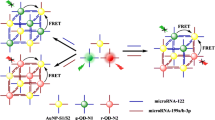
Abstract
An enzyme-free resonance light scattering (RLS) method is described for the determination of microRNA-122. A guanine nanowire (G-wire) is used that consists of a predesigned DNA1 and a G-quadruplex sequence DNA2. These hybridize with microRNA-122 and partially hybridize with DNA2. After formation of stable double strands with DNA1, DNA2 is released. On addition of K+ and Mg2+ ions, the G-quadruplex sequences undergo self-assembly to form long filamentous G-wires. This increases the intensity of RLS. A 6.1 pM detection limit was obtained, and the linear response covers the 50 pM to 300 nM microRNA concentration range. The method was successfully applied to the quantitation of microRNA-122 in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lysates. Conceivably, this assay can be extended to other RLS methods for biomarker detection by simply changing the sequence of DNA1.

The G-quadruplex sequences of DNA2 were locked with DNA1. The G-quadruplex fragments of DNA2 were released after the hybridization of microRNA-122 with DNA1. These liberated G-quadruplex sequences were self-assembled into long filamentous guanine nanowires (G-wires) which increased resonance light intensity in the presence of Mg2+.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marsh TC, Henderson E (1994) G-wires: self-assembly of a Telomeric oligonucleotide, d (GGGGTTGGGG), into large superstructures. Biochemistry 33:10718–10724. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00201a020
Marsh TC, Vesenka J, Henderson E (1995) A new DNA nanostructure, the G-wire, imaged by scanning probe microscopy. Nucleic Acids Res 23:696–700. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/23.4.696
Kenir MA (2000) Quadruplex Structures in Nucleic Acids. Biopolymers 56:123–146. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0282(2000/2001)56:3<123::AID-BIP10010>3.0.CO;2-3
Sen D, Gilbert W (1990) A sodium-potassium swich in the formation of four-stranded G4-DNA. Nature 344:410–414. https://doi.org/10.1038/344410a0
Sen D, Gilbert W (1992) Novel DNA superstructures formed by telomere-like oligomers. Biochemistry 31:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00116a011
Liu S-P, Weisbrod SH, Tang Z, Marx A, Scheer E, Erbe A (2010) Direct measurement of electrical transport through G-Quadruplex DNA with mechanically controllable break junction electrodes. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:3313–3316. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201000022
Protozanova E, Macgregor RB (1996) Frayed wires: a thermally stable form of DNA with two distinct structural domains. Biochemistry 35:16638–16645. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi960412d
Fahlman RP, Sen D (1998) Cation-regulated self-association of "Synapsable" DNA duplexes. J Mol Biol 280:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1998.1875
Hessari NM, Spindler L, Troha T, Lam W-C, Drevenšek-Olenik I, Silva MW (2014) Programmed self-assembly of a Quadruplex DNA nanowire. Chem Eur J 20:3626–3630. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201300692
Ilc T, Plavec P, Šket J, Silva MW, Drevenšek-Olenik I, Spindler L (2013) Formation of G-wires: the role of G: C-base pairing and G-quartet stacking. J Phys Chem C 117:23208–23215. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp4019348
Yatsunyk LA, Piétrement O, Albrecht D, Tran PLT, Renčiuk D, Sugiyama H, Arbona J-M, Aimé J-P, Mergny J-L (2013) Guided assembly of Tetramolecular G-quadruplexes. ACS Nano 7:5701–5710. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn402321g
Qing M, Yuan Y, Cai W, Xie S, Tang Y, Yuan R, Zhang J (2018) An ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor based on multifunctional hemin/G-quadruplex nanowires simultaneously served as bienzyme and direct electron mediator for detection of lead ion. Sensors Actuators B Chem 263:469–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.02.109
Gao ZF, Huang YL, Ren W, Luo HQ, Li NB (2016) Guanine nanowire based amplification strategy: enzyme-free biosensing of nucleic acids and proteins. Biosens Bioelectron 78:351–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.11.070
Ye C, Wang MQ, Luo HQ, Li NB (2017) Label-free Photoelectrochemical “off-on” platform coupled with G-wire-enhanced strategy for highly sensitive MicroRNA sensing in Cancer cells. Anal Chem 89:11697–11702. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03150
Xu Y, Luo J, Wu M, Hu F, Lu Z, Jing H, Chen R, Zhan H (2018) Ultrasensitive and specific imaging of circulating microRNA based on split probe, exponential amplification, and topological guanine nanowires. Sensors Actuators B Chem 269:158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.04.122
