Abstract
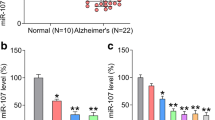
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most prevalent and age-related dementia accompanied by neurodegenerative disorder, memory loss, and abnormal behaviors. Recent studies have shown an increasing interest in studying the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) and their potential values in the early diagnostics of AD. MiR-425-5p has extensively expression within various tissues and organs, acting as an important regulator in many pathological procedures. The functions of miR-425-5p involved in AD were investigated in the present study. The results showed that miR-425-5p was upregulated in patients with AD and HEK293/tau cells. Transfections with miR-425-5p overexpression vector significantly enhanced cell apoptosis, activated glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), and increased tau phosphorylation in HEK293/tau cells. Heat shock protein B8 (HSPB8) was directly targeted by miR-425-5p. Upregulation of miR-425-5p induced cell apoptosis and promoted tau phosphorylation partially via targeting HSPB8 in AD. Therefore, miR-425-5p might act as a new therapeutic target for AD treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Absalon S, Kochanek DM, Raghavan V, Krichevsky AM (2013) MiR-26b, upregulated in Alzheimer's disease, activates cell cycle entry, tau-phosphorylation, and apoptosis in postmitotic neurons. J Neurosci 33:14645–14659
Banzhaf-Strathmann J et al (2014) MicroRNA-125b induces tau hyperphosphorylation and cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease. EMBO J. 33:1667–1680
Crippa V et al (2010a) A role of small heat shock protein B8 (HspB8) in the autophagic removal of misfolded proteins responsible for neurodegenerative diseases. Autophagy 6:958–960. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.6.7.13042
Crippa V et al (2010b) The small heat shock protein B8 (HspB8) promotes autophagic removal of misfolded proteins involved in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Hum Mol Genet 19:3440–3456. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq257
Delay C, Mandemakers W, Hébert SS (2012) MicroRNAs in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis 46:285–290
Fang F, Song T, Zhang T, Cui Y, Zhang G, Xiong Q (2017) MiR-425-5p promotes invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through SCAI-mediated dysregulation of multiple signaling pathways. Oncotarget 8:31745
Fontaine JM, Sun X, Hoppe AD, Simon S, Vicart P, Welsh MJ, Benndorf R (2006) Abnormal small heat shock protein interactions involving neuropathy-associated HSP22 (HSPB8) mutants. FASEB J 20:2168–2170. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.06-5911fje
Geekiyanage H, Chan C (2011) MicroRNA-137/181c regulates serine palmitoyltransferase and in turn amyloid β, novel targets in sporadic Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 31:14820–14830
Geekiyanage H, Jicha GA, Nelson PT, Chan C (2012) Blood serum miRNA: non-invasive biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. Exp Neurol 235:491–496
Hamouda MA et al (2014) The small heat shock protein B8 (HSPB8) confers resistance to bortezomib by promoting autophagic removal of misfolded proteins in multiple myeloma cells. Oncotarget 5:6252–6266. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2193
Hardy JA, Higgins GA (1992) Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 256:184–186
Irobi J et al (2010) Mutant HSPB8 causes motor neuron-specific neurite degeneration. Hum Mol Genet 19:3254–3265
Jiang B et al (2017) MicroRNA-126a-5p enhances myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through suppressing Hspb8 expression. Oncotarget 8:94172
Khachaturian ZS (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 42:1097–1105
Kumar S, Vijayan M, Bhatti JS, Reddy PH (2017) Chapter three-microRNAs as peripheral biomarkers in aging and age-related diseases. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 146:47–94
Lu M, Zhang Q, Deng M, Miao J, Guo Y, Gao W, Cui Q (2008) An analysis of human microRNA and disease associations. PLoS ONE 3:e3420
Ma X, Liu L, Meng J (2017) MicroRNA-125b promotes neurons cell apoptosis and Tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 661:57–62
Nelson PT, Wang WX, Rajeev BW (2008) MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Pathol 18:130–138
Nunez-Iglesias J, Liu C-C, Morgan TE, Finch CE, Zhou XJ (2010) Joint genome-wide profiling of miRNA and mRNA expression in Alzheimer's disease cortex reveals altered miRNA regulation. PLoS ONE 5:e8898
Schonrock N, Ke YD, Humphreys D, Staufenbiel M, Ittner LM, Preiss T, Götz J (2010) Neuronal microRNA deregulation in response to Alzheimer's disease amyloid-β. PLoS ONE 5:e11070
Sun L, Jiang R, Li J, Wang B, Ma C, Lv Y, Mu N (2017) MicoRNA-425-5p is a potential prognostic biomarker for cervical cancer. Ann Clin Biochem 54:127–133
Wang X et al (2009) miR-34a, a microRNA up-regulated in a double transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease, inhibits bcl2 translation. Brain Res Bull 80:268–273
Yu G, Li Y, Tian Q, Liu R, Wang Q, Wang J-Z, Wang X (2011) Berberine attenuates calyculin A-induced cytotoxicity and Tau hyperphosphorylation in HEK293 cells. J Alzheimer's Dis 24:525–535
Zhang Z, Li Y, Fan L, Zhao Q, Tan B, Li Z, Zang A (2015) microRNA-425-5p is upregulated in human gastric cancer and contributes to invasion and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Exp Therap Med 9:1617–1622
Zhang Y et al (2016) Micro RNA-425-5p regulates chemoresistance in colorectal cancer cells via regulation of Programmed Cell Death 10. J Cell Mol Med 20:360–369
Zhu H-C, Wang L-M, Wang M, Song B, Tan S, Teng J-F, Duan D-X (2012) MicroRNA-195 downregulates Alzheimer's disease amyloid-β production by targeting BACE1. Brain Res Bull 88:596–601
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by JY, YW, LL, and CL. The first draft of the manuscript was written by CL, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Qingdao Mental Health Center (No. QMHC2015021156673). All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, J., Wu, Y., Li, L. et al. MicroRNA-425-5p promotes tau phosphorylation and cell apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease by targeting heat shock protein B8. J Neural Transm 127, 339–346 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-02134-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-02134-5