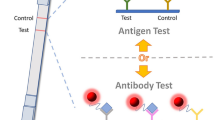
Abstract
There is an urgent need for a point-of-care testing (POCT) method in developing and underserved regions to distinguish between two Monkeypox virus (MPXV) clades, given their varying transmissibility and clinical manifestations. In this paper, we target the specific complement protein gene fragment of two MPXV clades and construct a high-performance upconversion nanoparticles–based lateral flow assay (UCNPs-based LFA) with double T-lines and a shared C-line. This enables qualitative and quantitative dual-mode detection when combined with a smartphone and a benchtop fluorescence analyzer. The developed LFA exhibits stable performance, convenient operation, rapid readout (within 8 min), and a much lower limit of detection (LOD) (~ pM level) compared to existing POCT methods. The proposed detection platform demonstrates significant potential for pathogen diagnosis using a POCT approach.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO (2023) 2022–23 Mpox (Monkeypox) outbreak: global trends. https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/mpx_global/. Accessed 25 Jan 2024
WHO (2022) Monkeypox: experts give virus variants new names. https://www.who.int/news/item/12-08-2022-monkeypox--experts-give-virusvariants-new-names. Accessed 13 Aug 2022
Lai C-C, Hsu C-K, Yen M-Y, Lee P-I, Ko W-C, Hsueh P-R (2022) Monkeypox: an emerging global threat during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 55:787–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2022.07.004
McCollum AM, Damon IK (2014) Human monkeypox. Clin Infect Dis 58:260–267. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciu196
Zandi M, Adli AH, Shafaati M (2022) Comments on “diagnosis of monkeypox virus—an overview.” Travel Med Infect Dis 51:102511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmaid.2022.102511
Li Y, Zhao H, Wilkins K, Hughes C, Damon IK (2010) Real-time PCR assays for the specific detection of monkeypox virus West African and Congo Basin strain DNA. J Virol Methods 169:223–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2010.07.012
Li Y, Olson VA, Laue T, Laker MT, Damon IK (2006) Detection of monkeypox virus with real-time PCR assays. J Clin Virol 36:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2006.03.012
Sharkey ME, Babler KM, Shukla BS, Abelson SM, Alsuliman B, Amirali A, Comerford S, Grills GS, Kumar N, Laine J (2023) Monkeypox viral nucleic acids detected using both DNA and RNA extraction workflows. Sci Total Environ 890:164289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164289
Cui X, Du B, Feng J, Feng Y, Cui J, Yan C, Zhao H, Gan L, Fan Z, Fu T (2023) Rapid detection of mpox virus using recombinase aided amplification assay. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 13:145. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1008783
Gul I, Liu C, Yuan X, Du Z, Zhai S, Lei Z, Chen Q, Raheem MA, He Q, Hu Q (2022) Current and perspective sensing methods for monkeypox virus. Bioengineering 9:571. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100571
Rohrman B, Richards-Kortum R (2015) Inhibition of recombinase polymerase amplification by background DNA: a lateral flow-based method for enriching target DNA. Anal Chem 87:1963–1967. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac504365v
You M, Lin M, Gong Y, Wang S, Li A, Ji L, Zhao H, Ling K, Wen T, Huang Y (2017) Household fluorescent lateral flow strip platform for sensitive and quantitative prognosis of heart failure using dual-color upconversion nanoparticles. ACS Nano 11:6261–6270. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b02466
Corstjens PL, De Dood CJ, Kornelis D, Fat EMTK, Wilson RA, Kariuki TM, Nyakundi RK, Loverde PT, Abrams WR, Tanke HJ (2014) Tools for diagnosis, monitoring and screening of Schistosoma infections utilizing lateral-flow based assays and upconverting phosphor labels. Parasitology 141:1841–1855. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182014000626
Martiskainen I, Talha SM, Vuorenpää K, Salminen T, Juntunen E, Chattopadhyay S, Kumar D, Vuorinen T, Pettersson K, Khanna N (2021) Upconverting nanoparticle reporter–based highly sensitive rapid lateral flow immunoassay for hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Anal Bioanal Chem 413:967–978. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-03055-z
Guo J, Chen S, Tian S, Liu K, Ma X, Guo J (2021) A sensitive and quantitative prognosis of C-reactive protein at picogram level using mesoporous silica encapsulated core-shell up-conversion nanoparticle based lateral flow strip assay. Talanta 230:122335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122335
