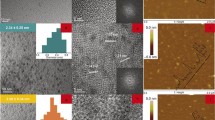
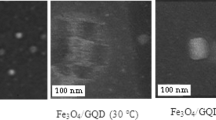
Abstract
We have prepared graphene quantum dot-europium(III) complex composites by noncovalently connecting chelating ligands dibenzoylmethane (DBM) and 1,10-phenanthroline (Phen) with graphene quantum dots (GQDs) first, followed by coordination to Eu(III). The resulting composites are well water-soluble and display red fluorescence of high color purity. The composites were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. Aqueous solutions of the composites under 365 nm excitation display fluorescence with a peak at 613 nm and a quantum yield as high as 15.5 %. The good water solubility and stable photoluminescence make the composites very different from other Eu(III)-based coordination complexes. The composites are cell viable and can be used to label both the cell membrane and the cytoplasm of MCF-7 cells. They are also shown to act as bioprobes for in-vivo localization of tumorous tissue. In our perception, such composites are expected to possess wide scope because of the many functionalizations that are possible with GQDs.

Synthesis of red fluorescent graphene quantum dot-europium complex composites for use in bioimaging.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zuo PL, Lu XH, Sun ZG, Guo YH, He H (2016) A review on syntheses, properties, characterization and bioanalytical applications of fluorescent carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183:519
Wolfbeis OS (2015) An overview of nanoparticles commonly used in fluorescent bioimaging. Chem Soc Rev 44:4743
Li LL, Ji J, Fei R, Wang CZ, Lu Q, Zhang JR, Jiang LP, Zhu JJ (2012) A facile microwave avenue to electrochemiluminescent two-color graphene quantum dots. Adv Funct Mater 22:2971–2979
Zhu SJ, Zhang JH, Tang SJ, Qiao CY, Wang L, Wang HY, Liu X, Li B, Li YF, Yu WL, Wang XF, Sun HC, Yang B (2012) Surface chemistry routes to modulate the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots: from fluorescence mechanism to up-conversion bioimaging applications. Adv Funct Mater 22:4732–4740
Zhang M, Bai LL, Shang WH, Xie WJ, Ma H, Fu YY, Fang DC, Sun H, Fan LZ, Han M, Liu CM, Yang SH (2012) Facile synthesis of water-soluble, highly fluorescent graphene quantum dots as a robust biological label for stem cells. J Mater Chem 22:7461–7467
Fan ZT, Li YC, Li XH, Fan LZ, Zhou SX, Fang DC, Yang SH (2014) Surrounding media sensitive photoluminescence of boron-doped graphene quantum dots for highly fluorescent dyed crystals, chemical sensing and bioimaging. Carbon 70:149–156
Bhaisare ML, Talib A, Khan MS, Pandey S, Wu HF (2015) Synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots via microwave carbonization of citric acid in presence of tetraoctylammonium ion, and their application to cellular bioimaging. Microchim Acta 182:2173–2181
Li H, Shao FQ, Zou SY, Yang QJ, Huang H, Feng JJ, Wang AJ (2016) Microwave-assisted synthesis of N,P-doped carbon dots for fluorescent cell imaging. Microchim Acta 183:821–826
Yuan XC, Liu ZM, Guo ZY, Ji YH, Jin M, Wang XP (2014) Cellular distribution and cytotoxicity of graphene quantum dots with different functional groups. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:108
Hu SL, Zhao Q, Chang Q, Yang JL, Liu J (2014) Enhanced performance of Fe3+ detection via fluorescence resonance energy transfer between carbon quantum dots and Rhodamine B. RSC Adv 4:41069–41075
Fuyuno N, Kozawa D, Miyauchi Y, Mouri S, Kitaura R, Shinohara H, Yasuda T, Komatsu N, Matsuda K (2014) Drastic change in photoluminescence properties of graphene quantum dots by chromatographic separation. Adv Optical Mater 2:983–989
Ge JC, Lan MH, Zhou BJ, Liu WM, Guo L, Wang H, Jia QY, Niu GL, Huang X, Zhou HY, Meng XM, Wang PF, Lee CS, Zhang WJ, Han XD (2014) A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nat Commun 5:4596–4603
Dong HL, Kuzmanoski A, Gossl DM, Popescu R, Gerthsen D, Feldmann C (2014) Polyol-mediated C-dot formation showing efficient Tb3+/Eu3+ emission. Chem Commun 50:7503–7506
Tan XY, Li YC, Li XH, Zhou SX, Fan LZ, Yang SH (2015) Electrochemical synthesis of small-sized red fluorescent graphene quantum dots as a bioimaging platform. Chem Commun 51:2544–2546
