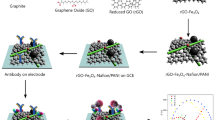
Abstract
A label-free direct electrochemical aptasensor is presented for the identification of cytochrome c (Cyt c) at the nM concentration level. Carbon nanofibers (CNF), as a highly conductive material, were used to modify a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) and thus increase its conductivity. Moreover, to enhance the immobilization of aptamers (Apt) on the electrode surface, graphene oxide functionalized with aspartic acid (GOAsp) was added to the surface. Aspartic acid with countless carboxyl groups (-COOH) on its surface caused more aptamers to be immobilized on the electrode surface. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), cyclic voltammetry (CV), and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) were used to monitor the step-by-step fabrication of the label-free direct electrochemical aptasensor. The label-free quantification of Cyt c was also done by the direct electron transfer between the Fe(III)/Fe(II)-heme redox-active sites which were selectively bound to the aptamers on the GCE and the surface of the electrode. Under optimum conditions, the peak currents of differential pulse voltammograms at 0.26 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) were used for calibration. The proposed aptasensor performs in a wide dynamic range from 10 nM to 100 µM with a low detection limit of 0.74 nM for cytochrome c. It also has high selectivity as well as acceptable stability. These advantages make the biosensor capable of detecting early-stage apoptotic cells that contribute to early cancer diagnosis.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott Mathews F (1985) The structure function and evolution of cytochromes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 45:1–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0079-6107(85)90004-5
Skulachev VP (1998) Cytochrome c in the apoptotic and antioxidant cascades. FEBS Lett 423:275–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00061-1
Jiang W, Irgum K (2002) Tentacle-type zwitterionic stationary phase prepared by surface-initiated graft polymerization of 3-[N, N-dimethyl-N-(methacryloyloxyethyl)-ammonium] propanesulfonate through peroxide groups tethered on porous silica. Anal Chem 74:4682–4687. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac020293+
Aghamiri ZS, Mohsennia M, Rafiee-Pour HA (2018) Immobilization of cytochrome c and its application as electrochemical biosensors. Talanta 176:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.08.039
Ocaña C, Lukic S, Valle M (2015) Aptamer-antibody sandwich assay for cytochrome c employing an MWCNT platform and electrochemical impedance, Microchim Acta :2045–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1540-6
Satchell MA, Lai Y, Kochanek PM, Wisniewski SR, Fink EL, Siedberg NA, Berger RP, DeKosky ST, Adelson PD, Clark RS (2005) Cytochrome c, a biomarker of apoptosis, is increased in cerebrospinal fluid from infants with inflicted brain injury from child abuse. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:919–927. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600088
Daoud H, Alharfi I, Alhelali I, Charyk Stewart T, Qasem H, Fraser DD (2014) Brain injury biomarkers as outcome predictors in pediatric severe traumatic brain injury. Neurocrit Care 20:427–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-013-9879-1
Liu H, Sarnaik SM, Manole MD, Chen Y, Shinde SN, Li W, Rose M, Alexander H, Chen J, Clark RSB, Graham SH, Hickey RW (2012) Increased cytochrome c in rat cerebrospinal fluid after cardiac arrest and its effects on hypoxic neuronal survival. Resuscitation 83:1491–1496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2012.04.009
Picklo MJ, Zhang J, Nguyen VQ, Graham DG, Montine TJ (1999) High-pressure liquid chromatography quantitation of cytochrome c using 393 nm detection. Anal Biochem 276:166–170. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1999.4349
Campos CBL, Paim BA, Cosso RG, Castilho RF, Rottenberg H, Vercesi AE (2006) Method for monitoring of mitochondrial cytochrome c release during cell death: Immunodetection of cytochrome c by flow cytometry after selective permeabilization of the plasma membrane. Cytom Part A 69A:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.20273
Langs-Barlow A, Selvaraj S, Ogbuagu O, Shabanova V, Shapiro ED, Paintsil E (2015) Association of circulating cytochrome c with clinical manifestations of antiretroviral-induced toxicity. Mitochondrion 20:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2014.11.004
