Abstract
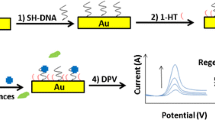
We describe a biosensor for dopamine that is based on the use of a gold electrode modified with carbon nanoparticles (CNPs) coupled to thionine labeled gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) acting as signal amplifiers. The biosensor was constructed by first modifying the CNPs on the gold electrode and adsorbing the thionine on the surface of the AuNPs, and then linking the complementary strand of the dopamine aptamer to the AuNPs via gold-thiol chemistry. Next, dopamine aptamer is added and the duplex is formed on the surface. On addition of a sample containing dopamine, it will interact with aptamer and cause the release of the electrochemical probe which then will be adsorbed on the surface of the CNP-modified gold electrode and detected by differential pulse voltammetry. The current is linearly related to the concentration of dopamine in the 30 nM to 6.0 μM ranges. The detection limit is as low as 10 nM, and the RSD is 3.1 % at a 0.3 μM level (for n = 11). The protocol was successfully applied to the determination of dopamine in spiked human urine samples. We perceive that this method holds promise as a widely applicable platform for aptamer-based electrochemical detection of small molecules.

The aptamer-based sensor for dopamine is based on the use of a gold electrode modified with carbon and gold nanoparticles for signal amplification.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wightman RM, Amatore C, Engstrom RC, Hale PD, Kristensen EW, Kuhr WG, May LJ (1988) Real-time characterization of dopamine overflow and uptake in the rat striatum. Neuroscience 25(2):513–523
Sanghavi BJ, Wolfbeis OS, Hirsch T, Swami NS (2015) Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensing of neurological drugs and neurotransmitters. Microchim Acta 182:1–43
Yang X, Feng B, He X, Li F, Ding Y, Fei J (2013) Carbon nanomaterial based electrochemical sensors for biogenic amines. Microchim Acta 180(11–12):935–956
Velasco M, Luchsinger A (1998) Dopamine: pharmacologic and therapeutic aspects. Am J Ther 5(1):37–43
Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR (2011) The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 63(1):182–217
Jankovic J (2008) Parkinson’s disease: clinical features and diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79(4):368–376
Venton BJ, Wightman RM (2003) Psychoanalytical Electrochemistry: Dopamine and Behavior. Anal Chem 75(19):414 A–421 A
Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessel TM (2000) Principles of Neural Science, 4th edn. York, New
Reinhoud NJ, Brouwer HJ, van Heerwaarden LM, Korte-Bouws GA (2013) Analysis of glutamate, GABA, noradrenaline, dopamine, serotonin, and metabolites using microbore UHPLC with electrochemical detection. ACS Chem Neurosci 4(5):888–894
Cui R, Gu YP, Bao L, Zhao JY, Qi BP, Zhang ZL, Xie ZX, Pang DW (2012) Near-infrared electrogenerated chemiluminescence of ultrasmall Ag2Se quantum dots for the detection of dopamine. Anal Chem 84(21):8932–8935
Wang Y, Chen H (2005) Integrated capillary electrophoresis amperometric detection microchip with replaceable microdisk working electrode. II. Influence of channel cross-sectional area on the separation and detection of dopamine and catechol. J Chromatogr A 1080(2):192–198
Shou M, Ferrario CR, Schultz KN, Robinson TE, Kennedy RT (2006) Monitoring dopamine in vivo by microdialysis sampling and on-line CE-laser-induced fluorescence. Anal Chem 78(19):6717–6725
Baron R, Zayats M, Willner I (2005) Dopamine-, L-DOPA-, adrenaline-, and noradrenaline-induced growth of Au nanoparticles: assays for the detection of neurotransmitters and of tyrosinase activity. Anal Chem 77(6):1566–1571
Zheng Y, Wang Y, Yang X (2011) Aptamer-based colorimetric biosensing of dopamine using unmodified gold nanoparticles. Sens Actuators B 156(1):95–99
Fabregat G, Armelin E, Aleman C (2014) Selective detection of dopamine combining multilayers of conducting polymers with gold nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 118(17):4669–4682
Zhou J, Wang W, Yu P, Xiong E, Zhang X, Chen J (2014) A simple label-free electrochemical aptasensor for dopamine detection. RSC Advances 4(94):52250–52255
Hartman MR, Yang D, Tran TN, Lee K, Kahn JS, Kiatwuthinon P, Yancey KG, Trotsenko O, Minko S, Luo D (2013) Thermostable branched DNA nanostructures as modular primers for polymerase chain reaction. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(33):8699–8702
Wen Y, Xu Y, Mao X, Wei Y, Song H, Chen N, Huang Q, Fan C, Li D (2012) DNAzyme-based rolling-circle amplification DNA machine for ultrasensitive analysis of microRNA in Drosophila larva. Anal Chem 84(18):7664–7669
