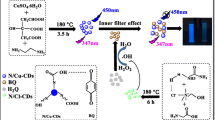
Abstract
N/S/P-codoped carbon dots (CDs) are shown to be a viable fluorescent probe in a turn-off-on fluorometric assay for hydroquinone (HQ). The preparation of CDs was carried out using a one-step hydrothermal reaction starting with glyoxal and isocarbophos. The method is based on the formation of ground state complexes between CD and Fe(III) which leads to quenching of blue fluorescence (with excitation/emission peaks at 363/448 nm). On addition of HQ, it will be oxidized by Fe(III) upon which fluorescence recovers. This turn-off-on system can be utilized to quantify HQ. A linear relationship exists between fluorescence recovery and HQ concentration in range between 0.56 and 375 μM. The limit of detection is 0.16 μM. The assay was successfully applied to the determination of HQ in spiked water samples and developer samples.

Fluorometric determination of hydroquinone (with good selectivity over catechol and resorcinol) by using blue-emitting N/S/P-codoped carbon dots and the quenching effect of Fe(III).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Terashima C, Rao TN, Sarada BV, Tryk DA, Fujishima A (2002) Electrochemical oxidation of chlorophenols at a boron-doped diamond electrode and their determination by high-performance liquid chromatography with amperometric detection. Anal Chem 74:895–902. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac010681w
Wang Y, Xiong YY, Qu JY, Qu JH, Li SF (2016) Selective sensing of hydroquinone and catechol based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes/polydopamine/gold nanoparticles composites. Sensors Actuators B Chem 223:501–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.09.117
Wei C, Huang QT, Hu SR, Zhang HQ, Zhang WX, Wang ZM, Zhu M, Dai P, Huang L (2014) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of hydroquinone, catechol and resorcinol at Nafion/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/carbon dots/multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim Acta 149:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.10.051
Carvalho RM, Mello C, Kubota LT (2000) Simultaneous determination of phenol isomers in binary mixtures by differential pulse voltammetry using carbon fibre electrode and neural network with pruning as a multivariate calibration tool. Anal Chim Acta 420:109–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)01012-6
Moldoveanu S, Kiser M (2007) Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry versus liquidchromatography/fluorescence detection in the analysis of phenols in main-stream cigarette smoke. J Chromatogr A 1141:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.11.100
Ahmed J, Rahman MM, Siddiquey IA, Asiri AM, Hasnat MA (2018) Efficient hydroquinone sensor based on zinc, strontium and nickelbased ternary metal oxide (TMO) composites by differential pulsevoltammetry. Sensors Actuators B Chem 256:383–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.10.076
Shahbakhsh M, Noroozifar M (2018) Poly (dopamine quinone-chromium (III) complex) microspheres as new modifier for simultaneous determination of phenolic compounds. Biosens Bioelectron 102:439–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.11.042
Sun YG, Cui H, Li YH, Lin XQ (2000) Determination of some catechol derivatives by a flow injection electrochemiluminescent inhibition method. Talanta 53:661–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(00)00550-6
Han SQ, Liu BB, Liu Y, Fan ZY (2016) Silver nanoparticle induced chemiluminescence of the hexacyanoferrate-fluorescein system, and its application to the determination of catechol. Microchim Acta 183:917–921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1704-4
Chao YJ, Zhang X, Liu L, Tian LH, Pei MS, Cao W (2015) Determination of hydroquinone by flow injection chemiluminescence and using magnetic surface molecularly imprinted particles. Microchim Acta 182:943–948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1415-2
Yang HG, Zha JQ, Zhang P, Qin YM, Chen T, Ye FG (2017) Fabrication of CeVO4as nanozyme for facile colorimetricdiscrimination of hydroquinone from resorcinol and catechol. Sensors Actuators B Chem 247:469–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.03.042
Liu Y, Wang Y-M, Zhu W-Y, Zhang C-H, Tang H, Jiang J-H (2018) Conjugated polymer nanoparticles-based fluorescent biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of hydroquinone. Anal Chim Acta 1012:60–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.01.027
Sun S, Jiang K, Qian SH, Wang YH, Lin HW (2017) Applying carbon dots-metal ions ensembles as a multichannel fluorescent sensor array: detection and discrimination of phosphate anions. Anal Chem 89:5542–5548. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00602
Shangguan JF, Huang J, He DG, He XX, Wang KM, Ye RZ, Yang X, Qing T, Tang J (2017) Highly Fe3+−selective fluorescent nanoprobe based on ultrabright N/P codoped carbon dots and its application in biological samples. Anal Chem 89:7477–7484. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01053
Yang WQ, Ni JC, Luo F, Weng W, Wei QH, Lin ZY, Chen G (2017) Cationic carbon dots for modification-free detection of hyaluronidase via an electrostatic-controlled ratiometric fluorescence assay. Anal Chem 89:8384–8390. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01705
