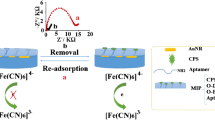
Abstract
We describe a method for the determination of cocaine that is based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of multiwalled carbon nanotubes, an ionic liquid, and chitosan. The electrode was made cocaine-responsive by immobilizing a cocaine-specific aptamer and platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs) on the modified electrode. The use of PtNPs resulted in the acceleration of the electron transfer kinetics of the reduction of the redox probe rutin and enhances sensitivity. The sensor, best operated at a working voltage of 260 mV vs. Ag/AgCl, has a linear response to cocaine in the 1 nM to 11 μM concentration range, and the detection limit is 100 pM (at an S/N ratio of 3). We think this strategy to represent a promising platform for the sensitive and selective determination of cocaine. The sensor is adequately stable and was successfully applied to the determination of cocaine in spiked serum.

We developed an electrochemical aptasensor for cocaine by using rutin as a redox probe. The MWCNTs/IL/Chit in nanocomposite was used as a unique platform for the covalent attachment of aptamer functionalized PtNPs. The LOD for cocaine detection is 100 pM.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346(6287):818–822
Wu ZS, Zheng F, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2009) A hairpin aptamer-based electrochemical biosensing platform for the sensitive detection of proteins. Biomaterials 30(15):2950–2955
Bai Y, Feng F, Yhao L, Wang C, Wang H, Tian M, Qin J, Duan Y, He X (2013) Aptamer/thrombin/aptamer-AuNPs sandwich enhanced surface plasmon resonance sensor for the detection of subnanomolar thrombin. Biosens Bioelectron 47(1):265–270
Zou X, Song S, Zhang J, Pan D, Wang L, Fan C (2007) A target-responsive electro-chemical aptamer switch (TREAS) for reagentless detection of nanomolar ATP. J Am Chem Soc 129(5):1042–1043
Kleinjung F, Klubmann S, Erdmann VA, Scheller FW, Furste JP, Bier FF (1998) High-affinity RNA as a recognition element in a biosensor. Anal Chem 70(2):328–331
Ferapontova EE, Olsen EM, Gothelf KV (2008) An RNA aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for detection of theophylline in serum. J Am Chem Soc 130(13):4256–4258
Radi AE, Acero Sanchez JL, Baldrich E, OSullivan CK (2006) Reagentless, reusable, ultrasensitive electrochemical molecular beacon aptasensor. J Am Chem Soc 128(1):117–124
Wilson DL, Martin R, Hong S, Cronin-Golomb M, Mirkin CA, Kaplan DL (2001) Surface organization and nanopatterning of collagen by dip-pen nanolithography. PNAS 98(24):13660–13664
Demers LM, Ginger DS, Park SJ, Li Z, Chung SW, Mirkin CA (2002) Direct patterning of modified oligonucleotides on metals and insulators by dip-pen nanolithography. Science 296(5574):1836–1838
Hayat A, Haider W, Rolland M, Marty JL (2013) Electrochemical grafting of long spacer arms of hexamethyldiamine on screen printed carbon electrode surface: application in target induced ochratoxin: a electrochemical aptasensor. Analyst 138:2951–2957
Abbaspour A, Norouz-Sarvestani F, Noori A, Soltani N (2015) Aptamer-conjugated silver nanoparticles for electrochemical dual-aptamer-based sandwich detection of staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron 68(1):149–155
Polsky R, Gill R, Kaganovsky L, Willner I (2006) Nucleic acid-functionalized Pt nanoparticles: catalytic labels for the amplified electrochemical detection of biomolecules. Anal Chem 78(7):2268–2271
Roushani M, Shahdost-fard F (2015) A highly selective and sensitive cocaine aptasensor based on covalent attachment of the aptamer-functionalized AuNPs onto nanocomposite as the support platform. Anal Chim Acta 853(1):214–221
Dhar S, Gu FX, Langer R, Farokhzad OC, Lippard SJ (2008) Targeted delivery of cisplatin to prostate cancer cells by aptamer functionalized Pt (IV) prodrug-PLGA-PEG nanoparticles. PNAS 105(45):17356–17361
Huang YF, Chang HT, Tan W (2008) Cancer cell targeting using multiple aptamers conjugated on nanorods. Anal Chem 80(3):567–572