Xie R, Liu Y, Yang P, Huang L, Zou X, Liu J, Ren Q, Tao J, Zhao P (2020) “French fries”-like luminescent metal organic frameworks for the fluorescence determination of cytochrome c released by apoptotic cells and screening of anticancer drug activity. Microchim Acta 187:221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4207-x
Liu M, Zhou J, He Y, Cai Z, Ge Y, Zhou J, Song G (2019) ε-Poly-L-lysine-protected Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots with high quantum yield for fluorometric determination of cytochrome c and trypsin. Microchim Acta 186:770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3945-0
Bin N, Li W, Yin X, Huang X, Cai Q (2016) Electrochemiluminescence aptasensor of TiO2/CdS: Mn hybrids for ultrasensitive detection of cytochrome c. Talanta 160:570–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.07.046
Manickam P, Kaushik A, Karunakaran C, Bhansali S (2017) Recent advances in cytochrome c biosensing technologies. Biosens Bioelectron 87:654–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.09.013
Wang J (2006) Electrochemical biosensors: towards point-of-care cancer diagnostics. Biosens Bioelectron 21:1887–1892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2005.10.027
Asturias-Arribas L, Alonso-Lomillo MA, Domínguez-Renedo O, Arcos-Martínez MJ (2013) Electrochemical determination of cocaine using screen-printed cytochrome P450 2B4 based biosensors. Talanta 105:131–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.11.078
Gai P, Gu C, Hou T, Li F (2017) Ultrasensitive self-powered aptasensor based on enzyme biofuel cell and DNA bioconjugate: a facile and powerful tool for antibiotic residue detection. Anal Chem 89:2163–2169
Yang L, Yin X, An B, Li F (2020) Precise capture and direct quantification of tumor exosomes via a highly efficient dual-aptamer recognition-assisted ratiometric immobilization-free electrochemical strategy. Anal Chem 93:1709–1716
Yin X, Hou T, Huang B, Yang L, Li F (2019) Aptamer recognition-trigged label-free homogeneous electrochemical strategy for an ultrasensitive cancer-derived exosome assay. Chem Commun 55:13705–13708
Salimi A, Khezrian S, Hallaj R, Vaziry A (2014) Highly sensitive electrochemical aptasensor for immunoglobulin E detection based on sandwich assay using enzyme-linked aptamer. Anal Biochem 466:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2014.08.019
Munge BS, Krause CE, Malhotra R, Patel V, Silvio Gutkind J, Rusling JF (2009) Electrochemical immunosensors for interleukin-6 Comparison of carbon nanotube forest and gold nanoparticle platforms. Electrochem Commun 11:1009–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2009.02.044
Chiu N-F, Fan S-Y, Yang C-D, Huang T-Y (2017) Carboxyl-functionalized graphene oxide composites as SPR biosensors with enhanced sensitivity for immunoaffinity detection. Biosens Bioelectron 89:370–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.06.073
Yazdanparast S, Benvidi A, Abbasi S, Rezaeinasab M (2019) Enzyme-based ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor using poly(L-aspartic acid)/MWCNT bio-nanocomposite for xanthine detection: a meat freshness marker. Microchem J 149:104000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104000
Yazdanparast S, Benvidi A, Banaei M, Nikukar H, Tezerjani MD, Azimzadeh M (2018) Dual-aptamer based electrochemical sandwich biosensor for MCF-7 human breast cancer cells using silver nanoparticle labels and a poly(glutamic acid)/MWNT nanocomposite. Microchim Acta 185:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2918-z
Yazdanparast S, Benvidi A, Azimzadeh M, Tezerjani MD, Ghaani MR (2020) Experimental and theoretical study for miR-155 detection through resveratrol interaction with nucleic acids using magnetic core-shell nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 187:479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04447-9
Wang J (2005) Nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors. Analyst 130:421. https://doi.org/10.1039/b414248a
Lau IPM, Ngan EKS, Loo JFC, Suen YK, Ho HP, Kong SK (2010) Aptamer-based bio-barcode assay for the detection of cytochrome-c released from apoptotic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 395:560–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.04.066
Lecoeur H, Langonné A, Baux L, Rebouillat D, Rustin P, Prévost M-C, Brenner C, Edelman L, Jacotot E (2004) Real-time flow cytometry analysis of permeability transition in isolated mitochondria. Exp Cell Res 294:106–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2003.10.030
Mallakpour S, Abdolmaleki A, Borandeh S (2014) Covalently functionalized graphene sheets with biocompatible natural amino acids. Appl Surf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.04.070
