Abstract
Background
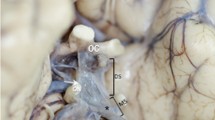
Bochdalek’s flower basket (Bfb) is the distal part of the horizontal segment of the fourth ventricle’s choroid plexus protruding through the lateral aperture (foramen of Luschka). The microsurgical anatomy of the cerebellopontine angle, fourth ventricle and its inner choroid plexus is well described in the literature, but only one radiological study has investigated the Bfb so far. The goal of the present study was to give an extensive morphometric analysis of the Bfb for the first time and discuss the surgically relevant anatomical aspects.
Method
Forty-two formalin-fixed human brains (84 cerebellopontine angles) were involved in this study. Photomicrographs with scale bars were taken in every step of dissection to perform further measurements with Fiji software. The lengths and widths of the Bfb, rhomboid lip and lateral aperture of the fourth ventricle as well as the related neurovascular and arachnoid structures were measured. The areas of two sides were compared with paired t-tests using R software. Significance level was set at p < 0.05.
Results
Protruding choroid plexus was present in 77 cases (91.66%). In 6 cases (7.14%), the Bfb was totally covered by the rhomboid lip, and in one case (1.19%), it was absent. The mean width of the Bfb was 6.618 mm (2–14 mm), the mean height 5.658 mm (1.5–14 mm) and mean area 25.80 mm2 (3.07–109.83 mm2). There was no statistically significant difference between the two sides (p = 0.1744). The Bfb was in contact with 20 AICAs (23.80%), 6 PICAs (7.14%) and 39 vestibulocochlear nerves (46.42%). Arachnoid trabecules, connecting the lower cranial nerves to the Bfb or rhomboid lip, were found in 57 cases (67.85%).
Conclusions
The Bfb is an important landmark during various surgical procedures. Detailed morphology, dimensions and relations to the surrounding neurovascular structures are described in this study. These data are essential for surgeons operating in this region.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker FG 2nd, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Shields PT, Larkins MV, Jho HD (1995) Microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm. J Neurosurg 82:201–210. doi:10.3171/jns.1995.82.2.0201
Bochdalek VA (1833) Anleitung zur praktischen Zergliederung des menschlichen Gehirnes, nebst einer anatomischen Beschreibung desselben; mit besonderer Rücksicht auf das kleine Gehirn. Gottlieb Haase Söhne, Prage
Bradac GB, Simon RS, Fiegler W, Schneider H (1976) A radioanatomical study of the choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle. Neuroradiology 11:87–91
Chung SS, Chang JH, Choi JY, Chang JW, Park YG (2001) Microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm: a long-term follow-up of 1,169 consecutive cases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 77:190–193
Cohen NL (1992) Retrosigmoid approach for acoustic tumor removal. Otolaryngol Clin N am 25:295–310
Friedmann DR, Grobelny B, Golfinos JG, Roland JT Jr (2015) Nonschwannoma tumors of the cerebellopontine angle. Otolaryngol Clin N am 48:461–475. doi:10.1016/j.otc.2015.02.006
Fujii K, Lenkey C, Rhoton AL Jr (1980) Microsurgical anatomy of the choroidal arteries. Fourth ventricle and cerebellopontine angles. J Neurosurg 52:504–524. doi:10.3171/jns.1980.52.4.0504
Funaki T, Matsushima T, Masuoka J, Nakahara Y, Takase Y, Kawashima M (2010) Adhesion of rhomboid lip to lower cranial nerves as special consideration in microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm: report of two cases. Surg Neurol Int 1:71. doi:10.4103/2152-7806.72581
Hayman LA, Evans RA, Hinck VC (1979) Choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle: a useful CT landmark. AJR am J Roentgenol 133:285–288. doi:10.2214/ajr.133.2.285
Hitotsumatsu T, Matsushima T, Inoue T (2003) Microvascular decompression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia, hemifacial spasm, and glossopharyngeal neuralgia: three surgical approach variations: technical note. Neurosurgery 53:1436–1441 discussion 1442-1433
Horsburgh A, Kirollos RW, Massoud TF (2012) Bochdalek’s flower basket: applied neuroimaging morphometry and variants of choroid plexus in the cerebellopontine angles. Neuroradiology 54:1341–1346. doi:10.1007/s00234-012-1065-1
Huh R, Han IB, Moon JY, Chang JW, Chung SS (2008) Microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm: analyses of operative complications in 1582 consecutive patients. Surg Neurol 69:153–157; discussion 157. doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2007.07.027
Jallo GI, Woo HH, Meshki C, Epstein FJ, Wisoff JH (1997) Arachnoid cysts of the cerebellopontine angle: diagnosis and surgery. Neurosurgery 40:31–37 discussion 37-38
Jannetta PJ, Abbasy M, Maroon JC, Ramos FM, Albin MS (1977) Etiology and definitive microsurgical treatment of hemifacial spasm. Operative techniques and results in 47 patients. J Neurosurg 47:321–328. doi:10.3171/jns.1977.47.3.0321
