Abstract
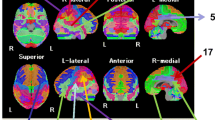
The aim of this study was to examine brain hypoperfusion and its relationship with cognitive dysfunction in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Forty patients with late-onset AD and not receiving acetylcholinesterase inhibitors were recruited from outpatient clinics. We examined cognitive function using the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-cognitive subscale (ADAS-cog) and brain perfusion using single-photon emission computed tomography, and analyzed classified gyrus level segments with three-dimensional stereotactic surface projection and the stereotactic extraction estimation method level 3. ADAS-cog subscales were grouped into three domains: language, memory, and praxis. Patients with late-onset AD showed an apparent reduction in regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) with a z score >1.5 in the frontal, temporal, and limbic lobes, with lesser reduction in the parietal and occipital lobes. Although hypoperfusion in the orbital, rectal, and subcallosal gyri of the frontal lobe was prominent, rCBF in the inferior frontal gyrus of the frontal lobe was significantly correlated with ADAS-cog total and language and praxis subscale scores. The parahippocampal gyrus of the limbic lobe was also significantly correlated with the ADAS-cog total, language, and praxis subscale scores. Additionally, the cingulate of the limbic lobe was significantly related with ADAS-cog memory. In spite of lesser hypoperfusion, the posterior cingulate gyrus of the limbic lobe was significantly related with ADAS-cog total, language, and memory subscale scores. Further, each subdivision of ADAS-cog was found to be related with various brain regions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistic manual of mental disorders (DSN-IV-TR), 4th edn. American Psychiatric Press, Washington DC (text rev)
Balsis S, Unger AA, Benge JF, Geraci L, Dooby RS (2012) Gaining precision on the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-cognitive: a Comparison of item response theory-based scores and total scores. Alzheimer’s Dement 8:288–294
Bartenstein P, Minoshima S, Hirsch C, Buch K, Willoch F, Mösch D, Schad D, Schwaiger M, Kurz A (1997) Quantitative assessment of cerebral blood flow in patients with Alzheimer’s disease by SPECT. J Nucl Med 38:1095–1101
Benge JF, Balsis S, Geraci L, Massman PJ, Doody RS (2009) How well do the ADAS-cog and its subscales measure cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease? Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 28:63–69
Cavedo E, Pievani M, Boccardi M, Galluzzi S, Bocchetta M, Bonetti M, Thompson PM, Frisoni GB (2014) Medial temporal atrophy in early and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 35:2004–2012
Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Cummings JL, DeKosky ST, Barberger-Gateau P, Delacourte A, Frisoni G, Fox NC, Galasko D, Gauthier S, Hampel H, Jicha GA, Meguro K, O’Brien J, Pasquier F, Robert P, Rossor M, Salloway S, Sarazin M, de Souza LC, Stern Y, Visser PJ, Scheltens P (2010) Revising the definition of Alzheimer’s disease: a new lexicon. Lancet Neurol 9:1118–1127
Elgh E, Sundström T, Näsman B, Åhlström KR, Nyberg L (2002) Memory functions and rCBF 99 mTc-HMPAO SPET: developing diagnostics in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med 29:1140–1148
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) Mini-mental state. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinicians. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Frisoni GB, Pievani M, Testa C, Sabattoli F, Bresciani L, Bonetti M, Beltramello A, Hayashi KM, Toga AW, Thompson PM (2007) The topography of grey matter involvement in early and late onset Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 130:720–730
Frlich L, Eilles R, Ihl K, Maurer K, Lanczik M (1989) Stage-dependent reduction of regional cerebral blood flow measured by HMPAO-SPECT in dementia of Alzheimer type. Psychiatry Res 29:347–350
Grady CL, Haxby JV, Horwitz B, Berg G, Rapoport SI (1987) Neuropsychological and cerebral metabolic function in early vs late onset dementia of the Alzheimer type. Neuropsychologia 25:807–816
Hachinski VC, Iliff LD, Zilhka E, Du Boulay GH, McAllister VL, Marshall J, Russell RW, Symon L (1975) Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol 32:632–637
