Abstract
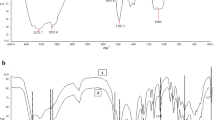
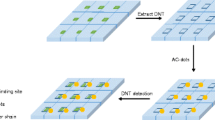
We are introducing functionalized carbon dots (C-dots) coated with a shell of molecularly imprinted sol-gel as a new tool in molecular imprint-based detection. Specifically, an imprint recognizing nicotinic acid (NA) was prepared in two steps. The first involves pyrolytic decomposition of citric acid in the presence of aminopropyltriethoxysilane to yield triethoxysilyl-modified C-dots with a typical size of 2.8 ± 1.1 nm. These are then polycondensed in the presence of tetraethoxysilane and NA at room temperature to give spherical silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) with a typical size of ~300 nm and containing C-dots and NA in the silica matrix. NA was then removed by extraction. The resulting SiNPs are well permeable to NA, photostable, display strong blue luminescence and can bind NA fairly selectively. The fluorometric detection scheme is based on the finding that increasing concentrations of NA quench the fluorescence of the C-dots in the SiNPs. NA can be determined by this method in the 0.5 to 10.5 μM concentration range, with a 12.6 nM detection limit. The composite was successfully utilized as a fluorescent probe for the determination of NA in spiked human urine samples. The method is believed to have a wider scope in being applicable to other analytes that are capable of quenching the fluorescence of C-dots.

A new type of nicotinic acid sensitive molecularly imprinted polymers functionalized carbon dots (SiNPs) were fabricated by the sol-gel polymerization. The composite was utilized as a fluorescent probe for the determination of nicotinic acid in human urine samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vlatakis G, Andersson LI, Muller R, Mosbach K (1993) Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature 361:645–647. doi:10.1038/361645a0
Ge Y, Turner AP (2008) Too large to fit? Recent developments in macromolecular imprinting. Trends Biotechnol 26(4):218–224. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2008.01.001
Wulff G (2013) Fourty years of molecular imprinting in synthetic polymers: origin, features and perspectives. Microchim Acta 180(15–16):1359–1370. doi:10.1007/s00604-013-0992-9
Gupta R, Kumar A (2008) Molecular imprinting in sol-gel matrix. Biotechnol Adv 26(6):533–547. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.07.002
Lim SY, Shen W, Gao ZQ (2015) Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:362–381. doi:10.1039/C4CS00269E
Shughart EL, Ahsan K, Detty MR, Bright FV (2006) Site selectively templated and tagged xerogels for chemical sensors. Anal Chem 78(9):3165–3170. doi:10.1021/ac060113m
Dai H, Xiao DL, He H, Li H, Yuan DH, Zhang C (2015) Synthesis and analytical applications of molecularly imprinted polymers on the surface of carbon nanotubes: a review. Microchim Acta. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1376-5
Lin CI, Joseph AK, Chang CK, Lee YD (2004) Synthesis and photoluminescence study of molecularly imprinted polymers appended onto CdSe/ZnS core-shells. Biosens Bioelectron 20(1):127–131. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2003.10.017
Lin HY, Ho MS, Lee MH (2009) Instant formation of molecularly imprinted poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol)/quantum dot composite nanoparticles and their use in one-pot urinalysis. Biosens Bioelectron 25(3):579–586. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2009.03.039
Wang HF, He Y, Ji TR, Yan XP (2009) Surface molecular imprinting on Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots for room-temperature phosphorescence optosensing of pentachlorophenol in water. Anal Chem 81(4):1615–1621. doi:10.1021/ac802375a
Mao Y, Bao Y, Han DX, Li FH, Niu L (2012) Efficient one-pot synthesis of molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres embedded carbon dots for fluorescent dopamine optosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 38(1):55–60. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2012.04.043
Carlson LA (2005) Nicotinic acid: the broad-spectrum lipid drug. A 50th anniversary review. J Intern Med 258(2):94–114. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2005.01528.x
Pfuhl P, Karcher U, Haring N, Baumeister A, Tawab MA, Schubert-Zsilavecz M (2005) Simultaneous determination of niacin, niacinamide and nicotinuric acid in human plasma. J Pharm Biomed Anal 36(5):1045–1052. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2004.08.033
Iwaki M, Murakami E, Kikuchi M, Wada A, Ogiso T, Oda Y, Kubo K, Kakehi K (1998) Simultaneous determination of nicotinic acid and its metabolites in rat urine by micellar electrokinetic chromatography with photodiode array detection. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 716(1–2):335–342. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(98)00327-2
HamanoT MY, Kojima N, Aoki N, Semma M, Ito Y, Oji Y (1995) Enzymic method for the amperometric determination of nicotinic acid in meat products. Analyst 120:135–138. doi:10.1039/AN9952000135
