Abstract
The multifunctional hemin@carbon dot hybrid nanozymes (hemin@CD) with simultaneous peroxidase-like activity and fluorescence signalling property was prepared for the first time. Based on these properties, hemin@CD was applied to develop a dual-channel fluorescent probe for H2O2 and H2O2-based biocatalytic systems. By virtue of the peroxidase-like activity, hemin@CD can catalyze the oxidative coupling of 4-aminoantipyrine with phenol in the presence of H2O2 to form a pink-red quinoneimine dye with a maximum absorbance at 505 nm. Under the excitation wavelength of 480 nm, the green fluorescence of hemin@CD peaks at 540 nm and is quenched by the generated quinoneimine dye due to an inner filter effect, and also by H2O2 because of dynamic quenching. Thus, a colorimetric and fluorimetric dual-channel optical probe for H2O2 is obtained. Due to the glucose/xanthine transformations under formation of H2O2 by the relevant oxidase catalysis, the probe can be applied for detection of glucose and xanthine. The colorimetric detection limits for H2O2, glucose and xanthine are 0.11, 0.15, 0.11 μM, and the and fluorimetric detection limits are 0.15, 0.15, 0.12 μM, respectively.

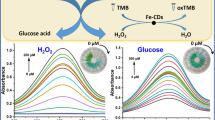
Schematic representation of the colorimetric and fluorimetric dual probe for H2O2, glucose and xanthine based on the multifunctional emin@carbon dot) hybrid nanozymes with simultaneous peroxidase-like activity and fluorescence signalling property.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei H, Wang E (2013) Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem Soc Rev 42(14):6060–6093
Wu J, Wang X, Wang Q, Lou Z, Li S, Zhu Y, Qin L, Wei H (2019) Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem Soc Rev 48(4):1004–1076
Wu J, Li S, Wei H (2018) Multifunctional nanozymes: enzyme-like catalytic activity combined with magnetism and surface plasmon resonance. Nanoscale Horiz 3(4):367–382
Hu Y, Cheng H, Zhao X, Wu J, Muhammad F, Lin S, He J, Zhou L, Zhang C, Deng Y (2017) Surface-enhanced raman scattering active gold nanoparticles with enzyme-mimicking activities for measuring glucose and lactate in living tissues. ACS Nano 11(6):5558–5566
Wu J, Qin K, Yuan D, Tan J, Qin L, Zhang X, Wei H (2018) Rational design of au@ Pt multibranched nanostructures as bifunctional nanozymes. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10(15):12954–12959
Dong Y-L, Zhang H-G, Rahman ZU, Su L, Chen X-J, Hu J, Chen X-G (2012) Graphene oxide-Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposites with peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric detection of glucose. Nanoscale 4(13):3969–3976
Xue T, Jiang S, Qu Y, Su Q, Cheng R, Dubin S, Chiu CY, Kaner R, Huang Y, Duan X (2012) Graphene-supported hemin as a highly active biomimetic oxidation catalyst. Angew Chem Int Edit 51(16):3822–3825
Guo Y, Deng L, Li J, Guo S, Wang E, Dong S (2011) Hemin-graphene hybrid nanosheets with intrinsic peroxidase-like activity for label-free colorimetric detection of single-nucleotide polymorphism. ACS Nano 5(2):1282–1290
Qin F-X, Jia S-Y, Wang F-F, Wu S-H, Song J, Liu Y (2013) Hemin@ metal-organic framework with peroxidase-like activity and its application to glucose detection. Catal Sci Technol 3(10):2761–2768
Zhang F-T, Long X, Zhang D-W, Sun Y-L, Zhou Y-L, Ma Y-R, Qi L-M, Zhang X-X (2014) Layered double hydroxide-hemin nanocomposite as mimetic peroxidase and its application in sensing. Sensors Actuat. B-Chem. 192:150–156
Liu H, Hua Y, Cai Y, Feng L, Li S, Wang H (2019) Mineralizing gold-silver bimetals into hemin-melamine matrix: a nanocomposite nanozyme for visual colorimetric analysis of H2O2 and glucose. Anal Chim Acta 1092:57–65
Shamsipur M, Barati A, Karami S (2017) Long-wavelength, multicolor, and white-light emitting carbon-based dots: achievements made, challenges remaining, and applications. Carbon 124:429–472
Liu H, Li Z, Sun Y, Geng X, Hu Y, Meng H, Ge J, Qu L (2018) Synthesis of luminescent carbon dots with ultrahigh quantum yield and inherent folate receptor-positive cancer cell targetability. Sci Rep 8(1):1086
Liu H, Sun Y, Yang J, Hu Y, Yang R, Li Z, Qu L, Lin Y (2019) High performance fluorescence biosensing of cysteine in human serum with superior specificity based on carbon dots and cobalt-derived recognition. Sensors Actuat. B-Chem. 280:62–68
Liu H, Yang J, Li Z, Xiao L, Aryee AA, Sun Y, Yang R, Meng H, Qu L, Lin Y, Zhang X (2019) Hydrogen-bond-induced emission of carbon dots for wash-free nucleus imaging. Anal Chem 91(14):9259–9265
Geng X, Sun Y, Li Z, Yang R, Zhao Y, Guo Y, Xu J, Li F, Wang Y, Lu S, Qu L (2019) Retrosynthesis of tunable fluorescent carbon dots for precise long-term mitochondrial tracking. Small 15(48):e1901517–e1901517
Li N, Than A, Wang X, Xu S, Sun L, Duan H, Xu C, Chen P (2016) Ultrasensitive profiling of metabolites using tyramine-functionalized graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 10(3):3622–3629