Hanaoka T, Kimura N, Aso Y, Takemaru M, Kimura Y, Ishibashi M, Matsubara E (2015) Relationship between white matter lesions and regional cerebral blood flow changes during longitudinal follow up in Alzheimer’s disease. Geriatr Gerontol Int 16:836–842
Hanyu H, Sato T, Hirao K, Kanetaka H, Iwamoto T, Koizumi K (2010) The progression of cognitive deterioration and regional cerebral blood flow patterns in Alzheimer’s disease: a longitudinal SPECT study. J Neurol Sci 290:96–101
Hirano N, Mori E, Ishii K, Ikejiri Y, Imamura T, Shimomura T, Hashimoto M, Yamashita H, Sasaki M (1998) Hypofunction in the posterior cingulate gyrus correlates with disorientation for time and place in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64:552–554
Holman BL, Johnson KA, Gerada B, Carvalho PA, Satlin A (1992) The scintigraphic appearance of Alzheimer’s disease: a prospective study using technetium-99m-HMPAO SPECT. J Nucl Med 33:181–185
Hongo J, Nakaaki S, Shinagawa Y, Murata Y, Sato J, Tatsumi H, Tohyama J, Soma T, Iidaka T, Fukui T, Mimura M, Furukawa T (2008) SPECT-identified neuroanatomical predictor of the cognitive effects of donepezil treatment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Dementia Geriatr Cog Disord 26:556–566
Imabayashi E, Matsuda H, Asada T, Ohnishi T, Sakamoto S, Nakano S, Inoue T (2004) Superiority of 3-dimensional stereotactic surface projection analysis over visual inspection in discrimination of patients with very early Alzheimer’s disease from controls using brain perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med 45:1450–1457
Ishii K, Willoch F, Minoshima S, Drzezga A, Ficaro EP, Cross DJ, Kuhl DE, Schwaiger M (2001) Statistical brain mapping of 18F-FDG PET in Alzheimer’s disease: validation of anatomic standardization for atrophied brains. J Nucl Med 42:548–557
Ishii K, Kawachi T, Sasaki H, Kono AK, Fukuda T, Kojima Y, Mori E (2005) Voxel-based morphometric comparison between early- and late-onset mild Alzheimer’s disease and assessment of diagnostic performance of Z score images. Am J Neuroradiol 26:333–340
Kaiser NC, Melrose RJ, Liu C, Sultzer DL, Jimenez E, Su M, Monserratt L, Mendez MF (2012) Neuropsychological and neuroimaging markers in early versus late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 27:520–529
Kemp PM, Holmes C, Hoffmann SM, Bolt L, Holmes R, Rowden J, Fleming JS (2003) Alzheimer’s disease: differences in technetium-99m HMPAO SPECT scan findings between early onset and late onset dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:715–719
Kim EJ, Cho SS, Jeong Y, Park KC, Kang SJ, Kang E, Kim SE, Lee KH, Na DL (2005) Glucose metabolism in early onset versus late onset Alzheimer’s disease: an SPM analysis of 120 patients. Brain 128:1790–1801
Kuczynski B, Reed B, Mungas D, Weiner M, Chui HC, Jagust W (2008) Cognitive and anatomic contributions of metabolic decline in Alzheimer disease and cerebrovascular disease. Arch Neurol 65:650–655
Kumar A, Schapiro MB, Grady C, Haxby JV, Wagner E, Salerno JA, Friedland RP, Rapoport SI (1991) High-resolution PET studies in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 4:35–46
Kume K, Hanyu H, Sato T, Hirao K, Shimizu S, Kanetaka H, Sakurai H, Iwamoto T (2011) Vascular risk factors are associated with faster decline of Alzheimer disease: a longitudinal SPECT study. J Neurol 258:1295–1303
Li W, Antuono PG, Xie C, Chen G, Jones JL, Ward BD, Franczak MB, Goveas JS, Li SJ (2012) Changes in regional cerebral blood flow and functional connectivity in the cholinergic pathway associated with cognitive performance in subjects with mild Alzheimer’s disease after 12-week donepezil treatment. Neuroimage 60:1083–1091
McKeith IG, Bartholomew PH, Irvine EM, Cook J, Adams R, Simpson AE (1993) Single photon emission computerised tomography in elderly patients with Alzheimer’s disease and multi-infarct dementia. Regional uptake of technetium-labelled HMPAO related to clinical measurements. Br J Psychiatry 163:597–603
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 34:939–944
Minoshima S, Frey KA, Koeppe RA, Foster NL, Kuhl DE (1995) A diagnostic approach in Alzheimer’s disease using three-dimensional stereotactic surface projections of fluorine-18-FDG PET. J Nucl Med 36:1238–1248
Mizumura S, Kumita S, Cho K, Ishihara M, Nakajo H, Toba M, Kumazaki T (2003) Development of quantitative analysis method for stereotactic brain image: assessment of reduced accumulation in extent and severity using anatomical segmentation. Ann Nucl Med 17:289–295
