropathological hallmarks of these diseases, grouped in the generic term of proteinopathies. Apart from these, other neurodegenerative diseases are characterized by genetic abnormalities like unstable repetitive simple sequence tracts (microsatellites) dispersed throughout the human genome. They are called repeat expansion disorders and include, for example, Huntington’s disease or frontotemporal dementia/amyotrophic lateral sclerosis phenotypes associated to an expansion in C9ORF72. The presence of the expanded DNA tract leads to molecular alterations at the DNA, RNA and protein levels associated to distinct mechanisms, such as loss-of-function (LOF), gain-of-function (GOF) including misfolding of physiological or mutant proteins, favoring their polymerization and aggregation. Therefore, specific proteinopathies also arise from these repeat expansion disorders. The molecular description of the nature and location of expanded tracts, highlighting the consequences onto clinical phenotypes will be first described. Specific focuses on the three pathomechanisms of the repeat expansions associated to proteinopathies will then be addressed. Lastly, we will show how progress in the understanding of these different mechanisms has led to recent advances in new/innovative therapeutic approaches and emergence of associated biomarkers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aisen PS, Cummings J, Doody R, Kramer L, Salloway S, Selkoe DJ, Sims J, Sperling RA, Vellas B (2020) The future of anti-amyloid trials. J Prev Alzheimer’s Dis 7(3):146–151. https://doi.org/10.14283/jpad.2020.24
Al-Sarraj S, King A, Troakes C, Smith B, Maekawa S, Bodi I, Rogelj B, Al-Chalabi A, Hortobagyi T, Shaw CE (2011) p62 positive, TDP-43 negative, neuronal cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusions in the cerebellum and hippocampus define the pathology of C9orf72-linked FTLD and MND/ALS. Acta Neuropathol 122(6):691–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0911-2
Ayhan F, Perez BA, Shorrock HK, Zu T, Banez-Coronel M, Reid T, Furuya H, Clark HB, Troncoso JC, Ross CA, Subramony SH, Ashizawa T, Wang ET, Yachnis AT, Ranum LP (2018) SCA8 RAN polySer protein preferentially accumulates in white matter regions and is regulated by eIFF. EMBO J https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201899023
Aziz NA, van Belzen MJ, Coops ID, Belfroid RD, Roos RA (2011) Parent-of-origin differences of mutant HTT CAG repeat instability in Huntington’s disease. Eur J Med Genet 54(4):e413-418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2011.04.002
Bakkar N, Boehringer A, Bowser R (2015) Use of biomarkers in ALS drug development and clinical trials. Brain Res 1607:94–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.031
Banez-Coronel M, Ayhan F, Tarabochia AD, Zu T, Perez BA, Tusi SK, Pletnikova O, Borchelt DR, Ross CA, Margolis RL, Yachnis AT, Troncoso JC, Ranum LP (2015) RAN translation in Huntington disease. Neuron 88(4):667–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.10.038
Bayer TA (2015) Proteinopathies, a core concept for understanding and ultimately treating degenerative disorders? Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 25(5):713–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2013.03.007
Benn CL, Gibson KR, Reynolds DS (2021) Drugging DNA damage repair pathways for trinucleotide repeat expansion diseases. J Huntington’s Dis 10(1):203–220. https://doi.org/10.3233/JHD-200421
Bois P, Jeffreys AJ (1999) Minisatellite instability and germline mutation. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 55(12):1636–1648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050402
Boudreau RL, Davidson BL (2010) RNAi therapeutics for CNS disorders. Brain Res 1338:112–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.03.038
Brenner D, Ludolph AC, Weishaupt JH (2020) Gene specific therapies - the next therapeutic milestone in neurology. Neurolog Res Pract 2:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42466-020-00075-z