Hu M, Zhu L, Li Z, Guo C, Wang M, Wang C, Du M (2021) CoNi bimetallic metal–organic framework as an efficient biosensing platform for miRNA 126 detection. Appl Surf Sci 542:148586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148586
Benvidi A, Yazdanparast S, Rezaeinasab M, Tezerjani MD, Abbasi S (2018) Designing and fabrication of a novel sensitive electrochemical aptasensor based on poly (L-glutamic acid)/MWCNTs modified glassy carbon electrode for determination of tetracycline. J Electroanal Chem 808:311–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.12.032
Gravance CG, Garner DL, Miller MG, Berger T (2000) Fluorescent probes and flow cytometry to assess rat sperm integrity and mitochondrial function. Reprod Toxicol 15:5–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6238(00)00113-1
Drewniak S, Muzyka R, Stolarczyk A, Pustelny T, Kotyczka-Morańska M, Setkiewicz M (2016) Studies of reduced graphene oxide and graphite oxide in the aspect of their possible application in gas sensors. Sensors 16:103. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010103
Rattana S, Chaiyakun N, Witit-anun N, Nuntawong P, Chindaudom S, Oaew C, Kedkeaw P (2012) Limsuwan Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide nanosheets. Procedia Eng 32:759–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2012.02.009
Mekassa B, Tessema M, Chandravanshi BS, Baker PGL, Muya FN (2017) Sensitive electrochemical determination of epinephrine at poly(L-aspartic acid)/electro-chemically reduced graphene oxide modified electrode by square wave voltammetry in pharmaceutics. J Electroanal Chem 807:145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.11.045
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2001) Fundamentals and applications, Electrochem. Methods, 2nd Ed.; Wiley New York
Yadav D, Amini F, Ehrmann A (2020) Recent advances in carbon nanofibers and their applications – A review. Eur Polym J 138:109963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.109963
Rashid JIA, Yusof NA (2017) The strategies of DNA immobilization and hybridization detection mechanism in the construction of electrochemical DNA sensor: A review. Sens Bio-Sensing Res 16:19–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2017.09.001
Ugo P, Pepe N, Moretto LM, Battagliarin M (2003) Direct voltammetry of cytochrome c at trace concentrations with nanoelectrode ensembles. J Electroanal Chem 560:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2003.06.007
Mohsin MA, Banica F, Oshima T, Hianik T (2011) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for assessing the recognition of cytochrome c by immobilized calixarenes. Electroanalysis 23:1229–1235. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201000686
Lee T, Kim H, Moon J, Shim Y (2021) Determination of cytochrome C with cellulose ± DNA modified carbon paste electrodes. 821–826. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200302885.
Pandiaraj M, Madasamy T, Gollavilli PN, Balamurugan M, Kotamraju S, Rao VK, Bhargava K, Karunakaran C (2013) Nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors for cytochrome c using cytochrome c reductase. Bioelectrochemistry 91:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2012.09.004
Wen Q, Zhang X, Cai J, Yang P-H (2014) A novel strategy for real-time and in situ detection of cytochrome c and caspase-9 in Hela cells during apoptosis. Analyst 139:2499. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3an02205f
Shumyantseva VV, Bulko TV, Kuzikov AV, Masamrekh RA, Pergushov DV, Schacher FH, Sigolaeva LV (2020) Electrochemical fingerprint of cytochrome c on a polymer/MWCNT nanocomposite electrode. Mendeleev Commun 30:299–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mencom.2020.05.012
Loo JFC, Lau PM, Ho HP, Kong SK (2013) An aptamer-based bio-barcode assay with isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification for cytochrome-c detection and anti-cancer drug screening. Talanta 115:159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.04.051
Pandiaraj M, Sethy NK, Bhargava K, Kameswararao V, Karunakaran C (2014) Designing label-free electrochemical immunosensors for cytochrome c using nanocomposites functionalized screen printed electrodes. Biosens Bioelectron 54:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.10.030
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Yazd University Research Council for supporting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadrabadi, E.A., Benvidi, A., Yazdanparast, S. et al. Fabrication of a label-free electrochemical aptasensor to detect cytochrome c in the early stage of cell apoptosis. Microchim Acta 189, 279 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05373-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05373-8