Xu S, Zhang G, Fang B, Xiong Q, Duan H, Lai W (2019) Lateral flow immunoassay based on polydopamine-coated gold nanoparticles for the sensitive detection of zearalenone in maize. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:31283–31290. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b08789
Wu K-H, Huang W-C, Chang S-C, Shyu R-H (2022) Colloidal silver-based lateral flow immunoassay for detection of profenofos pesticide residue in vegetables. RSC Adv 12:13035–13044. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA01654K
Lou D, Fan L, Jiang T, Zhang Y (2022) Advances in nanoparticle-based lateral flow immunoassay for point-of-care testing. View 3:20200125. https://doi.org/10.1002/VIW.20200125
Jiang J, Luo P, Liang J, Shen X, Lei H, Li X (2022) A highly sensitive and quantitative time resolved fluorescent microspheres lateral flow immunoassay for streptomycin and dihydrostreptomycin in milk, honey, muscle, liver, and kidney. Anal Chim Acta 1192:339360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339360
Wang C, Yang X, Gu B, Liu H, Zhou Z, Shi L, Cheng X, Wang S (2020) Sensitive and simultaneous detection of SARS-CoV-2-specific IgM/IgG using lateral flow immunoassay based on dual-mode quantum dot nanobeads. Anal Chem 92:15542–15549. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03484
Zhang J, Shikha S, Mei Q, Liu J, Zhang Y (2019) Fluorescent microbeads for point-of-care testing: a review. Microchim Acta 186:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3449-y
Brandmeier JC, Raiko K, Farka Z, Peltomaa R, Mickert MJ, Hlaváček A, Skládal P, Soukka T, Gorris HH (2021) Effect of particle size and surface chemistry of photon-upconversion nanoparticles on analog and digital immunoassays for cardiac troponin. Adv Healthcare Mater 10:2100506. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202100506
Gong Y, Zheng Y, Jin B, You M, Wang J, Li X, Lin M, Xu F, Li F (2019) A portable and universal upconversion nanoparticle-based lateral flow assay platform for point-of-care testing. Talanta 201:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.03.105
Jin B, Li Z, Zhao G, Ji J, Chen J, Yang Y, Xu R (2022) Upconversion fluorescence-based paper disc for multiplex point-of-care testing in water quality monitoring. Anal Chim Acta 1192:339388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339388
Sivakumar R, Lee NY (2021) Recent progress in smartphone-based techniques for food safety and the detection of heavy metal ions in environmental water. Chemosphere 275:130096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130096
Jin B, Du Z, Ji J, Bai Y, Tang D, Qiao L, Lou J, Hu J, Li Z (2023) Regulation of probe density on upconversion nanoparticles enabling high-performance lateral flow assays. Talanta 256:124327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124327
Jin B, Yang Y, He R, Park YI, Lee A, Bai D, Li F, Lu TJ, Xu F, Lin M (2018) Lateral flow aptamer assay integrated smartphone-based portable device for simultaneous detection of multiple targets using upconversion nanoparticles. Sens Actuators, B 276:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.08.074
Ammanath G, Yeasmin S, Srinivasulu Y, Vats M, Cheema JA, Nabilah F, Srivastava R, Yildiz UH, Alagappan P, Liedberg B (2019) Flow-through colorimetric assay for detection of nucleic acids in plasma. Anal Chim Acta 1066:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.03.036
Liu Q, Li L, Zhao Y, Chen Z (2018) Colorimetric detection of DNA at the nanomolar level based on enzyme-induced gold nanoparticle de-aggregation. Microchim Acta 185:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2833-3
Porchetta A, Ippodrino R, Marini B, Caruso A, Caccuri F, Ricci F (2018) Programmable nucleic acid nanoswitches for the rapid, single-step detection of antibodies in bodily fluids. J Am Chem Soc 140:947–953. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b09347
Funding
This work was supported by the Opening Research Fund from Key Laboratory of Shaanxi Province for Craniofacial Precision Medicine Research, College of Stomatology, Xi’an Jiaotong University (2019LHM-KFKT005); the General Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M673418); the Natural Science Foundation of the Anhui Higher Education Institutions of China (KJ2021ZD0150); and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61904143).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, B., Ma, C., Zhang, C. et al. Point-of-care detection of Monkeypox virus clades using high-performance upconversion nanoparticle-based lateral flow assay. Microchim Acta 191, 177 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06241-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06241-3