Brys M, Fanning L, Hung S, Ellenbogen A, Penner N, Yang M, Welch M, Koenig E, David E, Fox T, Makh S, Aldred J, Goodman I, Pepinsky B, Liu Y, Graham D, Weihofen A, Cedarbaum JM (2019) Randomized phase I clinical trial of anti-alpha-synuclein antibody BIIB054. Movem Disord off J Movem Disord Soc 34(8):1154–1163. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27738
Bugaut A, Murat P, Balasubramanian S (2012) An RNA hairpin to G-quadruplex conformational transition. J Am Chem Soc 134(49):19953–19956. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja308665g
Byrne LM, Rodrigues FB, Blennow K, Durr A, Leavitt BR, Roos RAC, Scahill RI, Tabrizi SJ, Zetterberg H, Langbehn D, Wild EJ (2017) Neurofilament light protein in blood as a potential biomarker of neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease: a retrospective cohort analysis. Lancet Neurol 16(8):601–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30124-2
Cabal-Herrera AM, Tassanakijpanich N, Salcedo-Arellano MJ, Hagerman RJ (2020) Fragile X-associated tremor/Ataxia syndrome (FXTAS): pathophysiology and clinical implications. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124391
Campuzano V, Montermini L, Molto MD, Pianese L, Cossee M, Cavalcanti F, Monros E, Rodius F, Duclos F, Monticelli A, Zara F, Canizares J, Koutnikova H, Bidichandani SI, Gellera C, Brice A, Trouillas P, De Michele G, Filla A, De Frutos R, Palau F, Patel PI, Di Donato S, Mandel JL, Cocozza S, Koenig M, Pandolfo M (1996) Friedreich’s ataxia: autosomal recessive disease caused by an intronic GAA triplet repeat expansion. Science (new York, NY) 271(5254):1423–1427. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.271.5254.1423
Castelli LM, Huang WP, Lin YH, Chang KY, Hautbergue GM (2021) Mechanisms of repeat-associated non-AUG translation in neurological microsatellite expansion disorders. Biochem Soc Trans 49(2):775–792. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20200690
Chan HY (2014) RNA-mediated pathogenic mechanisms in polyglutamine diseases and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Cell Neurosci 8:431. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2014.00431
Chang YJ, Jeng US, Chiang YL, Hwang IS, Chen YR (2016) The glycine-alanine dipeptide repeat from C9orf72 Hexanucleotide expansions forms toxic amyloids possessing cell-to-cell transmission properties. J Biol Chem 291(10):4903–4911. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.694273
Chintalaphani SR, Pineda SS, Deveson IW, Kumar KR (2021) An update on the neurological short tandem repeat expansion disorders and the emergence of long-read sequencing diagnostics. Acta Neuropathol Commun 9(1):98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-021-01201-x
Ciesiolka A, Jazurek M, Drazkowska K, Krzyzosiak WJ (2017) Structural characteristics of simple RNA repeats associated with disease and their deleterious protein interactions. Front Cell Neurosci 11:97. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00097
Cooper JK, Schilling G, Peters MF, Herring WJ, Sharp AH, Kaminsky Z, Masone J, Khan FA, Delanoy M, Borchelt DR, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Ross CA (1998) Truncated N-terminal fragments of huntingtin with expanded glutamine repeats form nuclear and cytoplasmic aggregates in cell culture. Hum Mol Genet 7(5):783–790. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/7.5.783
Cortese A, Simone R, Sullivan R, Vandrovcova J, Tariq H, Yau WY, Humphrey J, Jaunmuktane Z, Sivakumar P, Polke J, Ilyas M, Tribollet E, Tomaselli PJ, Devigili G, Callegari I, Versino M, Salpietro V, Efthymiou S, Kaski D, Wood NW, Andrade NS, Buglo E, Rebelo A, Rossor AM, Bronstein A, Fratta P, Marques WJ, Zuchner S, Reilly MM, Houlden H (2019) Biallelic expansion of an intronic repeat in RFC1 is a common cause of late-onset ataxia. Nat Genet 51(4):649–658. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0372-4