Zhou J, Zhou H, Tang JB, Deng SE, Yan F, Li WJ, Qu M (2017) Carbon dots doped with heteroatoms for fluorescent bioimaging: a review. Microchim Acta 184:343–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2043-9
Yan X, Song Y, Zhu CZ, Li HX, Du D, Su XG et al (2018) MnO2 nanosheet-carbon dots sensing platform for sensitive detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Anal Chem 90:2618–2624. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04193
Yue QL, Hou YN, Yue SZ, Du KM, Shen TF, Wang L et al (2015) Construction of an off-on fluorescence system based on carbon dots for trace pyrophosphate sensing. J Fluoresc 25:585–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-015-1538-9
Zu FL, Yan FY, Bai ZJ, Xu JX, Wang YY, Huang YC, Zhou X (2017) The quenching of the fluorescence of carbon dots: a review on mechanisms and applications. Microchim Acta 184:1899–1914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2318-9
Han CP, Wang R, Wang KY, Xu HT, Sui MR, Li JJ, Xu K (2016) Highly fluorescent carbon dots as selective and sensitive "on-off-on" probes for iron(III) ion and apoferritin detection and imaging in living cells. Biosens Bioelectron 83:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.04.066
Chen T-H, Tseng W-L (2017) Self-assembly of monodisperse carbon dots into high-brightness nanoaggregates for cellular uptake imaging and iron(III) sensing. Anal Chem 89:11348–11356. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02193
Wang RX, Wang XF, Sun YM (2017) One-step synthesis of self-doped carbon dots with highly photoluminescence as multifunctional biosensors for detection of iron ions and pH. Sensors Actuators B Chem 241:73–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.10.043
Zhang HJ, Chen YL, Liang MJ, Xu LF, Qi SD, Chen HL, Chen X (2014) Solid-phase synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for sensitive and selective probing ferric ions in living cells. Anal Chem 86:9846–9852. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac502446m
Hu CG, Xiao Y, Zhao Y, Chen N, Zhang ZP, Cao MH, Qu L (2013) Highly nitrogen-doped carbon capsules: scalable preparation and high-performance applications in fuel cells and lithium ion batteries. Nanoscale 5:2726–2733. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR34002C
Garg S, Rose AL, Waite TD (2011) Photochemical production of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide from natural organic matter. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75:4310–4320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2011.05.014
Uchimiya M, Stone AT (2006) Redox reactions between iron and quinones: thermodynamic constraints. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:1388–1401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2005.11.020
Yuan X, Pham AN, Miller CJ, Waite TD (2013) Copper catalyzed hydroquinone oxidation and associated redox cycling of copper under conditions typical of natural saline waters. Environ Sci Technol 47:8355–8364. https://doi.org/10.1021/es4014344
Jiang C, Garg S, Waite TD (2015) Hydroquinone-mediated redox cycling of iron and concomitant oxidation of hydroquinone in oxic waters under acidic conditions: comparison with iron−natural organic matter interactions. Environ Sci Technol 49:14076–14084. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b03189
Reckmeier CJ, Schneider J, Xiong Y, Hausler J, Kasak P, Schnick W et al (2017) Aggregated molecular fluorophores in the ammonothermal synthesis of carbon dots. Chem Mater 29:10352–10361. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b03344
Song W, Duan WX, Liu YH, Ye ZJ, Chen YL, Chen HL, Qi S, Wu J, Liu D, Xiao L, Ren C, Chen X (2017) Ratiometric detection of intracellular lysine and ph with one-pot synthesized dual emissive carbon dots. Anal Chem 89:13626–13633. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04211
Zuo GC, Xie AM, Li JJ, Su T, Pan XH, Dong W (2017) Large emission red-shift of carbon dots by fluorine doping and their applications for red cell imaging and sensitive intracellular Ag+ detection. J Phys Chem C 121:26558–26565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.11.006
Xu SX, Li JL, Li XM, Su M, Shi ZM, Zeng Y et al (2016) A chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer systemcomposed of cobalt (II), luminol, hydrogen peroxide and CdTe quantum dots for highly sensitive determination of hydroquinone. Microchim Acta 183:667–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.11.006
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by Natural Science Foundation (NSF) of China (91543206, 21729501), NSF (ZR2014BQ017, ZR2015BM024, and 2013SJGZ07) and Tai-Shan Scholar Research Fund of Shandong Province and research foundation of Liaocheng University. Dr. Li also thanks the support sponsored by NSF Independent Research/Development (IRD) Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 11078 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Yue, Q., Tao, L. et al. Fluorometric determination of hydroquinone by using blue emitting N/S/P-codoped carbon dots. Microchim Acta 185, 550 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3082-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3082-1