Abstract
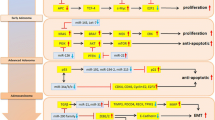
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small, endogenous, non-coding, single-stranded RNAs that act as post-transcriptional regulators. Their discovery has provided new avenues for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. The expression of both oncogenic and tumor suppressor miRNAs can be aberrantly either up- or down-regulated in cancer cells. These miRNAs target mRNAs of genes that either promote or inhibit tumor growth, and are one of several epigenetic factors that control the initiation and progression of colorectal cancer (CRC) and other cancers. Investigations of miRNAs as CRC biomarkers have employed the expression profiling of traditional tissue samples and, more recently, non-invasive samples, such as feces and body fluids, have been analyzed. MiRNAs may also be able to predict responses to chemo- and radiotherapy, and may be manipulated to modify CRC characteristics. We herein discuss the use of circulating miRNAs as possible non-invasive biomarkers of early CRC onset, relapse, or response to treatment. We also discuss the obstacles that currently limit the routine use of epigenetic biomarkers in clinical settings.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29.
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917.
Matsuda T, Marugame T, Kamo K, Katanoda K, Ajiki W, Sobue T. Cancer incidence and incidence rates in Japan in 2005: based on data from 12 population-based cancer registries in the Monitoring of Cancer Incidence in Japan (MCIJ) project. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2011;41:139–47.
Pfister DG, Benson AB 3rd, Somerfield MR. Clinical practice. Surveillance strategies after curative treatment of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2375–82.
Shaukat A, Mongin SJ, Geisser MS, Lederle FA, Bond JH, Mandel JS, et al. Long-term mortality after screening for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1106–14.
Graser A, Stieber P, Nagel D, Schafer C, Horst D, Becker CR, et al. Comparison of CT colonography, colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy and faecal occult blood tests for the detection of advanced adenoma in an average risk population. Gut. 2009;58:241–8.
Mandel JS, Bond JH, Church TR, Snover DC, Bradley GM, Schuman LM, et al. Reducing mortality from colorectal cancer by screening for fecal occult blood. Minnesota Colon Cancer control study. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1365–71.
Ouyang DL, Chen JJ, Getzenberg RH, Schoen RE. Non-invasive testing for colorectal cancer: a review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100:1393–403.
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–54.
Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;75:855–62.
Hoshino I, Matsubara H. MicroRNAs in cancer diagnosis and therapy: from bench to bedside. Surg Today. 2013;43:467–78.
Siomi H, Siomi MC. Posttranscriptional regulation of microRNA biogenesis in animals. Mol Cell. 2010;38:323–32.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–69.
Mendell JT, Olson EN. MicroRNAs in stress signaling and human disease. Cell. 2012;148:1172–87.
Taft RJ, Pang KC, Mercer TR, Dinger M, Mattick JS. Non-coding RNAs: regulators of disease. J Pathol. 2010;220:126–39.
Cortez MA, Bueso-Ramos C, Ferdin J, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK, Calin GA. MicroRNAs in body fluids—the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8:467–77.
Slaby O, Svoboda M, Michalek J, Vyzula R. MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer: translation of molecular biology into clinical application. Mol Cancer. 2009;8:102.
Nagel R, le Sage C, Diosdado B, van der Waal M, Oude Vrielink JA, Bolijn A, et al. Regulation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene by the miR-135 family in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68:5795–802.
Necela BM, Carr JM, Asmann YW, Thompson EA. Differential expression of microRNAs in tumors from chronically inflamed or genetic (APC(Min/+)) models of colon cancer. PLoS One. 2011;6:e18501.
Wang X, Lam EK, Zhang J, Jin H, Sung JJ. MicroRNA-122a functions as a novel tumor suppressor downstream of adenomatous polyposis coli in gastrointestinal cancers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;387:376–80.
Feng Z, Zhang C, Wu R, Hu W. Tumor suppressor p53 meets microRNAs. J Mol Cell Biol. 2011;3:44–50.
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan Z, Liang Y, et al. A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature. 2007;447:1130–4.
