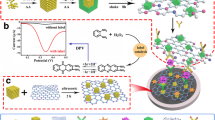
Abstract
A label-free chemical bonding strategy mediated by reduced graphene oxide (rGO) basal plane functional groups has been developed for cardiac Troponin I (cTnI) detection. Four different chemical strategies on respective electrode sensing surface were precedingly examined using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The impedimetric assessment was carried out by sweeping frequency at the range 0.1–500 kHz perturbated at a small amplitude of AC voltage (25 mV). The chemical strategy-4 denoted as S-4 shows a significant analytical performance on cTnI detection in spiked buffer and human serum, whereby the pre-mixture of rGO and (3-Aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES) creates a large number of amine sites (−NH2), which significantly enhanced the antibody immobilization without excessive functionalization. The as-fabricated immunosensor exhibited an ultra-low limit of detection of 6.3 ag mL−1 and the lowest antigen concentration measured was at 10 ag mL−1. The immunosensor showed a linear and wide range of cTnI detection (10 ag mL−1–100 ng mL−1) in human serum with a regression coefficient of 0.9716, rapid detection (5 min of binding time), and stable and highly reproducible bioelectrode response with RSD < 5%. Hence, the demonstrated S-4 strategy is highly recommended for other downstream biosensors applications.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vilian ATE, Kim W, Park B, Oh SY, Kim TY, Huh YS, Hwangbo CK, Han YK (2019) Efficient electron-mediated electrochemical biosensor of gold wire for the rapid detection of C-reactive protein: a predictive strategy for heart failure. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111549
Starnberg K, Fridén V, Muslimovic A (2020) A possible mechanism behind faster clearance and higher peak concentrations of cardiac troponin I compared with troponin T in acute myocardial infarction. Clin Chem 66:333–341. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/hvz003
Dalila NR, Arshad MKM, Gopinath SCB, Nuzaihan MNM, Fathil MFM (2020) Molybdenum disulfide-gold nanoparticle nanocomposite in field-effect transistor back-gate for enhanced C-reactive protein detection. Microchim Acta 187:588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04562-7
Ribeiro JA, Pereira CM, Silva AF, Sales MGF (2017) Electrochemical detection of cardiac biomarker myoglobin using polyphenol as imprinted polymer receptor. Anal Chim Acta 981:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.05.017
World Health Organisation (2018) Noncommunicable diseases country profiles 2018
Taniselass S, Arshad MKM, Gopinath SCB (2019) Graphene-based electrochemical biosensors for monitoring noncommunicable disease biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron 130:276–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.01.047
Wang Y, Hsine Z, Sauriat-Dorizon H, Mlika R, Korri-Youssoufi H (2020) Structural and electrochemical studies of functionalization of reduced graphene oxide with alkoxyphenylporphyrin mono- and tetra-carboxylic acid: application to DNA sensors. Electrochim Acta 357:136852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136852
Rabchinskii MK, Dideikin AT, Kirilenko (2018) Facile reduction of graphene oxide suspensions and films using glass wafers. Sci Rep 8:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32488-x
Sethi J, Van Bulck M, Suhail A et al (2020) A label-free biosensor based on graphene and reduced graphene oxide dual-layer for electrochemical determination of beta-amyloid biomarkers. Microchim Acta 187:288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04267-x
Taniselass S, Md Arshad MK, Gopinath SCB (2019) Current state of green reduction strategies: solution-processed reduced graphene oxide for healthcare biodetection. Mater Sci Eng C 96:904–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.062
Choi W, Chun K-Y, Kim J, Han C-S (2017) Ion transport through thermally reduced and mechanically stretched graphene oxide membrane. Carbon N Y 114:377–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.12.041
Govindasamy M, Wang SF, Pan WC, Subramanian B, Ramalingam RJ, al-lohedan H (2019) Facile sonochemical synthesis of perovskite-type SrTiO3 nanocubes with reduced graphene oxide nanocatalyst for an enhanced electrochemical detection of α-amino acid (tryptophan). Ultrason Sonochem 56:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.04.004
Vinoth S, Govindasamy M, Wang SF, Anandaraj S (2020) Layered nanocomposite of zinc sulfide covered reduced graphene oxide and their implications for electrocatalytic applications. Ultrason Sonochem 64:105036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105036
Wang Y, Chen Y, Lacey SD, Xu L, Xie H, Li T, Danner VA, Hu L (2018) Reduced graphene oxide film with record-high conductivity and mobility. Mater Today 21:186–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2017.10.008
Liu J, Yang C, Shang Y, Zhang P, Liu J, Zheng J (2018) Preparation of a nanocomposite material consisting of cuprous oxide, polyaniline and reduced graphene oxide, and its application to the electrochemical determination of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 185:172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2717-6
Niu Y, Xie H, Luo G, Zhuang Y, Wu X, Li G, Sun W (2020) ZnO-reduced graphene oxide composite based photoelectrochemical aptasensor for sensitive Cd(II) detection with methylene blue as sensitizer. Anal Chim Acta 1118:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.04.042, 1
Govindasamy M, Wang SF, Kumaravel S, Ramalingam RJ, al-lohedan HA (2019) Facile synthesis of copper sulfide decorated reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for high sensitive detection of toxic antibiotic in milk. Ultrason Sonochem 52:382–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.12.015
Chauhan D, Nirbhaya V, Mohan C, Chandra R (2020) Nanostructured transition metal chalcogenide embedded on reduced graphene oxide based highly efficient biosensor for cardiovascular disease detection. Microchem J 155:104697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104697
