Abstract
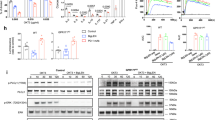
In previous studies we found that several Neurotransmitters and Neuropeptides among them: Glutamate, Dopamine, Gonadotropin-releasing-hormone (GnRH) I and II, Somatostatin, CGRP and Neuropeptide Y, can each by itself, at low physiological concentration (~10 nM) bind its receptors in human T cells and trigger several key T cell functions. These findings showed that the nervous system, via Neurotransmitters and Neuropeptides, can ‘talk’ directly to the immune system, and stimulate what we coined ‘Nerve-Driven Immunity’: immune responses dictated by the nervous system. In various human cancers, the immune system of the patients, and their T cells in particular, are not functioning well enough against the cancer due to several reasons, among them the suppressive effects on the immune system induced by: (1) the cancer itself, (2) the chemotherapy and radiotherapy, (3) the ongoing/chronic stress, anxiety, depression and pain felt by the cancer patients. In Head and Neck Cancer (HNC), 5-year survival rate remains below 50 %, primarily because of local recurrences or second primary tumors. Two-thirds of HNC patients are diagnosed at advanced clinical stage and have significantly poorer prognosis. Most HNC patients have multiple severe immunological defects especially in their T cells. A major defect in T cells of patients with HNC or other types of cancer is low CD3zeta expression that correlates with poor prognosis, decreased proliferation, apoptotic profile, abnormal cytokine secretion and poor abilities of destructing cancer cells. T cells of cancer patients are often also unable to migrate properly towards the tumor. In this study we asked if Glutamate, Dopamine or GnRH-II can augment the spontaneous migration, chemotactic migration and towards autologous HNC migration, and also increase CD3zeta and CD3epsilon expression, of peripheral T cells purified from the blood of five HNC patients. These HNC patients had either primary tumor or recurrence, and have been already treated by surgery and/or radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy without satisfactory outcomes. We found that Glutamate, Dopamine and GnRH-II, each by itself, at 10 nM, and during 30 min incubation only with the peripheral T cells of the HNC patients increased substantially their: (1) spontaneous migration (up to 4.4 fold increase), (2) chemotactic migration towards the key chemokine SDF-1 (up to 2.3 fold increase), (3) migration towards the autologous HNC tumor removed surgically ~48 h earlier in a pre-planned operation (up to 3.5 fold increase). Each of the Neurotransmitters even ‘allowed’ the T cells of one HNC patient to overcome completely the suppressive anti-migration effect of his autologous tumor, (4) cell surface CD3zeta expression (up to 4.3 fold increase), (5) cell surface CD3epsilon expression (up to 1.9 fold increase). If the absolutely essential larger scale subsequent studies would validate our present findings, Glutamate, Dopamine and GnRH-II could be used for a completely novel indication: adoptive T cell immunotherapy for some patients with HNC and maybe also other types of cancer. We coin here a novel term-‘Neuroimmunotherapy’ for this new form of T cell immunotherapy, based on the direct activation of the patient’s own T cells by Neurotransmitters. Such ‘Neuroimmunotherapy’ could be reduced to practice by rather simple, painless and repeated/periodical removal of peripheral T cells from the cancer patients, activating them ex vivo for 30 min by either Glutamate, Dopamine or GnRH-II, and infusing them back to the patients by intravenous and/or intratumoral injection. The ‘rejuvenated’ Neurotransmitter-treated T cells are expected to have significantly improved abilities to reach and eradicate the cancer, and also combat infectious organisms that cancer patients often suffer from. Since the T cells are autologous, since the Neurotransmitters are physiological molecules, and since the ex vivo ‘parking period’ is very short, such Neuroimmunotherapy is expected to be very safe.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelstein DJ, Li Y, Adams GL, Wagner H Jr, Kish JA, Ensley JF, Schuller DE, Forastiere AA (2003) An intergroup phase III comparison of standard radiation therapy and two schedules of concurrent chemoradiotherapy in patients with unresectable squamous cell head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 21:92–98