Cummings J, Blennow K, Johnson K, Keeley M, Bateman RJ, Molinuevo JL, Touchon J, Aisen P, Vellas B (2019) Anti-tau trials for Alzheimer’s disease: a report from the EU/US/CTAD task force. J Prev Alzheimer’s Dis 6(3):157–163. https://doi.org/10.14283/jpad.2019.14
Davies SW, Beardsall K, Turmaine M, DiFiglia M, Aronin N, Bates GP (1998) Are neuronal intranuclear inclusions the common neuropathology of triplet-repeat disorders with polyglutamine-repeat expansions? Lancet 351(9096):131–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(97)08360-8
Depienne C, Mandel JL (2021) 30 years of repeat expansion disorders: What have we learned and what are the remaining challenges? Am J Hum Genet 108(5):764–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.03.011
Di Lascio S, Benfante R, Cardani S, Fornasari D (2020) Research Advances on Therapeutic Approaches to Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome (CCHS). Front Neurosci 14:615666. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.615666
DiFiglia M, Sapp E, Chase KO, Davies SW, Bates GP, Vonsattel JP, Aronin N (1997) Aggregation of huntingtin in neuronal intranuclear inclusions and dystrophic neurites in brain. Science (new York, NY) 277(5334):1990–1993. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.277.5334.1990
Dugger BN, Dickson DW (2017) Pathology of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a028035
Ekman FK, Ojala DS, Adil MM, Lopez PA, Schaffer DV, Gaj T (2019) CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing increases lifespan and improves motor deficits in a Huntington’s disease mouse model. Mol Therapy Nucleic Acids 17:829–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.07.009
Fan HC, Ho LI, Chi CS, Chen SJ, Peng GS, Chan TM, Lin SZ, Harn HJ (2014) Polyglutamine (PolyQ) diseases: genetics to treatments. Cell Transplant 23(4–5):441–458. https://doi.org/10.3727/096368914X678454
Gaj T, Gersbach CA, Barbas CF 3rd (2013) ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas-based methods for genome engineering. Trends Biotechnol 31(7):397–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.04.004
Gatchel JR, Zoghbi HY (2005) Diseases of unstable repeat expansion: mechanisms and common principles. Nat Rev Genet 6(10):743–755. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1691
Gendron TF, van Blitterswijk M, Bieniek KF, Daughrity LM, Jiang J, Rush BK, Pedraza O, Lucas JA, Murray ME, Desaro P, Robertson A, Overstreet K, Thomas CS, Crook JE, Castanedes-Casey M, Rousseau L, Josephs KA, Parisi JE, Knopman DS, Petersen RC, Boeve BF, Graff-Radford NR, Rademakers R, Lagier-Tourenne C, Edbauer D, Cleveland DW, Dickson DW, Petrucelli L, Boylan KB (2015) Cerebellar c9RAN proteins associate with clinical and neuropathological characteristics of C9ORF72 repeat expansion carriers. Acta Neuropathol 130(4):559–573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1474-4
Gendron TF, Chew J, Stankowski JN, Hayes LR, Zhang YJ, Prudencio M, Carlomagno Y, Daughrity LM, Jansen-West K, Perkerson EA, O’Raw A, Cook C, Pregent L, Belzil V, van Blitterswijk M, Tabassian LJ, Lee CW, Yue M, Tong J, Song Y, Castanedes-Casey M, Rousseau L, Phillips V, Dickson DW, Rademakers R, Fryer JD, Rush BK, Pedraza O, Caputo AM, Desaro P, Palmucci C, Robertson A, Heckman MG, Diehl NN, Wiggs E, Tierney M, Braun L, Farren J, Lacomis D, Ladha S, Fournier CN, McCluskey LF, Elman LB, Toledo JB, McBride JD, Tiloca C, Morelli C, Poletti B, Solca F, Prelle A, Wuu J, Jockel-Balsarotti J, Rigo F, Ambrose C, Datta A, Yang W, Raitcheva D, Antognetti G, McCampbell A, Van Swieten JC, Miller BL, Boxer AL, Brown RH, Bowser R, Miller TM, Trojanowski JQ, Grossman M, Berry JD, Hu WT, Ratti A, Traynor BJ, Disney MD, Benatar M, Silani V, Glass JD, Floeter MK, Rothstein JD, Boylan KB, Petrucelli L (2017) Poly(GP) proteins are a useful pharmacodynamic marker for C9ORF72-associated amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aai7866