Zhang XF, Li N, Ye C, Liang JY, Li NB, Luo HQ (2017) Sensitive label-free resonance Rayleigh scattering DNA machine-based dual amplification strategy for the active uracil-DNA glycosylase assay. Sensors Actuators B Chem 250:300–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.04.178
Ren W, Zhang Y, Chen HG, Gao ZF, Li NB, Luo HQ (2016) Ultrasensitive label-free resonance Rayleigh scattering Aptasensor for Hg2+ using Hg2+−triggered exonuclease III-assisted target recycling and growth of G-wires for signal amplification. Anal Chem 88:1385–1390. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03972
Pasternack RF, Bustamante C, Collings PJ, Giannetto A, Gibbs EJ (1993) Porphyrin assemblies on DNA as studied by a resonance light-scattering technique. J Am Chem Soc 115:5393–5399. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00066a006
Liu S, Luo H, Li N, Liu Z, Zheng W (2001) Resonance Rayleigh scattering study of the interaction of heparin with some basic diphenyl naphthylmethane dyes. Anal Chem 73:3907–3914. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac001454h
Jopling CL, Yi M, Lancaster AM, Lemon SM, Sarnow P (2005) Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a liver-specific MicroRNA. Science 309:1577–1581. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1113329
Bushati N, Cohen SM (2007) MicroRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:175–205. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123406
Young DD, Connelly CM, Grohmann C, Deiters A (2010) Small molecule modifiers of MicroRNA miR-122 function for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Chem Soc 132:7976–7981. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja910275u
Li L, Feng J, Liu H, Li Q, Tong L, Tang B (2016) Two-color imaging of microRNA with enzyme-free signal amplification via hybridization chain reactions in living cells. Chem Sci 7:1940–1945. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC03909F
Song Y, Yan X, Ostermeyer G, Li S, Qu L, Du D, Li Z, Lin Y (2018) Direct cytosolic MicroRNA detection using single-layer Perfluorinated tungsten Diselenide Nanoplatform. Anal Chem 90:10369–10376. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02193
Liu H, Bei X, Xia Q, Fu Y, Zhang S, Liu M, Fan K, Zhang M, Yang Y (2016) Enzyme-free electrochemical detection of microRNA-21 using immobilized hairpin probes and a target-triggered hybridization chain reaction amplification strategy. Microchim Acta 183:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1636-z
Dong H, Jin S, Ju H, Hao K, Xu LP, Lu H, Zhang X (2012) Trace and label-free MicroRNA detection using oligonucleotide encapsulated silver nanoclusters as probes. Anal Chem 84:8670–8674. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac301860v
Park J, Yeo JS (2014) Colorimetric detection of microRNA miR-21 based on nanoplasmonic core–satellite assembly. Chem Commun 50:1366–1368. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CC48154A
Lv S, Chen F, Chen C, Chen X, Gong H, Cai C (2017) A novel CdTe quantum dots probe amplified resonance light scattering signals to detect microRNA-122. Talanta 165:659–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.01.020
Wu D, Shi H, Wang S, He Y, Bao Y, Liu K (2012) Rapid prediction of moisture content of dehydrated prawns using online hyperspectral imaging system. Anal Chim Acta 726:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.03.038
Jopling CL, Yi M, Lancaster AM, Lemon SM, Sarnow P (2005) Modulation of Hepatitis C Virus RNA ndance by a Liver-Specific MicroRNA. Science 309:1577–1581. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1113329
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21775132), Scientific Research Foundation of Hunan Provincial Education Department (No. 16A204), and the National Natural Science Foundation of Hunan province (No.2018JJ2388). Hunan 2011 Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Engineering & Technology with Environmental Benignity and Effective Resource Utilization, the project of innovation team of the ministry of education (IRT_17R90), and “1515”academic leader team program of Hunan Agricultural University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 23037 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, R., Zhang, F., Chen, C. et al. An ultrasensitive guanine wire-based resonance light scattering method using G-quadruplex self-assembly for determination of microRNA-122. Microchim Acta 186, 599 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3707-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3707-z