Albers A, Abe K, Hunt J, Wang J, Lopez-Albaitero A, Schaefer C, Gooding W, Whiteside TL, Ferrone S, DeLeo A, Ferris RL (2005) Antitumor activity of human papillomavirus type 16 E7-specific T cells against virally infected squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Res 65:11146–11155
Al-Sarraf M, LeBlanc M, Giri PG, Fu KK, Cooper J, Vuong T, Forastiere AA, Adams G, Sakr WA, Schuller DE, Ensley JF (1998) Chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal cancer: phase III randomized Intergroup study 0099. J Clin Oncol 16:1310–1317
Aune TM, McGrath KM, Sarr T, Bombara MP, Kelley KA (1993) Expression of 5HT1a receptors on activated human T cells. Regulation of cyclic AMP levels and T cell proliferation by 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Immunol 151:1175–1183
Basu S, Dasgupta PS (2000) Dopamine, a neurotransmitter, influences the immune system. J Neuroimmunol 102:113–124
Besser MJ, Ganor Y, Levite M (2005) Dopamine by itself activates either D2, D3 or D1/D5 dopaminergic receptors in normal human T-cells and triggers the selective secretion of either IL-10, TNFalpha or both. J Neuroimmunol 169:161–171
Cardoso A, el Ghamrawy C, Gautron JP, Horvat B, Gautier N, Enjalbert A, Krantic S (1998) Somatostatin increases mitogen-induced IL-2 secretion and proliferation of human Jurkat T cells via sst3 receptor isotype. J Cell Biochem 68:62–73
Chakraborty K, Bose A, Chakraborty T, Sarkar K, Goswami S, Pal S, Baral R (2008) Restoration of dysregulated CC chemokine signaling for monocyte/macrophage chemotaxis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients by neem leaf glycoprotein maximizes tumor cell cytotoxicity. Cell Mol Immunol 7:396–408
Chen A, Ganor Y, Rahimipour S, Ben-Aroya N, Koch Y, Levite M (2002) The neuropeptides GnRH-II and GnRH-I are produced by human T cells and trigger laminin receptor gene expression, adhesion, chemotaxis and homing to specific organs. Nat Med 8:1421–1426
Chowers Y, Cahalon L, Lahav M, Schor H, Tal R, Bar-Meir S, Levite M (2000) Somatostatin through its specific receptor inhibits spontaneous and TNF-alpha- and bacteria-induced IL-8 and IL-1 beta secretion from intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol 165:2955–2961
Cosentino M, Fietta AM, Ferrari M, Rasini E, Bombelli R, Carcano E, Saporiti F, Meloni F, Marino F, Lecchini S (2007) Human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells selectively express tyrosine hydroxylase and contain endogenous catecholamines subserving an autocrine/paracrine inhibitory functional loop. Blood 109:632–642
Dasgupta S, Bhattacharya-Chatterjee M, O’Malley BW Jr, Chatterjee SK (2006) Recombinant vaccinia virus expressing interleukin-2 invokes anti-tumor cellular immunity in an orthotopic murine model of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Ther 13:183–193
Denis F, Garaud P, Bardet E, Alfonsi M, Sire C, Germain T, Bergerot P, Rhein B, Tortochaux J, Calais G (2004) Final results of the 94-01 French Head and Neck Oncology and Radiotherapy Group randomized trial comparing radiotherapy alone with concomitant radiochemotherapy in advanced-stage oropharynx carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 22:69–76
Dixit VD, Yang H, Udhayakumar V, Sridaran R (2003) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone alters the T helper cytokine balance in the pregnant rat. Biol Reprod 68:2215–2221