Möller C, Vrenken H, Jiskoot L, Versteeg A, Barkhof F, Scheltens P, van der Flier WM (2013) Different patterns of gray matter atrophy in early-and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 34:2014–2022
Montaldi D, Brooks DN, McColl JH, Wyper D, Patterson J, Barron E, McCulloch J (1990) Measurements of regional cerebral blood flow and cognitive performance in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 53:33–38
Nobili F, Brugnolo A, Calvini P, Copello F, De Leo C, Girtler N, Morbelli S, Piccardo A, Vitali P, Rodriguez G (2005) Resting SPECT-neuropsychology correlation in very mild Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Neurophysiol 116:364–375
O’Brien JT, Eagger S, Syed GM, Sahakian BJ, Levy R (1992) A study of regional cerebral blood flow and cognitive performance in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:1182–1187
Palasí A, Gutiérrez-Iglesias B, Alegret M, Pujadas F, Olabarrieta M, Liébana D, Quintana M, Álvarez-Sabín J, Boada M (2015) Differentiated clinical presentation of early and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease: is 65 years of age providing a reliable threshold? J Neurol 262:1238–1246
Reisberg B, Ferris SH, Anand R, de Leon MJ, Schneck MK, Buttinger C, Borenstein J (1984) Functional staging of dementia of the Alzheimer’s type. Ann NY Scad Sci 435:481–483
Rodriguez G, Morbelli S, Brugnolo A, Calvini P, Girtler N, Piccardo A, Dougall NJ, Ebmeier KP, Baron JC, Nobili F (2005) Global cognitive impairment should be taken into account in SPECT-neuropsychology correlations: the example of verbal memory in very mild Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imag 32:1186–1192
Rosen WG, Mohs RC, Davis L (1984) A new rating scale for Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Psychiatry 141:1356–1364
Sá F, Pinto P, Cunha C, Lemos R, Letra L, Simões M, Santana I (2012) Differences between early and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in neuropsychological tests. Front Neurol 14:81
Sakamoto S, Ishii K, Sasaki M, Hosaka K, Mori T, Matsui M, Hirano N, Mori E (2002) Differences in cerebral metabolic impairment between early and late onset types of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 200:27–32
Smits LL, Pijnenburg YA, Koedam EL, van der Vlies AE, Reuling IE, Koene T, Teunissen CE, Scheltens P, van der Flier WM (2012) Early onset Alzheimer’s disease is associated with a distinct neuropsychological profile. J Alzheimers Dis 30:101–108
Song I, Chung Y, Chung S, Jeong J (2014) Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease associated with dementia using cerebral perfusion SPECT. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 37:276–285
Tippett WJ, Black SE (2008) Regional cerebral blood flow correlates of visuospatial tasks in Alzheimer’s disease. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 14:1034–1045
Verma N, Beretvas SN, Pascual B, Masdeu JC, Markey MK (2015) The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. New scoring methodology improves the sensitivity of the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive subscale (ADAS-Cog) in clinical trials. Alzheimers Res Ther 7:64
Waldemar G, Bruhn P, Kristensen M, Johnson A, Paulson OB, Lassen NA (1994) Heterogeneity of neocortical cerebral blood flow deficits in dementia of the Alzheimer type: a [99Tc]-d, l-HMPAO SPECT study. J Neuro Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:285–295
Yamashita K, Taniwaki Y, Utsunomiya H, Taniwaki T (2014) Cerebral blood flow reduction associated with orientation for time in amnesic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease patients. J Neuroimaging 24:590–594
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This research received no specific Grant from any funding agency or from commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of interest
Dr. Shirayama has received research support from Eli Lilly, Eisai, MSD, Pfizer, and Mitsubishi-Tanabe. Dr. Okubo has received research support from Eisai, Bayer, and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Takahashi and Dr. Oda have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, M., Oda, Y., Okubo, T. et al. Relationships between cognitive impairment on ADAS-cog and regional cerebral blood flow using SPECT in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 124, 1109–1121 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1734-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1734-7