Russell C, Welch K, Jarvius J, Cai Y, Brucas R, Nikolajeff F, Svedlindh P, Nilsson M (2014) Gold nanowire based electrical DNA detection using rolling circle amplification. ACS Nano 8(2):1147–1153
Dhama K, Karthik K, Chakraborty S, Tiwari R, Kapoor S, Kumar A, Thomas P (2014) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA (LAMP): a new diagnostic tool lights the world of diagnosis of animal and human pathogens: a review. Pak J Biol Sci 17(2):151–166
Zhou W, Gong X, Xiang Y, Yuan R, Chai Y (2014) Target-triggered quadratic amplification for label-free and sensitive visual detection of cytokines based on hairpin aptamer DNAzyme probes. Anal Chem 86(1):953–958
Hun X, Liu F, Mei Z, Ma L, Wang Z, Luo X (2013) Signal amplified strategy based on target-induced strand release coupling cleavage of nicking endonuclease for the ultrasensitive detection of ochratoxin A. Biosens Bioelectron 39(1):145–151
Joneja A, Huang X (2011) Linear nicking endonuclease-mediated strand-displacement DNA amplification. Anal Biochem 414(1):58–69
Huang YF, Liu H, Xiong X, Chen Y, Tan W (2009) Nanoparticle-mediated IgE-receptor aggregation and signaling in RBL mast cells. J Am Chem Soc 131(47):17328–17334
Fang Y, Guo S, Li D, Zhu C, Ren W, Dong S, Wang E (2012) Easy synthesis and imaging applications of cross-linked green fluorescent hollow carbon nanoparticles. ACS Nano 6(1):400–409
Liu J, Li J, Jiang Y, Yang S, Tan W, Yang R (2011) Combination of [small pi]-[small pi] stacking and electrostatic repulsion between carboxylic carbon nanoparticles and fluorescent oligonucleotides for rapid and sensitive detection of thrombin. Chem Commun 47(40):11321–11323
Ding Y, Zhang X, Liu X, Guo R (2006) Adsorption characteristics of thionine on gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 22(5):2292–2298
Wang W, Xu G, Cui XT, Sheng G, Luo X (2014) Enhanced catalytic and dopamine sensing properties of electrochemically reduced conducting polymer nanocomposite doped with pure graphene oxide. Biosens Bioelectron 58:153–156
Weaver CL, Li H, Luo X, Cui XT (2014) A graphene oxide/conducting polymer nanocomposite for electrochemical dopamine detection: origin of improved sensitivity and specificity. J Mater Chem B 2(32):5209–5219
Khoobi A, Ghoreishi SM, Behpour M, Masoum S (2014) Three-dimensional voltammetry: a chemometrical analysis of electrochemical data for determination of dopamine in the presence of unexpected interference by a biosensor based on gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem 86(18):8967–8973
Palanisamy S, Ku S, Chen S-M (2013) Dopamine sensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with a reduced graphene oxide and palladium nanoparticles composite. Microchim Acta 180(11–12):1037–1042
Xiangzhao A, Qiang M, Xingguang S (2013) Nanosensor for dopamine and glutathione based on the quenching and recovery of the fluorescence of silica-coated quantum dots. Microchim Acta 180(3–4):269–277
Zhao W, Wang K, Wei Y, Ma Y, Liu L, Huang X (2014) Laccase Biosensor Based on Phytic Acid Modification of Nanostructured SiO2 Surface for Sensitive Detection of Dopamine. Langmuir 30(37):11131–11137
Huang Y, Miao YE, Ji S, Tjiu WW, Liu T (2014) Electrospun carbon nanofibers decorated with Ag-Pt bimetallic nanoparticles for selective detection of dopamine. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(15):12449–12456
Fabregat G, Estrany F, Casas MT, Aleman C, Armelin E (2014) Detection of dopamine using chemically synthesized multilayered hollow microspheres. J Phys Chem B 118(17):4702–4709
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Scientific and Technical Development Project of Qingdao (12-1-4-3-(18)-jch), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21275085, 21305073), the Taishan Scholar Program of Shandong Province, the Open Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Jiangnan University (SKLF-KF-201112), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2012G0020221, ZR2014JL013) and the Scientific Research Startup Foundation of Qingdao University of Science and Technology for Talents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 114 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Hun, X., Liu, F. et al. Aptamer biosensor for dopamine based on a gold electrode modified with carbon nanoparticles and thionine labeled gold nanoparticles as probe. Microchim Acta 182, 1797–1802 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1509-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1509-5