Abstract
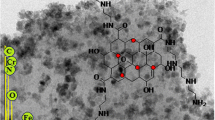
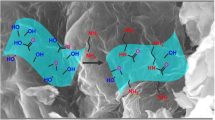
Graphene oxide (GO) was chemically functionalized with 5-amino-1,10-phenanthroline. The resulting conjugate (phen-GO) was characterized by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The experiments show that phen-GO has a high affinity for extraction of Pb(II) ions. Isotherms and kinetics fit the Langmuir model and pseudo-second-order equations. By using phen-GO as a sorbent, Pb(II) ions can be quantitatively adsorbed at pH 6.0. The adsorption capacity is 548 mg g−1. Following desorption with 2 mol L−1 HNO3, Pb(II) was quantified by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. The effects of pH value, eluent type, sorption time, sample volume, and matrix ions were optimized. The accuracy of the method was validated by analysis of the reference materials DOLT-3 (dogfish liver) and SRM 1640a (natural water). Under optimal conditions, the calibration plots cover the 0.25 to 500 ng mL−1 Pb(II) concentration range. The method was successfully applied to the analysis of spiked water and biological samples. Other figures of merit include a preconcentration factor of 250, a detection limit of 46 ng L−1, and a relative standard deviation of <5%.

Schematic presentation of the dispersive solid-phase extraction of lead(II) ions using graphene oxide modified with 5-amino-1,10-phenanthroline, followed by their determination by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP OES).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jia W, Lu S (2014) Few-layered graphene oxides as superior adsorbents for the removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions. Korean J Chem Eng 31:1265–1270
World Health Organization (1996) Health criteria and other supporting information. World Health Organization, Geneva
Su S, Chen B, He M, Hu B (2014) Graphene oxide–silica composite coating hollow fiber solid phase microextraction online coupled with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for the determination of trace heavy metals in environmental water samples. Talanta 123:1–9
Zhu X, Cui Y, Chang X, Wang H (2016) Selective solid-phase extraction and analysis of trace-level Cr(III), Fe(III), Pb(II), and Mn(II) ions in waste water using diethylenetriamine-functionalized carbon nanotubes dispersed in graphene oxide colloids. Talanta 146:358–363
Aghagoli MJ, Shemirani F (2017) Hybrid nanosheets composed of molybdenum disulfide and reduced graphene oxide for enhanced solid phase extraction of Pb(II) and Ni(II). Microchim Acta 184:237–244
Han X, Meng Z, Zhang H, Zheng J (2018) Fullerene-based anodic stripping voltammetry for simultaneous determination of Hg(II), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) in foodstuff. Microchim Acta 185:274–282
Feist B, Mikula B, Pytlakowska K, Puzio B, Sitko R (2012) Preconcentration via ion associated complexes combined with inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry for determination of heavy metals. Talanta 88:391–395
Daşbaşı T, Saçmacı Ş, Çankaya N, Soykan C (2016) Synthesis, characterization and application of a new chelating resin for solid phase extraction, preconcentration and determination of trace metals in some dairy samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem 211:68–73
Jalbani N, Soylak M (2015) Separation–preconcentration of nickel and lead in food samples by a combination of solid–liquid–solid dispersive extraction using SiO2 nanoparticles, ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction. Talanta 131:361–365
Li Z, Chen J, Liua M, Yang Y (2014) Ultrasound-assisted cloud point extraction coupled with flame atomic absorption spectrometry for the determination of lead and cadmium in water samples. Anal Methods 6:3241–3246
Zarezade V, Aliakbari A, Es’haghi M, Amini MM, Behbahani M, Omidi F, Hesam G (2017) Application of a new nanoporous sorbent for extraction and pre-concentration of lead and copper ions. Inter J Env Anal Chem 97:383–397
Tokalıoglu S, Papak A, Kartal S (2017) Separation/preconcentration of trace Pb(II) and cd(II) with 2-mercaptobenzothiazole impregnated Amberlite XAD-1180 resin and their determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Arab J Chem 10:19–23
Mendil D, Demirci Z, Uluozlu OD, Tuzen M, Soylak M (2017) A new separation and preconcentration method for selenium in some foods using modified silica gel with 2,6-diamino-4-phenil-1,3,5-triazine. Food Chem 221:1394–1399
Mikula B, Puzio B, Feist B (2009) Application of 1,10-phenanthroline for preconcentration of selected heavy metals on silica gel. Microchim Acta 166:337–341
Burham N (2009) Separation and preconcentration system for lead and cadmium determination in natural samples using 2-aminoacetylthiophenol modified polyurethane foam. Desalination 249:1199–1205
Zhang L, Li Z, Du X, Li R, Chang X (2012) Simultaneous separation and preconcentration of Cr(III), Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) from environmental samples prior to inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometric determination. Spectrochim Acta Part A 86:443–448