Dudley ME, Gross CA, Somerville RP, Hong Y, Schaub NP, Rosati SF, White DE, Nathan D, Restifo NP, Steinberg SM, Wunderlich JR, Kammula US, Sherry RM, Yang JC, Phan GQ, Hughes MS, Laurencot CM, Rosenberg SA (2013) Randomized selection design trial evaluating CD8+-enriched versus unselected tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes for adoptive cell therapy for patients with melanoma. J Clin Oncol 31:2152–2159
Duffey DC, Chen Z, Dong G, Ondrey FG, Wolf JS, Brown K, Siebenlist U, Van Waes C (1999) Expression of a dominant-negative mutant inhibitor-kappaBalpha of nuclear factor-kappaB in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma inhibits survival, proinflammatory cytokine expression, and tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res 59:3468–3474
Duray A, Descamps G, Decaestecker C, Remmelink M, Sirtaine N, Lechien J, Ernoux-Neufcoeur P, Bletard N, Somja J, Depuydt CE, Delvenne P, Saussez S (2013) Human papillomavirus DNA strongly correlates with a poorer prognosis in oral cavity carcinoma. Laryngoscope 122:1558–1565
Eshhar Z (2008) The T-body approach: redirecting T cells with antibody specificity. Handbook of experimental pharmacology pp 329–342
Eshhar Z (2010) Adoptive cancer immunotherapy using genetically engineered designer T-cells: first steps into the clinic. Curr Opin Mol Ther 12:55–63
Eugen-Olsen J, Afzelius P, Andresen L, Iversen J, Kronborg G, Aabech P, Nielsen JO, Hofmann B (1997) Serotonin modulates immune function in T cells from HIV-seropositive subjects. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 84:115–121
Farace F, Angevin E, Vanderplancke J, Escudier B, Triebel F (1994) The decreased expression of CD3zeta chains in cancer patients is not reversed by IL-2 administration. Int J Cancer 59:752–755
Ferris RL, Hunt JL, Ferrone S (2005) Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I defects in head and neck cancer: molecular mechanisms and clinical significance. Immunol Res 33:113–133
Forastiere AA, Trotti A (1999) Radiotherapy and concurrent chemotherapy: a strategy that improves locoregional control and survival in oropharyngeal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:2065–2066
Friedman KM, Prieto PA, Devillier LE, Gross CA, Yang JC, Wunderlich JR, Rosenberg SA, Dudley ME (2012) Tumor-specific CD4+ melanoma tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. J Immunother 35:400–408
Ganor Y, Levite M (2012) Glutamate in the immune system: glutamate receptors in immune cells, potent effects, endogenous production and involvement in disease. In: Levite M (ed) Nerve-Driven Immunity: Neurotransmitters and Neuropeptides in the immune system. Springer, Berlin pp 121–161
Ganor Y, Levite M (2014) The Neurotransmitter Glutamate and human T cells: glutamate receptors and glutamate-induced direct and potent effects on normal human T cells, cancerous human leukemia and lymphoma T cells, and autoimmune human T cells. J Neural Trans. (in press, Abstract available on line ahead of press)
Ganor Y, Besser M, Ben-Zakay N, Unger T, Levite M (2003) Human T cells express a functional ionotropic glutamate receptor GluR3, and glutamate by itself triggers integrin-mediated adhesion to laminin and fibronectin and chemotactic migration. J Immunol 170:4362–4372
Ganor Y, Teichberg VI, Levite M (2007) TCR activation eliminates glutamate receptor GluR3 from the cell surface of normal human T cells, via an autocrine/paracrine granzyme B-mediated proteolytic cleavage. J Immunol 178:683–692
Ganor Y, Grinberg I, Reis A, Cooper I, Goldstein RS, Levite M (2009) Human T-leukemia and T-lymphoma express glutamate receptor AMPA GluR3, and the neurotransmitter glutamate elevates the cancer-related matrix-metalloproteinases inducer CD147/EMMPRIN, MMP-9 secretion and engraftment of T-leukemia in vivo. Leuk Lymphoma 50:985–997