Goldberg YP, Nicholson DW, Rasper DM, Kalchman MA, Koide HB, Graham RK, Bromm M, Kazemi-Esfarjani P, Thornberry NA, Vaillancourt JP, Hayden MR (1996) Cleavage of huntingtin by apopain, a proapoptotic cysteine protease, is modulated by the polyglutamine tract. Nat Genet 13(4):442–449. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0896-442
Gomes-Pereira M, Monckton DG (2004) Chemically induced increases and decreases in the rate of expansion of a CAG*CTG triplet repeat. Nucleic Acids Res 32(9):2865–2872. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh612
Gomez-Deza J, Lee YB, Troakes C, Nolan M, Al-Sarraj S, Gallo JM, Shaw CE (2015) Dipeptide repeat protein inclusions are rare in the spinal cord and almost absent from motor neurons in C9ORF72 mutant amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and are unlikely to cause their degeneration. Acta Neuropathol Commun 3:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-015-0218-y
Graham RK, Deng Y, Slow EJ, Haigh B, Bissada N, Lu G, Pearson J, Shehadeh J, Bertram L, Murphy Z, Warby SC, Doty CN, Roy S, Wellington CL, Leavitt BR, Raymond LA, Nicholson DW, Hayden MR (2006) Cleavage at the caspase-6 site is required for neuronal dysfunction and degeneration due to mutant huntingtin. Cell 125(6):1179–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.026
Green KM, Linsalata AE, Todd PK (2016) RAN translation-What makes it run? Brain Res 1647:30–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.04.003
Gutekunst C-A, Li S-H, Yi H, Mulroy JS, Kuemmerle S, Jones R, Rye D, Ferrante RJ, Hersch SM, Li X-J (1999) Nuclear and neuropil aggregates in Huntington’s disease: relationship to neuropathology. J Neurosci 19(7):2522. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-07-02522.1999
Haacke A, Hartl FU, Breuer P (2007) Calpain inhibition is sufficient to suppress aggregation of polyglutamine-expanded ataxin-3. J Biol Chem 282(26):18851–18856. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M611914200
Hands SL, Wyttenbach A (2010) Neurotoxic protein oligomerisation associated with polyglutamine diseases. Acta Neuropathol 120(4):419–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0703-0
Hautbergue GM, Cleary JD, Guo S, Ranum LPW (2021) Therapeutic strategies for C9orf72 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Curr Opin Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0000000000000984
Hellen CU, Sarnow P (2001) Internal ribosome entry sites in eukaryotic mRNA molecules. Genes Dev 15(13):1593–1612. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.891101
Hoffner G, Island ML, Djian P (2005) Purification of neuronal inclusions of patients with Huntington’s disease reveals a broad range of N-terminal fragments of expanded huntingtin and insoluble polymers. J Neurochem 95(1):125–136. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03348.x
Jiang J, Zhu Q, Gendron TF, Saberi S, McAlonis-Downes M, Seelman A, Stauffer JE, Jafar-Nejad P, Drenner K, Schulte D, Chun S, Sun S, Ling SC, Myers B, Engelhardt J, Katz M, Baughn M, Platoshyn O, Marsala M, Watt A, Heyser CJ, Ard MC, De Muynck L, Daughrity LM, Swing DA, Tessarollo L, Jung CJ, Delpoux A, Utzschneider DT, Hedrick SM, de Jong PJ, Edbauer D, Van Damme P, Petrucelli L, Shaw CE, Bennett CF, Da Cruz S, Ravits J, Rigo F, Cleveland DW, Lagier-Tourenne C (2016) Gain of Toxicity from ALS/FTD-linked repeat expansions in C9ORF72 is alleviated by antisense oligonucleotides targeting GGGGCC-containing RNAs. Neuron 90(3):535–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.04.006
Kamsteeg EJ, Kress W, Catalli C, Hertz JM, Witsch-Baumgartner M, Buckley MF, van Engelen BG, Schwartz M, Scheffer H (2012) Best practice guidelines and recommendations on the molecular diagnosis of myotonic dystrophy types 1 and 2. Eur J Hum Genet EJHG 20(12):1203–1208. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2012.108
Kazantsev A, Preisinger E, Dranovsky A, Goldgaber D, Housman D (1999) Insoluble detergent-resistant aggregates form between pathological and nonpathological lengths of polyglutamine in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96(20):11404. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.20.11404
