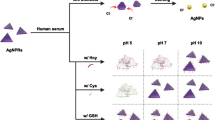
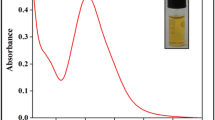
Abstract
The authors demonstrate a single-step histidine assay that is based on the use of silver nanoparticles modified with sulfanilic acid (SAA-AgNPs). The presence of histidine leads to a visually detectable gradual color change from bright yellow via orange to purple. The effect is assumed to be mainly due to strong π-π stacking, electrostatic interaction, and hydrogen bonding between SAA and histidine. The assay has a 52.7 nM detection limit and works in the 0 to 3.5 μM concentration range. It is selective over other compounds when using appropriate masking agents. The method has been successfully applied to the colorimetric determination of histidine in (spiked) serum samples. Recoveries ranged between 97 % and 107 %, and relative standard deviations are <0.92 % (for n = 3). The method was also applied to detect polyhistidine-tagged cysteine (His-His-His-His-His-His-Cys) which can be quantified in concentrations down to 5.57 nM. This finding links the method to His-tag technology.

A single-step colorimetric assay for histidine is developed using sulfanilic acid modified silver nanoparticles (SAA-AgNPs) via π stacking, electrostatic interaction, and hydrogen bonding resulting in the aggregation of the AgNPs and a color change from yellow to orange.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen GN, Wu XP, Duan JP, Chen HQ (1999) A study on electrochemistry of histidine and its metabolites based on the diazo coupling reaction. Talanta 49:319–330
Qiu S, Miao M, Wang T, Lin Z, Guo L, Qiu B, Chen G (2013) A fluorescent probe for detection of histidine in cellular homogenate and ovalbumin based on the strategy of clickchemistry. Biosens Bioelectron 42:332–336
Jones AL, Hulett MD, Parish CR (2005) Histidine-rich glycoprotein: A novel adaptor protein in plasma that modulates the immune, vascular and coagulation systems. Immunol Cell Biol 83:106–118
Ma DL, Wong WL, Chung WH, Chan FY, So PK, Lai TS, Zhou ZY, Leung YC, Wong KY (2008) A Highly Selective Luminescent Switch-On Probe for Histidine/Histidine-Rich Proteins and Its Application in Protein Staining. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:3735–3739
Watanabe M, Suliman ME, Qureshi AR, Garcia-Lopez E, Bárány P, Heimbürger O, Stenvinkel P, Lindholm B (2008) Consequences of low plasma histidine in chronic kidney disease patients: associations with inflammation, oxidative stress, and mortality. Am J Clin Nutr 87:1860–1866
Hermann K, Abeck D (2000) Determination of histidine and urocanic acid isomers in the human skin by high-performance capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr B 749:41–47
Hermann K, Abeck D (2001) Analysis of histidine and urocanic acid isomers by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 750:71–80
Amano M, Kobayashi N, Yabuta M, Uchiyama S, Fukui K (2014) Detection of Histidine Oxidation in a Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Gamma (IgG) 1 Antibody. Anal Chem 86:7536–7543
Chen Z, Liu J, Han Y, Zhu L (2006) A novel histidine assay using tetraphenylporphyrin manganese (III) chloride as a molecular recognition probe by resonance light scattering technique. Anal Chim Acta 570:109–115
Folmer-Andersen JF, Lynch VM, Anslyn EV (2005) “Naked-Eye” Detection of Histidine by Regulation of CuII Coordination Modes. Chem Eur J 11:5319–5326
Sun SK, Tu KX, Yan XP (2012) An indicator-displacement assay for naked-eye detection and quantification of histidine in human urine. Analyst 137:2124–2128
Lohar S, Banerjee A, Sahana A, Panja S, Hauli I, Mukhopadhyay SK, Das D (2014) Selective fluorescence and naked eye detection of histidine in aqueous medium via hydrogen bonding assisted Schiff base condensation. Tetrahedron Lett 55:174–176
Xu L, Xu Y, Zhu W, Zeng B, Yang C, Bin Wu B, Qian X (2011) Versatile trifunctional chemosensor of rhodamine derivative for Zn2+, Cu2+ and His/Cys in aqueous solution and living cells. Org Biomol Chem 9:8284–8287
Patel G, Menon S (2009) Recognition of lysine, arginine and histidine by novel p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene thiol functionalized gold nanoparticles in aqueous solution. Chem Commun 45:3563–3565
Xiong D, Chen M, Li H (2008) Synthesis of para-sulfonatocalix[4]arene-modified silver nanoparticles as colorimetric histidine probes. Chem Commun 44:880–882