Ghamrawy CE, Rabourdin-Combe C, Krantic S (1999) sst5 somatostatin receptor mRNA induction by mitogenic activation of human T-lymphocytes. Peptides 20:305–311
Ghosh MC, Mondal AC, Basu S, Banerjee S, Majumder J, Bhattacharya D, Dasgupta PS (2003) Dopamine inhibits cytokine release and expression of tyrosine kinases, Lck and Fyn in activated T cells. Int Immunopharmacol 3:1019–1026
Grandis JR, Pietenpol JA, Greenberger JS, Pelroy RA, Mohla S (2004) Head and neck cancer: meeting summary and research opportunities. Cancer Res 64:8126–8129
Guy CS, Vignali DA (2009) Organization of proximal signal initiation at the TCR: CD3 complex. Immunol Rev 232:7–21
Hathaway B, Landsittel DP, Gooding W, Whiteside TL, Grandis JR, Siegfried JM, Bigbee WL, Ferris RL (2005) Multiplexed analysis of serum cytokines as biomarkers in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck patients. Laryngoscope 115:522–527
Healy CG, Simons JW, Carducci MA, DeWeese TL, Bartkowski M, Tong KP, Bolton WE (1998) Impaired expression and function of signal-transducing zeta chains in peripheral T cells and natural killer cells in patients with prostate cancer. Cytometry 32:109–119
Heemskerk B, Liu K, Dudley ME, Johnson LA, Kaiser A, Downey S, Zheng Z, Shelton TE, Matsuda K, Robbins PF, Morgan RA, Rosenberg SA (2008) Adoptive cell therapy for patients with melanoma, using tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes genetically engineered to secrete interleukin-2. Hum Gene Ther 19:496–510
Hinrichs CS, Rosenberg SA (2014) Exploiting the curative potential of adoptive T-cell therapy for cancer. Immunol Rev 257:56–71
Hoffmann TK, Dworacki G, Tsukihiro T, Meidenbauer N, Gooding W, Johnson JT, Whiteside TL (2002) Spontaneous apoptosis of circulating T lymphocytes in patients with head and neck cancer and its clinical importance. Clin Cancer Res 8:2553–2562
Hoffmann TK, Bier H, Whiteside TL (2004) Targeting the immune system: novel therapeutic approaches in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Immunol Immunother 53:1055–1067
Josefsson E, Bergquist J, Ekman R, Tarkowski A (1996) Catecholamines are synthesized by mouse lymphocytes and regulate function of these cells by induction of apoptosis. Immunology 88:140–146
Kawamura N, Tamura H, Obana S, Wenner M, Ishikawa T, Nakata A, Yamamoto H (1998) Differential effects of neuropeptides on cytokine production by mouse helper T cell subsets. Neuroimmunomodulation 5:9–15
Kerrebijn JD, Simons PJ, Balm AJ, Tas M, Knegt PP, de Vries N, Tan IB, Drexhage HA (1996) Thymostimulin enhancement of T-cell infiltration into head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 18:335–342
Khan NA, Hichami A (1999) Ionotrophic 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 receptor activates the protein kinase C-dependent phospholipase D pathway in human T-cells. Biochem J 344(Pt 1):199–204
Kipnis J, Cardon M, Avidan H, Lewitus GM, Mordechay S, Rolls A, Shani Y, Schwartz M (2004) Dopamine, through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway, downregulates CD4+CD25+ regulatory T-cell activity: implications for neurodegeneration. J Neurosci 24:6133–6143
Kohm AP, Sanders VM (2001) Norepinephrine and beta 2-adrenergic receptor stimulation regulate CD4+ T and B lymphocyte function in vitro and in vivo. Pharmacol Rev 53:487–525
Kono K, Ressing ME, Brandt RM, Melief CJ, Potkul RK, Andersson B, Petersson M, Kast WM, Kiessling R (1996) Decreased expression of signal-transducing zeta chain in peripheral T cells and natural killer cells in patients with cervical cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2:1825–1828
Kuss I, Saito T, Johnson JT, Whiteside TL (1999) Clinical significance of decreased zeta chain expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res 5:329–334
Kut JL, Young MR, Crayton JW, Wright MA, Young ME (1992) Regulation of murine T-lymphocyte function by spleen cell-derived and exogenous serotonin. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 14:783–796
