Abstract
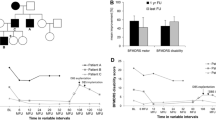
Status dystonicus (SD) is a rare and potentially life-threatening condition requiring intensive care management. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has emerged as an effective treatment for SD refractory to medical management, but its application in this field is still limited. Here, we report the long-term outcome of four pediatric patients treated with DBS at the University Hospital of Padua, Italy, for SD refractory to medications. In addition, we present the results of a systematic literature review aimed at identifying published cases of SD treated with DBS, with focus on motor outcome. In our cohort, two children were affected by methylmalonic acidemia and suffered acute basal ganglia lesions, while the other two carried a pathogenic mutation in GNAO1 gene. DBS target was subthalamic nucleus (STN) in one case and globus pallidus internus (GPi) in three. All patients experienced SD resolution within 8–19 days after surgery. Mean post-operative follow-up was 5 years. We identified in the literature 53 additional SD cases treated with DBS (median age at DBS implantation: 12 years) with reported positive outcome in 51 and resolution of SD in a mean of 17 days after surgery. Our findings indicate that DBS is an effective treatment for SD refractory to medications, even in patients with acute basal ganglia lesions; STN can be an appropriate target when GPi is damaged. Moreover, data from long-term follow-up show that SD recurrences can be significantly reduced in frequency or abolished after DBS implantation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananth AL, Robichaux-Viehoever A, Kim YM, Hanson-Kahn A, Cox R, Enns GM et al (2016) Clinical course of six children with GNAO1 mutations causing a severe and distinctive movement disorder. Pediatr Neurol 59:81–84
Angelini L, Nardocci N, Estienne M, Conti C, Dones I, Broggi G (2000) Life-threatening dystonia-dyskinesias in a child: successful treatment with bilateral pallidal stimulation. Mov Disord 15(5):1010–1012
Apetauerova D, Schirmer CM, Shils JL, Zani J, Arle JE (2010) Successful bilateral deep brain stimulation of the globus pallidus internus for persistent status dystonicus and generalized chorea. J Neurosurg 113(3):634–638
Aydin S, Abuzayed B, Uysal S, Unver O, Uzan M, Mengi M et al (2013) Pallidal deep brain stimulation in a 5-year-old child with dystonic storm: case report. Turk Neurosurg 23(1):125–128
Barbosa BJAP, Carra RB, Duarte KP, Godinho F, de Andrade DC, Teixeira MJ et al (2018) Bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation in refractory status dystonicus. J Neurol Sci 15(388):159–161
Ben-Haim S, Flatow V, Cheung T, Cho C, Tagliati M, Alterman RL (2016) Deep brain stimulation for status dystonicus: a case series and review of the literature. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 94(4):207–215
Canaz H, Karalok I, Topcular B, Agaoglu M, Yapici Z, Aydin S (2018) DBS in pediatric patients: institutional experience. Childs Nerv Syst 34(9):1771–1776
Carecchio M, Mencacci NE (2017) Emerging Monogenic Complex Hyperkinetic Disorders. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 17(12):97
Chakraborti S, Hasegawa H, Lumsden DE, Ali W, Kaminska M, Lin JP et al (2013) Bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for refractory total body dystonia secondary to metabolic autopallidotomy in a 4-year-old boy with infantile methylmalonic acidemia: case report. J Neurosurg Pediatr 12(4):374–379
Coubes P, Echenne B, Roubertie A, Vayssiere N, Tuffery S, Humbertclaude V et al (1999) Treatment of early-onset generalized dystonia by chronic bilateral stimulation of the internal globus pallidus. Apropos of a case. Neurochirurgie 45(2):139–144
Cury RG, Kalia SK, Shah BB, Jimenez-Shahed J, Prashanth LK, Moro E (2018) Surgical treatment of dystonia. Expert Rev Neurother 18:477–492
Danti FR, Galosi S, Romani M, Montomoli M, Carss KJ, Raymond FL et al (2017) GNAO1 encephalopathy: broadening the phenotype and evaluating treatment and outcome. Neurol Genet 3(2):e143
Elkaim LM, De Vloo P, Kalia SK, Lozano AM, Ibrahim GM (2018) Deep brain stimulation for childhood dystonia: current evidence and emerging practice. Expert Rev Neurother 18(10):773–784
Elkay M, Silver K, Penn RD, Dalvi A (2009) Dystonic storm due to Batten’s disease treated with pallidotomy and deep brain stimulation. Mov Disord 24(7):1048–1053
Fasano A, Ricciardi L, Bentivoglio AR, Canavese C, Zorzi G, Petrovic I et al (2012) Status dystonicus: predictors of outcome and progression patterns of underlying disease. Mov Disord 27(6):783–788
Franzini A, Cordella R, Rizzi M, Marras CE, Messina G, Zorzi G et al (2014) Deep brain stimulation in critical care conditions. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 121(4):391–398
Gill S, Curran A, Tripp J, Melarickas L, Hurran C, Stanley O (2001) Hyperkinetic movement disorder in an 11-year-old child treated with bilateral pallidal stimulators. Dev Med Child Neurol 43(5):350–353
Grandas F, Fernandez-Carballal C, Guzman-de-Villoria J, Ampuero I (2011) Treatment of a dystonic storm with pallidal stimulation in a patient with PANK2 mutation. Mov Disord 26(5):921–922