Kalluri R, Weinberg RA. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:1420–8.
Cottonham CL, Kaneko S, Xu L. miR-21 and miR-31 converge on TIAM1 to regulate migration and invasion of colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:35293–302.
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, et al. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:2128–36.
Yu Y, Kanwar SS, Patel BB, Oh PS, Nautiyal J, Sarkar FH, et al. MicroRNA-21 induces stemness by downregulating transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (TGFbetaR2) in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33:68–76.
Heusschen R, van Gink M, Griffioen AW, Thijssen VL. MicroRNAs in the tumor endothelium: novel controls on the angioregulatory switchboard. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1805:87–96.
Sundaram P, Hultine S, Smith LM, Dews M, Fox JL, Biyashev D, et al. p53-responsive miR-194 inhibits thrombospondin-1 and promotes angiogenesis in colon cancers. Cancer Res. 2011;71:7490–501.
Xu Q, Liu LZ, Qian X, Chen Q, Jiang Y, Li D, et al. MiR-145 directly targets p70S6K1 in cancer cells to inhibit tumor growth and angiogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:761–74.
Lawler J. Thrombospondin-1 as an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. J Cell Mol Med. 2002;6:1–12.
Dews M, Homayouni A, Yu D, Murphy D, Sevignani C, Wentzel E, et al. Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA cluster. Nat Genet. 2006;38:1060–5.
Michael MZ, SM OC, van Holst Pellekaan NG, Young GP, James RJ. Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1:882–91.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:2257–61.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:10513–8.
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008;18:997–1006.
Zhu W, Qin W, Atasoy U, Sauter ER. Circulating microRNAs in breast cancer and healthy subjects. BMC Res Notes. 2009;2:89.
Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, Ruf IK, Pritchard CC, Gibson DF, et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:5003–8.
Turchinovich A, Weiz L, Langheinz A, Burwinkel B. Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:7223–33.
Vickers KC, Remaley AT. Lipid-based carriers of microRNAs and intercellular communication. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2012;23:91–7.
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:654–9.
Creemers EE, Tijsen AJ, Pinto YM. Circulating microRNAs: novel biomarkers and extracellular communicators in cardiovascular disease? Circ Res. 2012;110:483–95.
Fabbri M. miRNAs as molecular biomarkers of cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2010;10:435–44.
Chen X, Liang H, Zhang J, Zen K, Zhang CY. Secreted microRNAs: a new form of intercellular communication. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22:125–32.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–8.
Lodes MJ, Caraballo M, Suciu D, Munro S, Kumar A, Anderson B. Detection of cancer with serum miRNAs on an oligonucleotide microarray. PLoS One. 2009;4:e6229.
Ng EK, Chong WW, Jin H, Lam EK, Shin VY, Yu J, et al. Differential expression of microRNAs in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: a potential marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut. 2009;58:1375–81.
Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, Peng Z, Sheng W, Du X. Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:118–26.
Wang Q, Huang Z, Ni S, Xiao X, Xu Q, Wang L, et al. Plasma miR-601 and miR-760 are novel biomarkers for the early detection of colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7:e44398.
Giraldez MD, Lozano JJ, Ramirez G, Hijona E, Bujanda L, Castells A, et al. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of colorectal cancer: results from a genome-wide profiling and validation study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11(681–8):e3.
Wang P, Zou F, Zhang X, Li H, Dulak A, Tomko RJ Jr, et al. microRNA-21 negatively regulates Cdc25A and cell cycle progression in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009;69:8157–65.
Kanaan Z, Rai SN, Eichenberger MR, Roberts H, Keskey B, Pan J, et al. Plasma miR-21: a potential diagnostic marker of colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 2012;256:544–51.
Liu GH, Zhou ZG, Chen R, Wang MJ, Zhou B, Li Y, et al. Serum miR-21 and miR-92a as biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:2175–81.
Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Hur K, Nagasaka T, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, et al. Serum miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:849–59.