Kearse MG, Todd PK (2014) Repeat-associated non-AUG translation and its impact in neurodegenerative disease. Neurotherapeutics 11(4):721–731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-014-0292-z
Khalil M, Pirpamer L, Hofer E, Voortman MM, Barro C, Leppert D, Benkert P, Ropele S, Enzinger C, Fazekas F, Schmidt R, Kuhle J (2020) Serum neurofilament light levels in normal aging and their association with morphologic brain changes. Nat Commun 11(1):812. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14612-6
Khristich AN, Mirkin SM (2020) On the wrong DNA track: Molecular mechanisms of repeat-mediated genome instability. J Biol Chem 295(13):4134–4170. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.REV119.007678
Koch P, Breuer P, Peitz M, Jungverdorben J, Kesavan J, Poppe D, Doerr J, Ladewig J, Mertens J, Tüting T, Hoffmann P, Klockgether T, Evert BO, Wüllner U, Brüstle O (2011) Excitation-induced ataxin-3 aggregation in neurons from patients with Machado-Joseph disease. Nature 480(7378):543–546. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10671
Komar AA, Hatzoglou M (2011) Cellular IRES-mediated translation: the war of ITAFs in pathophysiological states. Cell Cycle 10(2):229–240. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.10.2.14472
Konieczny P, Stepniak-Konieczna E, Sobczak K (2014) MBNL proteins and their target RNAs, interaction and splicing regulation. Nucleic Acids Res 42(17):10873–10887. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku767
Kovacs GG (2017) Concepts and classification of neurodegenerative diseases. Handb Clin Neurol 145:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-802395-2.00021-3
Kovacs GG (2019) Molecular pathology of neurodegenerative diseases: principles and practice. J Clin Pathol 72(11):725–735. https://doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2019-205952
Kraus-Perrotta C, Lagalwar S (2016) Expansion, mosaicism and interruption: mechanisms of the CAG repeat mutation in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Cerebell Ataxias 3:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40673-016-0058-y
Kumar V, Hasan GM, Hassan MI (2017) Unraveling the role of RNA mediated toxicity of C9orf72 repeats in C9-FTD/ALS. Front Neurosci 11:711. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00711
Kwon I, Xiang S, Kato M, Wu L, Theodoropoulos P, Wang T, Kim J, Yun J, Xie Y, McKnight SL (2014) Poly-dipeptides encoded by the C9orf72 repeats bind nucleoli, impede RNA biogenesis, and kill cells. Science (new York, NY) 345(6201):1139–1145. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254917
La Spada AR, Taylor JP (2010) Repeat expansion disease: progress and puzzles in disease pathogenesis. Nat Rev Genet 11(4):247–258. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2748
Lam JK, Chow MY, Zhang Y, Leung SW (2015) siRNA versus miRNA as therapeutics for gene silencing. Mol Therapy Nucleic Acids 4:e252. https://doi.org/10.1038/mtna.2015.23
Lambertsen KL, Soares CB, Gaist D, Nielsen HH (2020) Neurofilaments: The C-reactive protein of neurology. Brain Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010056
Lee JE, Bennett CF, Cooper TA (2012) RNase H-mediated degradation of toxic RNA in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(11):4221–4226. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1117019109
Lee BH, Collins E, Lewis L, Guntrum D, Eichinger K, Voter K, Abdel-Hamid HZ, Ciafaloni E (2019) Combination therapy with nusinersen and AVXS-101 in SMA type 1. Neurology 93(14):640–641. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000008207
Lo Scrudato M, Poulard K, Sourd C, Tome S, Klein AF, Corre G, Huguet A, Furling D, Gourdon G, Buj-Bello A (2019) Genome editing of expanded CTG repeats within the human DMPK gene reduces nuclear RNA foci in the muscle of DM1 mice. Mol Therapy 27(8):1372–1388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.05.021