Taquchi K, Fukusaki E, Bamba T (2014) Determination of niacin and its metabolites using supercritical fluid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo) 3(1):A0029. doi:10.5702/massspectrometry.A0029
Wang F, Xie Z, Zhang H, Liu CY, Zhang YG (2011) Highly luminescent organosilane-functionalized carbon dots. Adv Funct Mater 21(6):1027–1031. doi:10.1002/adfm.201002279
Chen L, Xu S, Li J (2011) Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev 40:2922–2942. doi:10.1039/C0CS00084A
Ding CQ, Zhu AW, Tian Y (2014) Functional surface engineering of C-dots for fluorescent biosensing and in vivo bioimaging. Acc Chem Res 47(1):20–30. doi:10.1021/ar400023s
Zhu SJ, Meng QN, Wang L, Zhang JH, Song YB, Jin H, Zhang K, Sun HC, Wang HY, Yang B (2013) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew Chem 125(14):4045–4049. doi:10.1002/ange.201300519
Yang Y, Gao MY (2005) Preparation of fluorescent SiO2 particles with single CdTe nanocrystal cores by the reverse microemulsion method. Adv Mater 17(19):2354–2357. doi:10.1002/adma.200500403
Sun J, Zhuang JQ, Guan SW, Yang WS (2008) Synthesis of robust water-soluble ZnS:Mn/SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles. J Nanoparticle Res 10(4):653–658. doi:10.1007/s11051-007-9296-5
Dong YQ, Wang RX, Li GL, Chen CQ, Chi YW, Chen GN (2012) Polyamine-functionalized carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probes for selective and sensitive detection of copper ions. Anal Chem 84(14):6220–6224. doi:10.1021/ac3012126
Lunz M, Bradley AL, Chen WY, Gerard VA, Byrne SJ, Gun’ko YK, Lesnyak V, Gaponik N (2010) Influence of quantum dot concentration on förster resonant energy transfer in monodispersed nanocrystal quantum dot monolayers. Phys Rev B 81:201356. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.81.205316
Wang X, Fang Q, Liu S, Chen L (2012) Preparation of a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer with pseudo template for rapid simultaneous determination of cyromazine and melamine in bio-matrix samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 404(5):1555–1564. doi:10.1007/s00216-012-6200-7
Li HB, Li YL, Cheng J (2010) Molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres embedded CdSe quantum dots for highly selective and sensitive optosensing of pyrethroids. Chem Mater 22(8):2451–2457. doi:10.1021/cm902856y
Lakowicz J (2006) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Springer Science Business Media, New York
Backhus DA, Golini C, Castellanos E (2003) Evaluation of fluorescence quenching for assessing the importance of interactions between nonpolar organic pollutants and dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37(20):4717–4723. doi:10.1021/es026388a
Yao LD, Tang YW, Huang ZF (2007) Nicotinic acid voltammetric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer membrane-modified electrode. Anal Lett 40(4):677–688. doi:10.1080/00032710601017755
Capella-Peiró ME, Carda-Broch S, Monferrer-Pons L, Esteve-Romero J (2004) Micellar liquid chromatographic determination of nicotinic acid and nicotinamide after precolumn könig reaction derivatization. Anal Chim Acta 517(1–2):81–87. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2004.05.014
Zhang J, Chakraborty U, Foley JP (2009) Determination of residual cell culture media components by MEKC. Electrophoresis 30(22):3971–3977. doi:10.1002/elps.200900169
Saccani G, Tanzi E, Mallozzi S, Cavalli S (2005) Determination of niacin in fresh and dry cured pork products by ion chromatography: experimental design approach for the optimisation of nicotinic acid separation. Food Chem 92(2):373–379. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.10.007
Ciulu M, Solinas S, Floris I, Panzanelli A, Pilo MI, Piu PC, Spano N, Sanna G (2011) RP-HPLC determination of water-soluble vitamins in honey. Talanta 83(3):924–929. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2010.10.059
Liu M, Zhang D, Wang XL, Zhang LN, Han J, Yang M, Xiao X, Zhang YN, Liu HC (2012) Simultaneous quantification of niacin and its three main metabolites in human plasma by LC–MS/MS. J Chromatogr B 904:107–114. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.07.030
Graeff R, Lee HC (2002) A novel cycling assay for nicotinic acid–adenine dinucleotide phosphate with nanomolar sensitivity. Biochem J 367:163–168. doi:10.1042/BJ20020644
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Graduate Students Innovative Projects of Jiangsu Province (No.CXZZ12_0308). We thank the editors and co-workers for help and constructive suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 15855 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, P., Gao, J., Peng, J. et al. A sol-gel based molecular imprint incorporating carbon dots for fluorometric determination of nicotinic acid. Microchim Acta 183, 329–336 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1630-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1630-5