Seo SH, Kim S, Han MS (2014) Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric chiral discrimination of histidine: application to determining the enantiomeric excess of histidine. Anal Methods 6:73–76
Zhang X, Kong X, Fan W, Du X (2011) Iminodiacetic Acid-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Optical Sensing of Myoglobin via Cu2+ Coordination. Langmuir 27:6504–6510
Li H, Bian Y (2009) Selective colorimetric sensing of histidine in aqueous solutions using cysteine modified silver nanoparticles in the presence of Hg2+. Nanotechnology 20:145502–145507
Kugimiya A, Takamitsu E (2013) Spectrophotometric detection of histidine and lysine using combined enzymatic reactions. Mater Sci Eng C 33:4867–4870
Zheng X, Yao T, Zhu Y, Shi S (2015) Cu2+ modulated silver nanoclusters as an on–off–on fluorescence probe for the selective detection of L-histidine. Biosens Bioelectron 66:103–108
Chen TT, Yin LY, Huang CS, Qin YQ, Zhu WP, Xu YF, Qian XH (2015) Highly selective “Off–On” fluorescent probe for histidine and its imaging in living cells. Biosens Bioelectron 66:259–265
Sun J, Yang F, Zhao D, Chen C, Yang X (2015) Integrated Logic Gate for Fluorescence Turn-on Detection of Histidine and Cysteine Based on Ag/Au Bimetallic Nanoclusters-Cu2+ Ensemble. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:6860–6866
Liu YR, Hu R, Liu T, Zhang XB, Tan W, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2013) Label-free dsDNA-Cu NPs-based fluorescent probe for highly sensitive detection of L-histidine. Talanta 107:402–407
Bian W, Wang F, Wei Y, Wang L, Liu Q, Dong W, Shuang SM, Choi MMF (2015) Doped zinc sulfide quantum dots based phosphorescence turn-off/on probe for detecting histidine in biological fluid. Anal Chim Acta 856:82–89
Un HL, Wu S, Huang CB, Xu Z, Xu L (2015) A naphthalimide-based fluorescent probe for highly selective detection of histidine in aqueous solution and its application in in vivo imaging. Chem Commun 51:3143–3146
Kim KY, Jung SH, Lee JH, Lee SS, Jung JH (2014) An imidazole-appended p-phenylene-Cu(II) ensemble as a chemoprobe for histidine in biological samples. Chem Commun 50:15243–15246
You Q, Lee AW, Chan W, Zhu X, Leung K (2014) A coumarin-based fluorescent probe for recognition of Cu2+ and fast detection of histidine in hard-to-transfect cells by a sensing ensemble approach. Chem Commun 50:6207–6210
He Y, Wang X, Zhu J, Zhong S, Song G (2012) Ni2+-modified gold nanoclusters for fluorescence turn-on detection of histidine in biological fluids. Analyst 137:4005–4009
Hu Y, Wang Q, Zheng C, Wu L, Hou X, Lv Y (2014) Recyclable Decoration of Amine-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles with Ni2+ for Determination of Histidine by Photochemical Vapor Generation Atomic Spectrometry. Anal Chem 86:842–848
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C, Li X, Rotello VM (2012) Gold Nanoparticles in Chemical and Biological Sensing. Chem Rev 112:2739–2779
Vilela D, González MC, Escarpa (2012) A Sensing colorimetric approaches based on gold and silver nanoparticles aggregation: Chemical creativity behind the assay. A review. Anal Chim Acta 751:24–43
Zamborini FP, Bao L, Dasari R (2012) Nanoparticles in Measurement Science. Anal Chem 84:541–576
Daniel MC, Astruc D (2004) Gold Nanoparticles: Assembly, Supramolecular Chemistry, Quantum-Size-Related Properties, and Applications toward Biology, Catalysis, and Nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104:293–346
Yao Y, Jie K, Zhou Y, Xue M (2014) Water-soluble pillar[6]arene stabilized silver nanoparticles: preparation and application in amino acid detection. Tetrahedron Lett 55:3195–3199
Song J, Wu F, Wan Y, Ma L (2015) Visual test for melamine using silver nanoparticles modified with chromotropic acid. Food Control 50:356–361
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21365014, 21505067), and Jiangxi Province Natural Science Foundation (JXNSF no. 20132BAB203011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 323 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, P., Li, J., Song, J. et al. Silver nanoparticles modified with sulfanilic acid for one-step colorimetric and visual determination of histidine in serum. Microchim Acta 183, 1865–1872 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1823-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1823-6