Loureiro JR, Oliveira CL, Silveira I (2016) Unstable repeat expansions in neurodegenerative diseases: nucleocytoplasmic transport emerges on the scene. Neurobiol Aging 39:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.12.007
Mahadevan M, Tsilfidis C, Sabourin L, Shutler G, Amemiya C, Jansen G, Neville C, Narang M, Barcelo J, O’Hoy K et al (1992) Myotonic dystrophy mutation: an unstable CTG repeat in the 3’ untranslated region of the gene. Science (new York, NY) 255(5049):1253–1255. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1546325
Malik I, Kelley CP, Wang ET, Todd PK (2021) Molecular mechanisms underlying nucleotide repeat expansion disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 22(9):589–607. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-021-00382-6
Marsh AP (2019) Molecular mechanisms of proteinopathies across neurodegenerative disease: a review. Neurolog Res Practice 1:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42466-019-0039-8
Marti E (2016) RNA toxicity induced by expanded CAG repeats in Huntington’s disease. Brain Pathol 26(6):779–786. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12427
McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR Jr, Kawas CH, Klunk WE, Koroshetz WJ, Manly JJ, Mayeux R, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rossor MN, Scheltens P, Carrillo MC, Thies B, Weintraub S, Phelps CH (2011) The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dementia 7(3):263–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005
Miller J, Arrasate M, Brooks E, Libeu CP, Legleiter J, Hatters D, Curtis J, Cheung K, Krishnan P, Mitra S, Widjaja K, Shaby BA, Lotz GP, Newhouse Y, Mitchell EJ, Osmand A, Gray M, Thulasiramin V, Saudou F, Segal M, Yang XW, Masliah E, Thompson LM, Muchowski PJ, Weisgraber KH, Finkbeiner S (2011) Identifying polyglutamine protein species in situ that best predict neurodegeneration. Nat Chem Biol 7(12):925–934. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.694
Mirkin SM (2007) Expandable DNA repeats and human disease. Nature 447(7147):932–940. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05977
Moumne L, Dipietromaria A, Batista F, Kocer A, Fellous M, Pailhoux E, Veitia RA (2008) Differential aggregation and functional impairment induced by polyalanine expansions in FOXL2, a transcription factor involved in cranio-facial and ovarian development. Hum Mol Genet 17(7):1010–1019. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddm373
Nakanishi K (2016) Anatomy of RISC: how do small RNAs and chaperones activate Argonaute proteins? Wiley Interdisciplin Rev RNA 7(5):637–660. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1356
Nguyen L, Cleary JD, Ranum LPW (2019) Repeat-Associated Non-ATG Translation: Molecular Mechanisms and Contribution to Neurological Disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 42:227–247. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-070918-050405
Noor A, Zafar S, Zerr I (2021) Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies in the Proteoform Spectrum-Tools and Challenges. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031085
Paulson H (2018) Repeat expansion diseases. Handb Clin Neurol 147:105–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63233-3.00009-9
Pearson CE, Nichol Edamura K, Cleary JD (2005) Repeat instability: mechanisms of dynamic mutations. Nat Rev Genet 6(10):729–742. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1689
Pesovic J, Peric S, Brkusanin M, Brajuskovic G, Rakocevic-Stojanovic V, Savic-Pavicevic D (2018) Repeat interruptions modify age at onset in myotonic dystrophy type 1 by stabilizing DMPK expansions in somatic cells. Front Genet 9:601. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00601
Pfister AS (2019) Emerging role of the nucleolar stress response in autophagy. Front Cell Neurosci 13:156. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00156