Feist B, Sitko R (2014) Preconcentration of trace lead via formation of the bis(2,2-bipyridyl) complex and its adsorption on oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 181:1035–1040
Pytlakowska K, Kozik V, Matussek M, Pilch M, Hachuła B, Kocot K (2016) Glycine modified graphene oxide as a novel sorbent for preconcentration of chromium, copper, and zinc ions from water samples prior to energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometric determination. RSC Adv 6:42836–42844
Zawisza B, Baranik A, Malicka E, Talik E, Sitko R (2016) Preconcentration of Fe(III), co(II), Ni(II), cu(II), Zn(II) and Pb(II) with ethylenediamine-modified graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 183:231–240
Behbahani M, Veisi A, Omidi F, Noghrehabadi A, Esrafili A, Ebrahimi MH (2018) Application of a dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction method for pre-concentration and ultra-trace determination of cadmium ions in water and biological samples. Appl Organomet Chem 32:4134–4143
Behbahani M, Omidi F, Kakavandi MG, Hesam G (2017) Selective and sensitive determination of silver ions at trace levels based on ultrasonic-assisted dispersive solid-phase extraction using ion-imprinted polymer nanoparticles. Appl Organomet Chem 31:3758–3766
Parvizi S, Behbahani M, Zeraatpisheh F, Esrafilic A (2018) Preconcentration and ultra-trace determination of hexavalent chromium ions using tailor-made polymer nanoparticles coupled with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry: ultrasonic assisted-dispersive solid-phase extraction. New J Chem 42:10357–10365
Zhang F, Song Y, Song S, Zhang R, Hou W (2015) Synthesis of magnetite−graphene oxide-layered double hydroxide composites and applications for the removal of Pb(II) and 2,4- dichlorophenoxyacetic acid from aqueous solutions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:7251–7263
Feist B (2016) Selective dispersive micro solid-phase extraction using oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified with 1,10-phenanthroline for preconcentration of lead ions. Food Chem 209:37–42
Feist B, Mikula B (2014) Preconcentration of heavy metals on activated carbon and their determination in fruits by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Food Chem 147:302–306
Deng D, Jiang X, Yang L, Hou X, Zheng C (2014) Organic solvent-free cloud point extraction-like methodology using aggregation of graphene oxide. Anal Chem 86:758–765
Zhao G, Li J, Ren X, Chen C, Wang X (2011) Few-layered graphene oxide Nanosheets as superior sorbents for heavy metal ion pollution management. Environ Sci Technol 45:10454–10462
Yukun W, Shutao G, Xiaohuan Z, Jingci L, Jingjun M (2012) Graphene-based solid-phase extraction combined with flame atomic absorption spectrometry for a sensitive determination of trace amounts of lead in environmental water and vegetable samples. Anal Chim Acta 716:112–118
Sitko R, Zawisza B, Talik E, Janik P, Osoba G, Feist B, Malicka E (2014) Spherical silica particles decorated with graphene oxide nanosheets as a new sorbent in inorganic trace analysis. Anal Chim Acta 834:22–29
Moghimi A, Abdouss M, Ghooshchi G (2013) Preconcentration of Pb(II) by graphene oxide with covalently linked porphyrin adsorbed on surfactant coated C18 before determination by FAAS. Int J Bio-Inorg Hybrid Nanomater 2:355–364
Khan M, Yilmaz E, Sevinc B, Sahmetlioglu E, Shah J, Jan MR, Soylak M (2016) Preparation and characterization of magnetic allylamine modified graphene oxide-poly(vinyl acetate-co-divinylbenzene) nanocomposite for vortex assisted magnetic solid phase extraction of some metal ions. Talanta 146:130–137
Sitko R, Janik P, Zawisza B, Talik E, Margui E, Queralt I (2015) Green approach for ultratrace determination of divalent metal ions and arsenic species using total-reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and mercapto-modified graphene oxide nanosheets as a novel adsorbent. Anal Chem 87:3535–3542
Baghban N, Yilmaz E, Soylak M (2018) Vortex assisted solid-phase extraction of lead(II) using orthorhombic nanosized Bi2WO6 as a sorbent. Microchim Acta 185:34–42
Baghban N, Yilmaz E, Soylak M (2017) A magnetic MoS2-Fe3O4 nanocomposite as an effective adsorbent for dispersive solid-phase microextraction of lead(II) and copper(II) prior to their determination by FAAS. Microchim Acta 184:3969–3976
Su S, He M, Zhang N, Cui C (2014) Calconcarboxylic acid dynamically modified nanometer-sized zirconia for on-line flow injection inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry determination of trace heavy metals in environmental water samples. Anal Methods 6:1182–1188
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 718 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feist, B., Pilch, M. & Nycz, J. Graphene oxide chemically modified with 5-amino-1,10-phenanthroline as sorbent for separation and preconcentration of trace amount of lead(II). Microchim Acta 186, 91 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3213-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3213-8