Laberge S, Cruikshank WW, Beer DJ, Center DM (1996) Secretion of IL-16 (lymphocyte chemoattractant factor) from serotonin-stimulated CD8+ T cells in vitro. J Immunol 156:310–315
Lai P, Rabinowich H, Crowley-Nowick PA, Bell MC, Mantovani G, Whiteside TL (1996) Alterations in expression and function of signal-transducing proteins in tumor-associated T and natural killer cells in patients with ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2:161–173
Laumbacher B, Gu S, Wank R (2012) Activated monocytes prime naïve T cells against autologous cancer: vigorous cancer destruction in vitro and in vivo. Scand J Immunol 75(3):314–328
Laumbacher B, Gu S, Wank R (2013) Prolongation of life by adoptive cell therapy with cascade primed immune cells in four patients with non-small cell lung cancer stages IIIB and IV and a pancoast tumor: a case series. J Med Case Rep 7(1):266
Leon-Ponte M, Ahern GP, O’Connell PJ (2007) Serotonin provides an accessory signal to enhance T-cell activation by signaling through the 5-HT7 receptor. Blood 109:3139–3146
Levite M (1998) Neuropeptides, by direct interaction with T cells, induce cytokine secretion and break the commitment to a distinct T helper phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:12544–12549
Levite M (2000) Nerve-driven immunity: the direct effects of neurotransmitters on T-cell function. Ann N Y Acad Sci 917:307–321
Levite M (2001) Nervous immunity: Neurotransmitters, extracellular K+ and T-cell function. Trends Immunol 22:2–5
Levite M (2008) Neurotransmitters activate T-cells and elicit crucial functions via neurotransmitter receptors. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8:460–471
Levite M (2012a) Dopamine in the immune system: dopamine receptors in immune cells, potent effects, endogenous production and involvement in immune and neuropsychiatric diseases. In: Levite M (ed) Nerve-driven immunity: Neurotransmitters and Neuropeptides in the immune system. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–45
Levite M (2012b) Nerve-driven immunity: Neurotransmitters and neuropeptides in the immune system. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–359
Levite M, Cahalon L, Hershkoviz R, Steinman L, Lider O (1998) Neuropeptides, via specific receptors, regulate T cell adhesion to fibronectin. J Immunol 160:993–1000
Levite M, Cahalon L, Peretz A, Hershkoviz R, Sobko A, Ariel A, Desai R, Attali B, Lider O (2000) Extracellular K(+) and opening of voltage-gated potassium channels activate T cell integrin function: physical and functional association between Kv1.3 channels and beta1 integrins. J Exp Med 191:1167–1176
Levite M, Chowers Y, Ganor Y, Besser M, Hershkovits R, Cahalon L (2001) Dopamine interacts directly with its D3 and D2 receptors on normal human T cells, and activates beta1 integrin function. Eur J Immunol 31:3504–3512
Lopez-Albaitero A, Nayak JV, Ogino T, Machandia A, Gooding W, DeLeo AB, Ferrone S, Ferris RL (2006) Role of antigen-processing machinery in the in vitro resistance of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck cells to recognition by CTL. J Immunol 176:3402–3409
Maccalli C, Pisarra P, Vegetti C, Sensi M, Parmiani G, Anichini A (1999) Differential loss of T cell signaling molecules in metastatic melanoma patient’s T lymphocyte subsets expressing distinct TCR variable regions. J Immunol 163:6912–6923
Maliar A, Servais C, Waks T, Chmielewski M, Lavy R, Altevogt P, Abken H, Eshhar Z (2012) Redirected T cells that target pancreatic adenocarcinoma antigens eliminate tumors and metastases in mice. Gastroenterology 143(1375–1384):e1371–e1375
Malissen B (2008) CD3 ITAMs count! Nat Immunol 9:583–584
Marcus A, Eshhar Z (2014) Allogeneic chimeric antigen receptor-modified cells for adoptive cell therapy of cancer. Expert Opinion Biol Ther 14(7):947–954