Pinto BS, Saxena T, Oliveira R, Mendez-Gomez HR, Cleary JD, Denes LT, McConnell O, Arboleda J, Xia G, Swanson MS, Wang ET (2017) Impeding transcription of expanded microsatellite repeats by deactivated Cas9. Mol Cell 68(3):479-490 e475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.09.033
Querido E, Gallardo F, Beaudoin M, Menard C, Chartrand P (2011) Stochastic and reversible aggregation of mRNA with expanded CUG-triplet repeats. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 10):1703–1714. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.073270
Rascovsky K, Hodges JR, Knopman D, Mendez MF, Kramer JH, Neuhaus J, van Swieten JC, Seelaar H, Dopper EG, Onyike CU, Hillis AE, Josephs KA, Boeve BF, Kertesz A, Seeley WW, Rankin KP, Johnson JK, Gorno-Tempini ML, Rosen H, Prioleau-Latham CE, Lee A, Kipps CM, Lillo P, Piguet O, Rohrer JD, Rossor MN, Warren JD, Fox NC, Galasko D, Salmon DP, Black SE, Mesulam M, Weintraub S, Dickerson BC, Diehl-Schmid J, Pasquier F, Deramecourt V, Lebert F, Pijnenburg Y, Chow TW, Manes F, Grafman J, Cappa SF, Freedman M, Grossman M, Miller BL (2011) Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia. Brain 134(Pt 9):2456–2477. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr179
Rinaldi C, Wood MJA (2018) Antisense oligonucleotides: the next frontier for treatment of neurological disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 14(1):9–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2017.148
Rudnicki DD, Margolis RL (2003) Repeat expansion and autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorders: consensus and controversy. Expert Rev Mol Med 5(21):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1462399403006598
Sarisozen C, Salzano G, Torchilin VP (2015) Recent advances in siRNA delivery. Biomol Concepts 6(5–6):321–341. https://doi.org/10.1515/bmc-2015-0019
Schmitz A, Pinheiro Marques J, Oertig I, Maharjan N, Saxena S (2021) Emerging Perspectives on Dipeptide Repeat Proteins in C9ORF72 ALS/FTD. Front Cell Neurosci 15:637548. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.637548
Schwartz JL, Jones KL, Yeo GW (2021) Repeat RNA expansion disorders of the nervous system: post-transcriptional mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 56(1):31–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409238.2020.1841726
Stoyas CA, La Spada AR (2018) The CAG-polyglutamine repeat diseases: a clinical, molecular, genetic, and pathophysiologic nosology. Handb Clin Neurol 147:143–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-63233-3.00011-7
Sudhakar V, Richardson RM (2019) Gene Therapy for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neurotherapeutics 16(1):166–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-018-00694-0
Sun J, Roy S (2021) Gene-based therapies for neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Neurosci 24(3):297–311. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-020-00778-1
Swinnen B, Robberecht W, Van Den Bosch L (2020) RNA toxicity in non-coding repeat expansion disorders. EMBO J 39(1):e101112. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2018101112
Tabrizi SJ, Flower MD, Ross CA, Wild EJ (2020) Huntington disease: new insights into molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Neurol 16(10):529–546. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-020-0389-4
Takahashi T, Kikuchi S, Katada S, Nagai Y, Nishizawa M, Onodera O (2008) Soluble polyglutamine oligomers formed prior to inclusion body formation are cytotoxic. Hum Mol Genet 17(3):345–356. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddm311
Todd PK, Oh SY, Krans A, He F, Sellier C, Frazer M, Renoux AJ, Chen KC, Scaglione KM, Basrur V, Elenitoba-Johnson K, Vonsattel JP, Louis ED, Sutton MA, Taylor JP, Mills RE, Charlet-Berguerand N, Paulson HL (2013) CGG repeat-associated translation mediates neurodegeneration in fragile X tremor ataxia syndrome. Neuron 78(3):440–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.03.026
Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Parker R (2006) Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev 20(5):515–524. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1399806