Baraniskin A, Nopel-Dunnebacke S, Ahrens M, Jensen SG, Zollner H, Maghnouj A, et al. Circulating U2 small nuclear RNA fragments as a novel diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic and colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:E48–57.
Wang S, Xiang J, Li Z, Lu S, Hu J, Gao X, et al. A plasma microRNA panel for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:152–61.
Wang J, Huang SK, Zhao M, Yang M, Zhong JL, Gu YY, et al. Identification of a circulating microRNA signature for colorectal cancer detection. PLoS One. 2014;9:e87451.
Hofsli E, Sjursen W, Prestvik WS, Johansen J, Rye M, Trano G, et al. Identification of serum microRNA profiles in colon cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:1712–9.
Kanaan Z, Roberts H, Eichenberger MR, Billeter A, Ocheretner G, Pan J, et al. A plasma microRNA panel for detection of colorectal adenomas: a step toward more precise screening for colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 2013;258:400–8.
Haller DG. An overview of adjuvant therapy for colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:1255–63.
Wein A, Hahn EG, Merkel S, Hohenberger W. Adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II (Dukes B) colon cancer: too early for routine use. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2000;26:730–2.
Figueredo A, Charette ML, Maroun J, Brouwers MC, Zuraw L. Adjuvant therapy for stage II colon cancer: a systematic review from the Cancer Care Ontario Program in evidence-based care’s gastrointestinal cancer disease site group. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3395–407.
Gill S, Loprinzi CL, Sargent DJ, Thome SD, Alberts SR, Haller DG, et al. Pooled analysis of fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy for stage II and III colon cancer: who benefits and by how much? J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1797–806.
Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U, Schmalhofer O, Vincan E, Spaderna S, et al. A reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep. 2008;9:582–9.
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC, Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A, et al. The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:1487–95.
Hur K, Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Balaguer F, Nagasaka T, Koike J, et al. MicroRNA-200c modulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human colorectal cancer metastasis. Gut. 2013;62:1315–26.
Toiyama Y, Hur K, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, Kusunoki M, Boland CR, et al. Serum miR-200c is a novel prognostic and metastasis-predictive biomarker in patients with colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 2014;259:735–43.
Cheng H, Zhang L, Cogdell DE, Zheng H, Schetter AJ, Nykter M, et al. Circulating plasma MiR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS One. 2011;6:e17745.
Menendez P, Padilla D, Villarejo P, Palomino T, Nieto P, Menendez JM, et al. Prognostic implications of serum microRNA-21 in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2013;108:369–73.
Pu XX, Huang GL, Guo HQ, Guo CC, Li H, Ye S, et al. Circulating miR-221 directly amplified from plasma is a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker of colorectal cancer and is correlated with p53 expression. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;25:1674–80.
Yang IP, Tsai HL, Huang CW, Huang MY, Hou MF, Juo SH, et al. The functional significance of microRNA-29c in patients with colorectal cancer: a potential circulating biomarker for predicting early relapse. PLoS One. 2013;8:e66842.
Wang LG, Gu J. Serum microRNA-29a is a promising novel marker for early detection of colorectal liver metastasis. Cancer Epidemiol. 2012;36:e61–7.
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2335–42.
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, et al. Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:337–45.
Poston GJ, Figueras J, Giuliante F, Nuzzo G, Sobrero AF, Gigot JF, et al. Urgent need for a new staging system in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4828–33.
Chen Q, Xia HW, Ge XJ, Zhang YC, Tang QL, Bi F. Serum miR-19a predicts resistance to FOLFOX chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer cases. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:7421–6.
Kjersem JB, Ikdahl T, Lingjaerde OC, Guren T, Tveit KM, Kure EH. Plasma microRNAs predicting clinical outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients receiving first-line oxaliplatin-based treatment. Mol Oncol. 2014;8:59–67.
Takahashi M, Cuatrecasas M, Balaguer F, Hur K, Toiyama Y, Castells A, et al. The clinical significance of MiR-148a as a predictive biomarker in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7:e46684.