Pinkernell U, Effkemann S, Karst U (1997) Simultaneous HPLC determination of peroxyacetic acid and hydrogen peroxide. Anal Chem 69(17):3623–3627
Antink WH, Choi Y, K-d S, Piao Y (2018) Simple synthesis of CuO/Ag nanocomposite electrode using precursor ink for non-enzymatic electrochemical hydrogen peroxide sensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem 255:1995–2001
Sherino B, Mohamad S, Halim SNA, Manan NSA (2018) Electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide on a new microporous Ni–metal organic framework material-carbon paste electrode. Sensors Actuat B-Chem 254:1148–1156
Ge S, Zhao J, Wang S, Lan F, Yan M, Yu J (2018) Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence assay of tumor cells and evaluation of H2O2 on a paper-based closed-bipolar electrode by in-situ hybridization chain reaction amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 102:411–417
Karimi A, Husain S, Hosseini M, Azar PA, Ganjali M (2018) Rapid and sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide in milk by enzyme-free electrochemiluminescence sensor based on a polypyrrole-cerium oxide nanocomposite. Sensors Actuat. B-Chem 271:90–96
Liu H, Ding Y, Yang B, Liu Z, Liu Q, Zhang X (2018) Colorimetric and ultrasensitive detection of H2O2 based on au/Co3O4-CeOx nanocomposites with enhanced peroxidase-like performance. Sensors Actuat B-Chem 271:336–345
Lin T, Qin Y, Huang Y, Yang R, Hou L, Ye F, Zhao S (2018) A label-free fluorescence assay for hydrogen peroxide and glucose based on the bifunctional MIL-53 (Fe) nanozyme. Chem Commun 54(14):1762–1765
Xiao N, Liu SG, Mo S, Yang YZ, Han L, Ju YJ, Li NB, Luo HQ (2018) B, N-carbon dots-based ratiometric fluorescent and colorimetric dual-readout sensor for H2O2 and H2O2-involved metabolites detection using ZnFe2O4 magnetic microspheres as peroxidase mimics. Sensors Actuat. B-Chem 273:1735–1743
Fang A, Wu Q, Lu Q, Chen H, Li H, Liu M, Zhang Y, Yao S (2016) Upconversion ratiometric fluorescence and colorimetric dual-readout assay for uric acid. Biosens Bioelectron 86:664–670
Li H, Yan X, Qiao S, Lu G, Su X (2018) Yellow-emissive carbon dot-based optical sensing platforms: cell imaging and analytical applications for biocatalytic reactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 10(9):7737–7744
Yang Z, Xu M, Liu Y, He F, Gao F, Su Y, Wei H, Zhang Y (2014) Nitrogen-doped, carbon-rich, highly photoluminescent carbon dots from ammonium citrate. Nanoscale 6(3):1890–1895
Yu X, Liu J, Yu Y, Zuo S, Li B (2014) Preparation and visible light photocatalytic activity of carbon quantum dots/TiO2 nanosheet composites. Carbon 68:718–724
Qu S, Zhou D, Li D, Ji W, Jing P, Han D, Liu L, Zeng H, Shen D (2016) Toward efficient orange emissive carbon nanodots through conjugated sp2-domain controlling and surface charges engineering. Adv Mater 28(18):3516–3521
Zhong H-X, Wang J, Zhang Y-W, Xu W-L, Xing W, Xu D, Zhang Y-F, Zhang X-B (2014) ZIF-8 derived graphene-based nitrogen-doped porous carbon sheets as highly efficient and durable oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 53(51):14235–14239
Metelitza DI, Litvinchuk AV, Savenkova MI (1991) Peroxidase-catalyzed co-oxidation of halogen-substituted phenols and 4-aminoantipyrine. J Mol Catal 67(3):401–411
Song Y, Zhu S, Xiang S, Zhao X, Zhang J, Zhang H, Fu Y, Yang B (2014) Investigation into the fluorescence quenching behaviors and applications of carbon dots. Nanoscale 6(9):4676–4682
Chen J, Chen Q, Chen J, Qiu H (2016) Magnetic carbon nitride nanocomposites as enhanced peroxidase mimetics for use in colorimetric bioassays, and their application to the determination of H2O2 and glucose. Microchim Acta 183(12):3191–3199
Ma Y, Cen Y, Sohail M, Xu G, Wei F, Shi M, Xu X, Song Y, Ma Y, Hu Q (2017) A Ratiometric fluorescence universal platform based on N, cu codoped carbon dots to detect metabolites participating in H2O2-generation reactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 9(38):33011–33019
Qiao F, Wang J, Ai S, Li L (2015) As a new peroxidase mimetics: the synthesis of selenium doped graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets and applications on colorimetric detection of H2O2 and xanthine. Sensors Actuat. B-Chem 216:418–427
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21405034, 21722501, 21976052). Key Project of Science and Technology of Henan Province (192102210041). Program for Science Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (18HASTIT001). Dr. start-up project funding of Henan Normal University (qd18014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 742 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, L., Cai, Y., Wang, L. et al. Hemin@carbon dot hybrid nanozymes with peroxidase mimicking properties for dual (colorimetric and fluorometric) sensing of hydrogen peroxide, glucose and xanthine. Microchim Acta 187, 132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4103-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4103-4