Eliseeva SV, Bunzli JCG (2010) Lanthanide luminescence for functional materials and bio-sciences. Chem Soc Rev 39:189–227
Ruan M, Niu CG, Zeng GM, Qin PZ, Wang XY, Huang DW, Huang J, Fan CZ (2011) Rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus via a sensitive DNA hybridization assay based on a long-lifetime luminescent europium marker. Microchim Acta 175:105–112
Kin E, Fukuda T, Kato S, Honda Z, Kamata N (2009) pH and concentration dependence of luminescent characteristics in glass-encapsulated Eu-complex. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 50:409–414
Maggini L, Traboulsi H, Yoosaf K, Mohanraj J, Wouters J, Pietraszkiewicz O, Pietraszkiewicz M, Armaroli N, Bonifazi D (2010) Electrostatically-driven assembly of MWCNTs with a europium complex. Chem Commun 47:1625–1627
Bai JM, Zhang L, Liang RP, Qiu JD (2013) Graphene quantum dots combined with europium ions as photoluminescent probes for phosphate sensing. Chem Eur J 19:3822–3826
Yuan FL, Ding L, Li YC, Li XH, Fan LZ, Fang DC, Yang SH (2015) Multicolor fluorescent graphene quantum dots colorimetrically responsive to all-pH and a wide temperature range. Nanoscle 7:11727–11733
Cao YW, Yang T, Feng JC, Wu PY (2010) Decoration of graphene oxide sheets with luminescent rare-earth complexes. Carbon 49:1502–1507
Ryu J, Lee E, Lee K, Jang J (2015) A graphene quantum dots based fluorescent sensor for anthrax biomarker detection and its size dependence. J Mater Chem B 3:4865–4870
Bian ZQ, Wang KZ, Jin LP (2002) Syntheses, spectroscopic and crystal structural studies of novel imidazo[4,5-f]1,10-phenanthroline derivatives and their Eu(III) ternary complexes with dibenzoylmethane. Polyhedron 21:313–319
Babij M, Mondry A (2011) Synthesis, structure and spectroscopic studies of europium complex with S(+)-mandelic acid. J Rare Earths 29:1188–1191
Yu MG, Chen GX, Liu JW, Tang BL, Huang WT (2013) Preparation and characteristics of core-shell structure Eu(DBM)3Phen@SiO2 micro-sphere. J Mater Sci Technol 29:801–805
Accorsi G, Armaroli N, Parisini A, Meneghetti M, Marega R, Parto M, Bonifazi D (2007) Wet adsorption of a luminescent EuIII complex on carbon nanotubes sidewalls. Adv Funct Mater 17:2975–2982
Ai KL, Zhang BH, Lu LH (2009) Europium-based fluorescence nanoparticle sensor for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of an anthrax biomarker. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:304–308
Azab HA, El-Korashy SA, Anwar ZM, Hussein BHM, Khairy GM (2010) Synthesis and fluorescence properties of Eu-anthracene-9-carboxylic acid towards N-acetyl amino acids and nucleotides in different solvents. Spectrochim Acta A 75:21
Fang J, Nakamura H, Maeda H (2011) The EPR effect: unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63:136–151
Nurunnabi M, Khatun Z, Huh KM, Park SY, Lee DY, Cho KJ, Lee YK (2013) In vivo biodistribution and toxicology of carboxylated graphene Quantum dots. ACS Nano 7:6858–6867
Yuan YY, Ding D, Li K, Liu J, Liu B (2014) Red-missive Carbon Dots for fluorescent, photoacoustic, and thermal theranostics in living. Small 10:1967–1975
Ge JC, Jia QY, Liu WM, Guo L, Liu QY, Lan MH, Zhang HY, Meng XM, Wang PF (2015) Red-emissive carbon dots for fluorescent, photoacoustic, and thermal theranostics in living mice. Adv Mater 27:4169–4177
Guo RH, Zhou SX, Li YC, Li XH, Fan LZ, Voelcker NH (2015) Rhodamine-functionalized graphene quantum dots for detection of Fe3+ in cancer stem cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:23958
Huang CL, Huang CC, Mai FD, Yen CL, Tzing SH, Hsieh HT, Lingd YC, Chang JY (2015) Application of paramagnetic graphene quantum dots as a platform for simultaneous dual-modality bioimaging and tumor-targeted drug delivery. J M Chem B 3:651
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by NSFC of China (21573019), the Major Research Plan of NSFC (21233003), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhou, S., Fan, L. et al. Synthesis of red fluorescent graphene quantum dot-europium complex composites as a viable bioimaging platform. Microchim Acta 183, 2605–2613 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1909-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1909-1