Honey CM, Malhotra AK, Tarailo-Graovac M, van Karnebeek CDM, Horvath G, Sulistyanto A (2018) GNAO1 mutation-induced pediatric dystonic storm rescue with pallidal deep brain stimulation. J Child Neurol 33(6):413–416
Jech R, Bares M, Urgosik D, Cerna O, Klement P, Adamovicova M et al (2009) Deep brain stimulation in acute management of status dystonicus. Mov Disord 24(15):2291–2292
Kovacs N, Balas I, Janszky J, Simon M, Fekete S, Komoly S (2011) Status dystonicus in tardive dystonia successfully treated by bilateral deep brain stimulation. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 113(9):808–809
Koy A, Cirak S, Gonzalez V, Becker K, Roujeau T, Milesi C et al (2018) Deep brain stimulation is effective in pediatric patients with GNAO1 associated severe hyperkinesia. J Neurol Sci 15(391):31–39
Krause P, Lauritsch K, Lipp A, Horn A, Weschke B, Kupsch A et al (2016) Long-term results of deep brain stimulation in a cohort of eight children with isolated dystonia. J Neurol 263(11):2319–2326
Lobato-Polo J, Ospina-Delgado D, Orrego-Gonzalez E, Gomez-Castro JF, Orozco JL, Enriquez-Marulanda A (2018) deep brain stimulation surgery for status dystonicus: a single-center experience and literature review. World Neurosurg 114:e992–e1001
Lumsden DE, King MD, Allen NM (2017) Status dystonicus in childhood. Curr Opin Pediatr 29(6):674–682
Manji H, Howard RS, Miller DH, Hirsch NP, Carr L, Bhatia K et al (1998) Status dystonicus: the syndrome and its management. Brain 121(Pt 2):243–252
Marsden CD, Marion MH, Quinn N (1984) The treatment of severe dystonia in children and adults. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47(11):1166–1173
Martinez-Torres I, Limousin P, Tisch S, Page R, Pinto A, Foltynie T et al (2009) Early and marked benefit with GPi DBS for Lubag syndrome presenting with rapidly progressive life-threatening dystonia. Mov Disord 24(11):1710–1712
Miyagi Y, Koike Y (2013) Tolerance of early pallidal stimulation in pediatric generalized dystonia. J Neurosurg Pediatr 12(5):476–482
Oterdoom DLM, van Egmond ME, Ascencao LC, van Dijk JMC, Saryyeva A, Beudel M et al (2018) Reversal of status dystonicus after relocation of pallidal electrodes in DYT6 generalized dystonia. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y) 13(8):530
Ruiz-Lopez M, Fasano A (2017) Rethinking status dystonicus. Mov Disord 32(12):1667–1676
Sato K, Nakagawa E, Saito Y, Komaki H, Sakuma H, Sugai K et al (2009) Hyperkinetic movement disorder in a child treated by globus pallidus stimulation. Brain Dev 31(6):452–455
Schumacher J, Wille C, Vesper J (2012) Management of postoperative respiratory failure in a patient with acute diaphragmatic status dystonicus. Br J Anaesth 108(2):329–330
Skogseid IM, Rosby O, Konglund A, Connelly JP, Nedregaard B, Jablonski GE et al (2018) Dystonia-deafness syndrome caused by ACTB p.Arg183Trp heterozygosity shows striatal dopaminergic dysfunction and response to pallidal stimulation. J Neurodev Disord 10(1):17-018-9235-z
Tanrikulu B, Ozen A, Gunal DI, Turkdogan D, Bayrakli F, Bayri Y et al (2015) Deep brain stimulation as treatment for dystonic storm in pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration syndrome: case report of a patient with homozygous mutation of the PANK2 gene. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 157(9):1513–1516 (discussion 1516–7)
Teive HA, Munhoz RP, Souza MM, Antoniuk SA, Santos ML, Teixeira MJ et al (2005) Status dystonicus: study of five cases. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 63(1):26–29
Termsarasab P, Frucht SJ (2017) Dystonic storm: a practical clinical and video review. J Clin Mov Disord 28(4):10-017-0057-z (eCollection 2017)
Timmermann L, Pauls KA, Wieland K, Jech R, Kurlemann G, Sharma N et al (2010) Dystonia in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation: outcome of bilateral pallidal stimulation. Brain 133(Pt 3):701–712
Trezza A, Antonini A, Sganzerla EP, Landi A (2016) Globus pallidus internus deep brain stimulation for the treatment of status dystonicus in tardive dystonia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 158(9):1789–1791
Waak M, Mohammad SS, Coman D, Sinclair K, Copeland L, Silburn P et al (2018) GNAO1-related movement disorder with life-threatening exacerbations: movement phenomenology and response to DBS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 89(2):221–222
Walcott BP, Nahed BV, Kahle KT, Duhaime AC, Sharma N, Eskandar EN (2012) Deep brain stimulation for medically refractory life-threatening status dystonicus in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 9(1):99–102
Yilmaz S, Turhan T, Ceylaner S, Gokben S, Tekgul H, Serdaroglu G (2016) Excellent response to deep brain stimulation in a young girl with GNAO1-related progressive choreoathetosis. Childs Nerv Syst 32(9):1567–1568
Zorzi G, Marras C, Nardocci N, Franzini A, Chiapparini L, Maccagnano E et al (2005) Stimulation of the globus pallidus internus for childhood-onset dystonia. Mov Disord 20(9):1194–1200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benato, A., Carecchio, M., Burlina, A. et al. Long-term effect of subthalamic and pallidal deep brain stimulation for status dystonicus in children with methylmalonic acidemia and GNAO1 mutation. J Neural Transm 126, 739–757 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-02010-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-02010-2