Klose AK, Sollmann WP (2000) Anatomical variations of landmarks for implantation at the cochlear nucleus. J Laryngol Otol 114:8–10
Kuroki A, Moller AR (1995) Microsurgical anatomy around the foramen of Luschka in relation to intraoperative recording of auditory evoked potentials from the cochlear nuclei. J Neurosurg 82:933–939. doi:10.3171/jns.1995.82.6.0933
Lalwani AK (1992) Meningiomas, epidermoids, and other nonacoustic tumors of the cerebellopontine angle. Otolaryngol Clin N am 25:707–728
Lee MH, Jee TK, Lee JA, Park K (2016) Postoperative complications of microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm: lessons from experience of 2040 cases. Neurosurg rev 39:151–158; discussion 158. doi:10.1007/s10143-015-0666-7
Li S, Savolaine ER (1996) Imaging of atypical choroid plexus papillomas. Clin Imaging 20:85–90
Luo W, Liu H, Li J, Yang J, Xu Y (2016) Choroid plexus papillomas of the cerebellopontine angle. World Neurosurg. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2016.07.094
Matsushima T, Rhoton AL Jr, Lenkey C (1982) Microsurgery of the fourth ventricle: part 1. Microsurgical anatomy. Neurosurgery 11:631–667
Matsushima K, Yagmurlu K, Kohno M, Rhoton AL Jr (2016) Anatomy and approaches along the cerebellar-brainstem fissures. J Neurosurg 124:248–263. doi:10.3171/2015.2.JNS142707
McLaughlin MR, Jannetta PJ, Clyde BL, Subach BR, Comey CH, Resnick DK (1999) Microvascular decompression of cranial nerves: lessons learned after 4400 operations. J Neurosurg 90:1–8. doi:10.3171/jns.1999.90.1.0001
Nakahara Y, Matsushima T, Hiraishi T, Takao T, Funaki T, Masuoka J, Kawashima M (2013) Importance of awareness of the rhomboid lip in microvascular decompression surgery for hemifacial spasm. J Neurosurg 119:1038–1042. doi:10.3171/2013.4.JNS121546
Quester R, Schroder R (1997) The shrinkage of the human brain stem during formalin fixation and embedding in paraffin. J Neurosci Methods 75:81–89
Rhoton AL Jr (2000) The cerebellopontine angle and posterior fossa cranial nerves by the retrosigmoid approach. Neurosurgery 47:S93–129
Rhoton AL Jr (2000) Cerebellum and fourth ventricle. Neurosurgery 47:S7–27
Samii M, Carvalho GA, Schuhmann MU, Matthies C (1999) Arachnoid cysts of the posterior fossa. Surg Neurol 51:376–382
Schindelin J, Arganda-Carreras I, Frise E, Kaynig V, Longair M, Pietzsch T, Preibisch S, Rueden C, Saalfeld S, Schmid B, Tinevez JY, White DJ, Hartenstein V, Eliceiri K, Tomancak P, Cardona A (2012) Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 9:676–682. doi:10.1038/nmeth.2019
Sennaroglu L, Ziyal I (2012) Auditory brainstem implantation. Auris Nasus Larynx 39:439–450. doi:10.1016/j.anl.2011.10.013
Sharifi M, Ciolkowski M, Krajewski P, Ciszek B (2005) The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 64:194–198
Sharifi M, Ungier E, Ciszek B, Krajewski P (2009) Microsurgical anatomy of the foramen of Luschka in the cerebellopontine angle, and its vascular supply. Surg Radiol Anat 31:431–437. doi:10.1007/s00276-009-0464-4
Sosa P, Dujovny M, Onyekachi I, Sockwell N, Cremaschi F, Savastano LE (2016) Microvascular anatomy of the cerebellar parafloccular perforating space. J Neurosurg 124:440–449. doi:10.3171/2015.2.JNS142693
Tubbs RS, Shoja MM, Aggarwal A, Gupta T, Loukas M, Sahni D, Ansari SF, Cohen-Gadol AA (2016) Choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle: review and anatomic study highlighting anatomical variations. J Clin Neurosci 26:79–83. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2015.10.006
Yuan Y, Wang Y, Zhang SX, Zhang L, Li R, Guo J (2005) Microvascular decompression in patients with hemifacial spasm: report of 1200 cases. Chin med J 118:833–836
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Comments
The authors present an anatomical cadaver study about a well-known cerebral structure. So far, Bochdalek’s flower basket has not been investigated in as much detail as in this study in human cadavers. It is surprising that the flower basket has not been described in such detail before. Thus, this detailed description provides new and useful knowledge to the field. This story is well told, and the information is new. However, there is only relative importance for surgery, because dealing with the flower basket is normally not too challenging: it is flexible and can usually be easily moved away from the surgical field. Of more relevance are the surrounding structures. The variability of the region is well described, proves to be relevant for surgery and patient safety, and is precisely photo-documented. This article bears the potential to become the standard (and also cited) description of the anatomical structure of Bochdalek’s flower basket.
Hans Clusmann, Christian Blume
Aachen, Germany
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barany, L., Baksa, G., Patonay, L. et al. Morphometry and microsurgical anatomy of Bochdalek’s flower basket and the related structures of the cerebellopontine angle. Acta Neurochir 159, 1539–1545 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3234-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3234-9