Marcus A, Waks T, Eshhar Z (2011) Redirected tumor-specific allogeneic T cells for universal treatment of cancer. Blood 118:975–983
McKenna F, McLaughlin PJ, Lewis BJ, Sibbring GC, Cummerson JA, Bowen-Jones D, Moots RJ (2002) Dopamine receptor expression on human T- and B-lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils and NK cells: a flow cytometric study. J Neuroimmunol 132:34–40
Miglio G, Varsaldi F, Dianzani C, Fantozzi R, Lombardi G (2005) Stimulation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors evokes calcium signals and c-jun and c-fos gene expression in human T cells. Biochem Pharmacol 70:189–199
Moore TC, Whitley GA, Lami JL, Said SI (1990) Substance P increases and prolongs increased output of T4 (CD4) lymphocytes from lymph nodes of sheep in vivo: is it a mediator of immunological memory? Immunopharmacology 20:207–216
Nakagomi H, Petersson M, Magnusson I, Juhlin C, Matsuda M, Mellstedt H, Taupin JL, Vivier E, Anderson P, Kiessling R (1993) Decreased expression of the signal-transducing zeta chains in tumor-infiltrating T-cells and NK cells of patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res 53:5610–5612
Park TS, Rosenberg SA, Morgan RA (2011) Treating cancer with genetically engineered T cells. Trends Biotechnol 29:550–557
Phan GQ, Rosenberg SA (2013) Adoptive cell transfer for patients with metastatic melanoma: the potential and promise of cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Control 20:289–297
Ramirez MJ, Ferriol EE, Domenech FG, Llatas MC, Suarez-Varela MM, Martinez RL (2003) Psychosocial adjustment in patients surgically treated for laryngeal cancer. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:92–97
Reichert TE, Rabinowich H, Johnson JT, Whiteside TL (1998) Mechanisms responsible for signaling and functional defects. J Immunother 21:295–306
Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Sherry RM, Kammula US, Hughes MS, Phan GQ, Citrin DE, Restifo NP, Robbins PF, Wunderlich JR, Morton KE, Laurencot CM, Steinberg SM, White DE, Dudley ME (2011) Durable complete responses in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic melanoma using T-cell transfer immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 17:4550–4557
Saito T, Kuss I, Dworacki G, Gooding W, Johnson JT, Whiteside TL (1999) Spontaneous ex vivo apoptosis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res 5:1263–1273
Santambrogio L, Lipartiti M, Bruni A, Dal Toso R (1993) Dopamine receptors on human T- and B-lymphocytes. J Neuroimmunol 45:113–119
Santoni G, Amantini C, Lucciarini R, Pompei P, Perfumi M, Nabissi M, Morrone S, Piccoli M (2002) Expression of substance P and its neurokinin-1 receptor on thymocytes: functional relevance in the regulation of thymocyte apoptosis and proliferation. Neuroimmunomodulation 10:232–246
Sarchielli P, Di Filippo M, Candeliere A, Chiasserini D, Mattioni A, Tenaglia S, Bonucci M, Calabresi P (2007) Expression of ionotropic glutamate receptor GluR3 and effects of glutamate on MBP- and MOG-specific lymphocyte activation and chemotactic migration in multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol 188:146–158
Sarkar C, Das S, Chakroborty D, Chowdhury UR, Basu B, Dasgupta PS, Basu S (2006) Cutting edge: stimulation of dopamine D4 receptors induce T cell quiescence by up-regulating Kruppel-like factor-2 expression through inhibition of ERK1/ERK2 phosphorylation. J Immunol 177:7525–7529
Saussez S (2010) Cancer of the upper aero-digestive tract: elevated incidence in Belgium, new risk factors and therapeutic perspectives. Bull Mem Acad R Med Belg 165:453–461 discussion 462–453
Saussez S, Camby I, Toubeau G, Kiss R (2007) Galectins as modulators of tumor progression in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Head Neck 29:874–884