Sandil D, Srivastava S, Malhotra BD, Sharma SC, Puri NK (2018) Biofunctionalized tungsten trioxide-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for sensitive electrochemical immunosensing of cardiac biomarker. J Alloys Compd 763:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.04.293
Li Z, Ma K, Cheng Z et al (2017) Fabrication of electrochemical immunosensor for cardiac biomarker troponin I determination and its potential for acute myocardial infarction diagnosis. Int J Electrochem Sci 12:2389–2399. https://doi.org/10.20964/2017.03.12
Taniselass S, Arshad MKM, Gopinath SCB, Ramli MM (2020) Self-assembled reduced graphene oxide nanoflakes assisted by post-sonication boosted electrical performance in gold interdigitated microelectrodes. J Colloid Interface Sci 577:345–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.05.070
Randviir EP, Banks CE (2013) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: an overview of bioanalytical applications. Anal Methods 5:1098–1115. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ay26476a
Uygun ZO, Ertuǧrul Uygun HD (2014) A short footnote: circuit design for faradaic impedimetric sensors and biosensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 202:448–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.05.029
Wang Y, Ye Z, Ying Y (2012) New trends in impedimetric biosensors for the detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Sensors 12:3449–3471. https://doi.org/10.3390/s120303449
Armbruster DA, Pry T (2008) Limit of blank, limit of detection and limit of quantitation. Clin Biochem Rev 29(Suppl 1):S49–S52
Zheng X, Peng Y, Yang Y, Chen J, Tian H, Cui X, Zheng W (2017) Hydrothermal reduction of graphene oxide; effect on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J Raman Spectrosc 48:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.4998
Ferrari AC, Meyer JC, Scardaci V (2006) Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys Rev Lett 97:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.187401
Gallerneault M, Truica-Marasescu F, Docoslis A (2018) Influence of dispersion medium on the morphological and physico-chemical characteristics of sprayed graphene oxide-based coatings. Surf Coatings Technol 334:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.11.030
Mat Zaid MH, Abdullah J, Yusof NA, Sulaiman Y, Wasoh H, Md Noh MF, Issa R (2017) PNA biosensor based on reduced graphene oxide/water soluble quantum dots for the detection of mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sensors Actuators B Chem 241:1024–1034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.10.045
Chua CK, Ambrosi A, Pumera M (2013) Prolonged exposure of graphite oxide to soft X-ray irradiation during XPS measurements leads to alterations of the chemical composition. Analyst 138:7012–7015. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3an00981e
Shin YE, Sa YJ, Park S, Lee J, Shin KH, Joo SH, Ko H (2014) An ice-templated, pH-tunable self-assembly route to hierarchically porous graphene nanoscroll networks. Nanoscale 6:9734–9741. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr01988a
Ganguly A, Sharma S, Papakonstantinou P, Hamilton J (2011) Probing the thermal deoxygenation of graphene oxide using high-resolution in situ X-ray-based spectroscopies. J Phys Chem C 115:17009–17019. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp203741y
Zhang J, Xu Y, Liu Z, Yang W, Liu J (2015) A highly conductive porous graphene electrode prepared via in situ reduction of graphene oxide using Cu nanoparticles for the fabrication of high performance supercapacitors. RSC Adv 5:54275–54282. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra07857a
Serodre T, Oliveira NAP, Miquita DR, Ferreira M, Santos A, Resende V, Furtado C (2019) Surface silanization of graphene oxide under mild reaction conditions. J Braz Chem Soc 30:2488–2499. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20190167
Dreyer DR, Park S, W CB, S R (2010) The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem Soc Rev 39:228–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-15500-5_3
Brennan K, Martin K, FitzGerald SP (2020) A comparison of methods for the isolation and separation of extracellular vesicles from protein and lipid particles in human serum. Sci Rep 10:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-57497-7
Demir Y, Köksal Z (2019) The inhibition effects of some sulfonamides on human serum paraoxonase-1 (hPON1). Pharmacol Reports 71:545–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2019.02.012
Aengevaeren VL, Hopman MTE, Thompson PD, Bakker EA, George KP, Thijssen DHJ, Eijsvogels TMH (2019) Exercise-induced cardiac troponin I increase and incident mortality and cardiovascular events. Circulation 140:804–814. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.041627
Sandil D, Sharma SC, Puri NK (2019) Protein-functionalized WO3 nanorods-based impedimetric platform for sensitive and label-free detection of a cardiac biomarker. J Mater Res 34:1331–1340. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.481
Chekin F, Vasilescu A, Jijie R, Singh (2018) Sensitive electrochemical detection of cardiac troponin I in serum and saliva by nitrogen-doped porous reduced graphene oxide electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 262:180–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.01.215
Grabowska I, Sharma N, Vasilescu (2018) Electrochemical aptamer-based biosensors for the detection of cardiac biomarkers. ACS Omega 3:12010–12018. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b01558
Habib S, Ghodsi E, Abdollahi S, Nadri S (2016) Porous graphene oxide nanostructure as an excellent scaffold for label-free electrochemical biosensor : detection of cardiac troponin I. Mater Sci Eng C 69:447–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.07.005
Funding
The author would like to acknowledge the support from the Ministry of Education Malaysia under grants FRGS/1/2017/STG05/UNIMAP/03/3 and MyPAIR/1/2020/STG05/UNIMAP//1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.78 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taniselass, S., Arshad, M.K.M., Gopinath, S.C.B. et al. Impedimetric cardiac biomarker determination in serum mediated by epoxy and hydroxyl of reduced graphene oxide on gold array microelectrodes. Microchim Acta 188, 257 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04922-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04922-x