Kwon SJ, Bard AJ (2012) DNA analysis by application of Pt nanoparticle electrochemical amplification with single label response. J Am Chem Soc 134(26):10777–10779
Shahdost-fard F, Salimi A, Khezrian S (2014) Highly selective and sensitive adenosine aptasensor based on platinum nanoparticles as catalytical label for amplified detection of biorecognition events through H2O2 reduction. Biosens Bioelectron 53(1):355–362
Schlesinger HL (1985) Topics in the chemistry of cocaine. Bull Narc 35(1):63–78
Bravo L (1998) Polyphenols: chemistry, dietary sources, metabolism, and nutritional significance. Nutr Rev 56:317–331
Zoulis NE (1996) Preconcentration at a carbon-paste electrode and determination by adsorptive-stripping voltammetry of rutin and other flavonoids. Anal Chim Acta 320(2–3):255–261
Kang J, Lu X, Zeng H, Liu H, Lu B (2002) Investigation on the electrochemistry of rutin and its analytical application. Anal Lett 35(4):677–686
Hendrickson HP, Sahafayen M, Bell MA, Kaufman AD, Hadwiger ME, Lunte CE (1994) Relationship of flavonoid oxidation potential and effect on rat hepatic microsomal metabolism of benzene and phenol. J Pharm Biomed Anal 12(3):335–341
Shahdost-fard F, Salimi A, Sharifi E, Korani A (2013) Fabrication of a highly sensitive adenosine aptasensor based on covalent attachment of aptamer onto chitosan-carbon nanotubes-ionic liquid nanocomposite. Biosens Bioelectron 48(1):100–107
Went Y, Pei H, Wan Y, Su Y, Huang Q, Song S, Fan C (2011) DNA nanostructure-decorated surfaces for enhanced aptamer-target binding and electrochemical cocaine sensors. Anal Chem 83(19):7418–7423
Golub SK, Freeman G, Zhang R, Willner H (2009) Electrochemical, photoelectrochemical, and surface plasmon resonance detection of cocaine using supramolecular aptamer complexes and metallic or semiconductor nanoparticles. Anal Chem 81(22):9291–9298
Jiang B, Wang M, Chen Y, Xie J, Xiang Y (2012) Biosens Bioelectron 32(1):305–308
Hua M, Tao M, Wang P, Zhang Y, Wu Z, Chang Y, Yang Y (2010) Label-free electrochemical cocaine aptasensor based on a target-inducing aptamer switching conformation. Anal Sci 26(12):1265–1270
Du Y, Chin C, Yin J, Li B, Zhou M, Dong S, Wang E (2010) Solid-state probe based electrochemical aptasensor for cocaine: a potentially convenient, sensitive, repeatable, and integrated sensing platform for drugs. Anal Chem 82(4):1556–1563
Zhang DW, Sun CJ, Zhang FT, Xu L, Zhou YL, Zhang XX (2012) An electrochemical aptasensor based on enzyme linked aptamer assay. Biosens Bioelectron 31(1):363–368
He JL, Yang YF, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2011) Electrochemical aptameric sensor based on the Klenow fragment polymerase reaction for cocaine detection. Biosens Bioelectron 26(10):4222–4226
Swensen JS, Xiao Y, Ferguson BS, Lubin AA, Lai RY, Heeger AJ, Plaxco WK, Soh HT (2009) Continuous, real time monitoring of cocaine in undiluted blood serum via a microfluidic, electrochemical aptamer-based sensor. J Am Chem Soc 131(12):4246–4266
Sheng Q, Liu R, Zhang S, Zheng J (2014) Ultrasensitive electrochemical cocaine biosensor based on reversible DNA nanostructure. Biosens Bioelectron 51(1):191–194
Acknowledgments
Presented work was supported by the grants from Ilam University of Iran. The authors would like to thank the Center of Narcotics and the Iranian Ministry of Sanitation for supplying some of the analgesic and narcotic drugs. Faeze Shahdost-fard also thanks Ilam University for her Ph.D course.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1.82 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roushani, M., Shahdost-fard, F. An aptasensor for voltammetric and impedimetric determination of cocaine based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with platinum nanoparticles and using rutin as a redox probe. Microchim Acta 183, 185–193 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1604-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1604-7