Schmidtner J, Distel LV, Ott OJ, Nkenke E, Sprung CN, Fietkau R, Lubgan D (2009) Hyperthermia and irradiation of head and neck squamous cancer cells causes migratory profile changes of tumour infiltrating lymphocytes. Int J Hyperthermia 25:347–354
Shah J, Patel S (2003) Head and neck surgery and oncology. New York Mosby 232–236:352p
Shurin GV, Ferris RL, Tourkova IL, Perez L, Lokshin A, Balkir L, Collins B, Chatta GS, Shurin MR (2005) Loss of new chemokine CXCL14 in tumor tissue is associated with low infiltration by dendritic cells (DC), while restoration of human CXCL14 expression in tumor cells causes attraction of DC both in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol 174:5490–5498
Smith-Garvin JE, Koretzky GA, Jordan MS (2009) T cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol 27:591–619
Straten P, Becker JC (2009) Adoptive cell transfer in the treatment of metastatic melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 129:2743–2745
Tanriverdi FD, Gonzalez-Martinez LF, Silveira Y, Hu GS, Maccoll P, Travers, Bouloux PM (2004) Expression of gonadotropin-releasing hormone type-I (GnRH-I) and type-II (GnRH-II) in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PMBCs) and regulation of B-lymphoblastoid cell proliferation by GnRH-I and GnRH-II. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 112:587–594
Tanriverdi F, Gonzalez-Martinez D, Hu Y, Kelestimur F, Bouloux PM (2005) GnRH-I and GnRH-II have differential modulatory effects on human peripheral blood mononuclear cell proliferation and interleukin-2 receptor gamma-chain mRNA expression in healthy males. Clin Exp Immunol 142:103–110
Vishwanath R, Mukherjee R (1996) Substance P promotes lymphocyte-endothelial cell adhesion preferentially via LFA-1/ICAM-1 interactions. J Neuroimmunol 71:163–171
Wank R, Song X, Gu S, Laumbacher B (2014) Benefits of a continuous therapy for cancer patients with a novel adoptive cell therapy by cascade priming (CAPRI). Immunotherapy 6(3):269–282
Watanabe Y, Nakayama T, Nagakubo D, Hieshima K, Jin Z, Katou F, Hashimoto K, Yoshie O (2006) Dopamine selectively induces migration and homing of naive CD8+ T cells via dopamine receptor D3. J Immunol 176:848–856
Whiteside TL (2004) Down-regulation of zeta-chain expression in T cells: a biomarker of prognosis in cancer? Cancer Immunol Immunother 53:865–878
Whiteside TL (2005) Immunobiology of head and neck cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24:95–105
Yin J, Albert RH, Tretiakova AP, Jameson BA (2006) 5-HT(1B) receptors play a prominent role in the proliferation of T-lymphocytes. J Neuroimmunol 181:68–81
Young MR, Kut JL, Coogan MP, Wright MA, Young ME, Matthews J (1993) Stimulation of splenic T-lymphocyte function by endogenous serotonin and by low-dose exogenous serotonin. Immunology 80:395–400
Young MR, Wright MA, Lozano Y, Matthews JP, Benefield J, Prechel MM (1996) Mechanisms of immune suppression in patients with head and neck cancer: influence on the immune infiltrate of the cancer. Int J Cancer 67:333–338
Zea AH, Curti BD, Longo DL, Alvord WG, Strobl SL, Mizoguchi H, Creekmore SP, O’Shea JJ, Powers GC, Urba WJ et al (1995) Alterations in T cell receptor and signal transduction molecules in melanoma patients. Clin Cancer Res 1:1327–1335
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial relationship with the organization that sponsored the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saussez, S., Laumbacher, B., Chantrain, G. et al. Towards Neuroimmunotherapy for Cancer: the Neurotransmitters Glutamate, Dopamine and GnRH-II augment substantially the ability of T cells of few Head and Neck cancer patients to perform spontaneous migration, chemotactic migration and migration towards the autologous tumor, and also elevate markedly the expression of CD3zeta and CD3epsilon TCR-associated chains. J Neural Transm 121, 1007–1027 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1242-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1242-y