Rasmussen MH, Jensen NF, Tarpgaard LS, Qvortrup C, Romer MU, Stenvang J, et al. High expression of microRNA-625-3p is associated with poor response to first-line oxaliplatin based treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Mol Oncol. 2013;7:637–46.
Zhang J, Zhang K, Bi M, Jiao X, Zhang D, Dong Q. Circulating microRNA expressions in colorectal cancer as predictors of response to chemotherapy. Anticancer Drugs. 2014;25:346–52.
Guo L, Yang Q, Lu J, Li H, Ge Q, Gu W, et al. A comprehensive survey of miRNA repertoire and 3′ addition events in the placentas of patients with pre-eclampsia from high-throughput sequencing. PLoS One. 2011;6:e21072.
Lee LW, Zhang S, Etheridge A, Ma L, Martin D, Galas D, et al. Complexity of the microRNA repertoire revealed by next-generation sequencing. RNA. 2010;16:2170–80.
Llorens F, Banez-Coronel M, Pantano L, del Rio JA, Ferrer I, Estivill X, et al. A highly expressed miR-101 isomiR is a functional silencing small RNA. BMC Genom. 2013;14:104.
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A, et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell. 2007;129:1401–14.
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;110:13–21.
Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS, Tewari M. Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods. 2010;50:298–301.
Pritchard CC, Kroh E, Wood B, Arroyo JD, Dougherty KJ, Miyaji MM, et al. Blood cell origin of circulating microRNAs: a cautionary note for cancer biomarker studies. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2012;5:492–7.
Kirschner MB, Kao SC, Edelman JJ, Armstrong NJ, Vallely MP, van Zandwijk N, et al. Haemolysis during sample preparation alters microRNA content of plasma. PLoS One. 2011;6:e24145.
Torres A, Torres K, Wdowiak P, Paszkowski T, Maciejewski R. Selection and validation of endogenous controls for microRNA expression studies in endometrioid endometrial cancer tissues. Gynecol Oncol. 2013;130:588–94.
Meyer SU, Pfaffl MW, Ulbrich SE. Normalization strategies for microRNA profiling experiments: a ‘normal’ way to a hidden layer of complexity? Biotechnol Lett. 2010;32:1777–88.
Wotschofsky Z, Meyer HA, Jung M, Fendler A, Wagner I, Stephan C, et al. Reference genes for the relative quantification of microRNAs in renal cell carcinomas and their metastases. Anal Biochem. 2011;417:233–41.
Schaefer A, Jung M, Miller K, Lein M, Kristiansen G, Erbersdobler A, et al. Suitable reference genes for relative quantification of miRNA expression in prostate cancer. Exp Mol Med. 2010;42:749–58.
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 2004;64:5245–50.
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, et al. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002;3:RESEARCH0034.
McDonald JS, Milosevic D, Reddi HV, Grebe SK, Algeciras-Schimnich A. Analysis of circulating microRNA: preanalytical and analytical challenges. Clin Chem. 2011;57:833–40.
Jones K, Nourse JP, Keane C, Bhatnagar A, Gandhi MK. Plasma microRNA are disease response biomarkers in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:253–64.
Day E, Dear PH, McCaughan F. Digital PCR strategies in the development and analysis of molecular biomarkers for personalized medicine. Methods. 2013;59:101–7.
Ho SL, Chan HM, Wong RN, Li HW. Self-assembling protein platform for direct quantification of circulating microRNAs in serum with total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy. Anal Chim Acta. 2014;823:61–8.
Cho WC. Circulating MicroRNAs as Minimally Invasive Biomarkers for Cancer Theragnosis and Prognosis. Front Genet. 2011;2:7.
Sturgeon CM, Hoffman BR, Chan DW, Ch’ng SL, Hammond E, Hayes DF, et al. National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory Medicine Practice Guidelines for use of tumor markers in clinical practice: quality requirements. Clin Chem. 2008;54:e1–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toiyama, Y., Tanaka, K., Inoue, Y. et al. Circulating cell-free microRNAs as biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Surg Today 46, 13–24 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-015-1138-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-015-1138-y