Verkerk AJ, Pieretti M, Sutcliffe JS, Fu YH, Kuhl DP, Pizzuti A, Reiner O, Richards S, Victoria MF, Zhang FP et al (1991) Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell 65(5):905–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(91)90397-h
Watson N, Brandel JP, Green A, Hermann P, Ladogana A, Lindsay T, Mackenzie J, Pocchiari M, Smith C, Zerr I, Pal S (2021) The importance of ongoing international surveillance for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nat Rev Neurol 17(6):362–379. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-021-00488-7
Wellington CL, Ellerby LM, Gutekunst CA, Rogers D, Warby S, Graham RK, Loubser O, van Raamsdonk J, Singaraja R, Yang YZ, Gafni J, Bredesen D, Hersch SM, Leavitt BR, Roy S, Nicholson DW, Hayden MR (2002) Caspase cleavage of mutant huntingtin precedes neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci 22(18):7862–7872. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.22-18-07862.2002
Wen X, Tan W, Westergard T, Krishnamurthy K, Markandaiah SS, Shi Y, Lin S, Shneider NA, Monaghan J, Pandey UB, Pasinelli P, Ichida JK, Trotti D (2014) Antisense proline-arginine RAN dipeptides linked to C9ORF72-ALS/FTD form toxic nuclear aggregates that initiate in vitro and in vivo neuronal death. Neuron 84(6):1213–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.010
Wetzel R (2012) Physical Chemistry of Polyglutamine: Intriguing Tales of a Monotonous Sequence. J Mol Biol 421(4):466–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2012.01.030
Wild EJ, Boggio R, Langbehn D, Robertson N, Haider S, Miller JR, Zetterberg H, Leavitt BR, Kuhn R, Tabrizi SJ, Macdonald D, Weiss A (2015) Quantification of mutant huntingtin protein in cerebrospinal fluid from Huntington’s disease patients. J Clin Investig 125(5):1979–1986. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI80743
Wong BKY, Ehrnhoefer DE, Graham RK, Martin DDO, Ladha S, Uribe V, Stanek LM, Franciosi S, Qiu X, Deng Y, Kovalik V, Zhang W, Pouladi MA, Shihabuddin LS, Hayden MR (2015) Partial rescue of some features of Huntington Disease in the genetic absence of caspase-6 in YAC128 mice. Neurobiol Dis 76:24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.12.030
Xia H, Mao Q, Eliason SL, Harper SQ, Martins IH, Orr HT, Paulson HL, Yang L, Kotin RM, Davidson BL (2004) RNAi suppresses polyglutamine-induced neurodegeneration in a model of spinocerebellar ataxia. Nat Med 10(8):816–820. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1076
Yuan A, Nixon RA (2021) Neurofilament Proteins as Biomarkers to Monitor Neurological Diseases and the Efficacy of Therapies. Front Neurosci 15:689938. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.689938
Zu T, Gibbens B, Doty NS, Gomes-Pereira M, Huguet A, Stone MD, Margolis J, Peterson M, Markowski TW, Ingram MA, Nan Z, Forster C, Low WC, Schoser B, Somia NV, Clark HB, Schmechel S, Bitterman PB, Gourdon G, Swanson MS, Moseley M, Ranum LP (2011) Non-ATG-initiated translation directed by microsatellite expansions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(1):260–265. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1013343108
Zu T, Cleary JD, Liu Y, Banez-Coronel M, Bubenik JL, Ayhan F, Ashizawa T, Xia G, Clark HB, Yachnis AT, Swanson MS, Ranum LPW (2017) RAN translation regulated by muscleblind proteins in myotonic dystrophy type 2. Neuron 95(6):1292–1305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.08.039
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AF and IQ authors drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content and approved the submitted version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest:
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fourier, A., Quadrio, I. Proteinopathies associated to repeat expansion disorders. J Neural Transm 129, 173–185 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-021-02454-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-021-02454-5