Abstract
Objective
Hypoglycemia is common in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). We aimed to update the incidence of severe and symptomatic hypoglycemia and investigate several correlated factors.
Methods
In this multicenter, observational retrospective study, the data of 206 T1DM patients from a sample of 2,229 consecutive patients seen at 18 diabetes clinics were analyzed. Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, severe hypoglycemia in the past 12 months, and symptomatic hypoglycemia in the past 4 weeks were recorded with a self-report questionnaire and a clinical form during a routine visit. Poisson multivariate models were applied.
Results
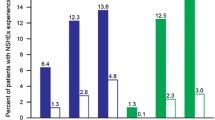
A minority of patients accounted for the majority of both severe and symptomatic episodes. The incidence rate (IR) of severe hypoglycemia was 0.49 (0.40–0.60) events/person-years. The incidence rate ratio (IRR) was higher in patients with previous severe hypoglycemia (3.71; 2.28–6.04), neuropathy (4.16; 2.14–8.05), long duration (>20 years, 2.96; 1.60–5.45), and on polypharmacy (1.24; 1.13–1.36), but it was lower when a complication was present. The IR of symptomatic hypoglycemia was 53.3 events/person-years, with an IRR significantly higher among women or patients with better education, or shorter duration or on pumps. The IRR was lower in patients with higher BMI or neuropathy or aged more than 50 years.
Conclusions
Fewer than 20 % of T1DM patients are free from hypoglycemia, with one in six having experienced at least one severe episode in the last year. The distribution is uneven, with a tendency of episodes to cluster in some patients. Severe and symptomatic episodes have different correlates and reflect different conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cryer PE (2008) The barrier of hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes 57(12):3169–3176
Briscoe VJ, Davis SN (2006) Hypoglycemia in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: physiology, pathophysiology, and management. Clin Diabetes 24(3):115–121
The DCCT Research Group (1991) Epidemiology of severe hypoglycemia in the diabetes control and complications trial. Am J Med 90(4):450–459
The DCCT Research Group (1997) Hypoglycemia in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes 46:271–286
Beck RW, Hirsch IB, Laffel L, Tamborlane WV, Bode BW, Buckingham B, Chase P, Clemons R, Fiallo-Scharer R, Fox LA, Gilliam LK, Huang ES, Kollman C, Kowalski AJ, Lawrence JM, Lee J, Mauras N, O’Grady M, Ruedy KJ, Tansey M, Tsalikian E, Weinzimer SA, Wilson DM, Wolpert H, Wysocki T, Xing D (2009) The effect of continuous glucose monitoring in well-controlled type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 32(8):1378–1383. doi:10.2337/dc09-0108
Donnelly LA, Morris AD, Frier BM, Ellis JD, Donnan PT, Durrant R et al (2005) Frequency and predictors of hypoglycemia in type 1 and insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a population based study. Diabet Med 22(6):749–755
Heller SR, Choudhary P, Davies C, Emery C, Campbell MJ et al (2007) Risk of hypoglycaemia in types 1 and 2 diabetes: effects of treatment modalities and their duration. Diabetologia 50(6):1140–1147
Pedersen-Bjergaard U, Pramming S, Thorsteinsson B (2003) Recall of severe hypoglycaemia and self-estimated state of awareness in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 19(3):232–240
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF III, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Greene T, Coresh J, CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) (2009) A New Equation to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate. Ann Intern Med 150(9):604–612
Giorda CB, Ozzello A, Gentile S, Corsi A, Iannarelli R, Baccetti F, Lucisano G, Nicolucci A, Rossi MC (2014) On behalf the HYPOS-1 study group. incidence and correlates of hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes. The hypos-1 study. J Diabetes Metab 5:3. doi:10.4172/2155-6156.1000344
ter Braak EW, Appelman AM, van de Laak M, Stolk RP, van Haeften TW, Erkelens DW (2000) Clinical characteristics of type 1 diabetic patients with and without severe hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 23(10):1467–1471
The DCCT Research Group (1993) The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long term complication in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 329:977–986
Hepburn DA, MacLeod KM, Pell AC, Scougal IJ, Frier BM (1993) Frequency and symptoms of hypoglycaemia experienced by patients with type 2 diabetes treated with insulin. Diabet Med 10:231–237
Pedersen-Bjergaard U, Kristensen PL, Beck-Nielsen H, Nørgaard K, Perrild H, Christiansen JS, Jensen T, Hougaard P, Parving HH, Thorsteinsson B, Tarnow L (2014) Effect of insulin analogues on risk of severe hypoglycaemia in patients with type 1 diabetes prone to recurrent severe hypoglycaemia (HypoAna trial): a prospective, randomised, open-label, blinded-endpoint crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2(7):553–561
Amiel SA, Maran A, Powrie JK, Umpleby AM, MacDonald IA (1993) Gender differences in counterregulation to hypoglycemia. Diabetologia 36:460–464
Davis SN, Goldstein RE, Price L, Jacobs J, Cherringon AD (1993) The effects of insulin on the counterregulatory response to equivalent hypoglycaemia in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 77:1300–1307
Diamond MP, Jones T, Caprio S, Hallarman L, Diamond MC, Addabbo M, Tamborlane WV, Sherwin RS (1993) Gender influences counterregulatory hormone responses to hypoglycemia. Metabolism 42:1568–1572
Davis SN, Fowler S, Costa F (2000) Hypoglycemic counterregulatory responses differ between men and women with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 49:65–72
Sandoval DA, Ertl AC, Richardson MA, Tate DB, Davis SN (2003) Estrogen blunts neuroendocrine and metabolic responses to hypoglycemia. Diabetes 52:1749–1755
Cherubini V, Pintaudi B, Rossi MC, Lucisano G, Pellegrini F, Chiumello G, Frongia AP, Monciotti C, Patera IP, Toni S, Zucchini S (2014) Nicolucci A; SHIP-D Study Group. Severe hypoglycemia and ketoacidosis over one year in Italian pediatric population with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a multicenter retrospective observational study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 24(5):538–546
McAulay V, Deary IJ, Frier BM (2001) Symptoms of hypoglycaemia in people with diabetes. Diabet Med 18(9):690–705
Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Goode K, Atkin SL (2007) Relating mean blood glucose and glucose variability to the risk of multiple episodes of hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 50:2553–2561
Sartore G, Chilelli NC, Burlina S, Di Stefano P, Piarulli F, Fedele D, Mosca A, Lapolla A (2012) The importance of HbA1c and glucose variability in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: outcome of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). Acta Diabetol 49(Suppl 1):S153–S160
Bergenstal RM, Klonoff DC, Garg SK, Bode BW, Meredith M, Slover RH, Ahmann AJ, Welsh JB, Lee SW (2013) Kaufman FR; ASPIRE In-Home Study Group. Threshold-based insulin-pump interruption for reduction of hypoglycemia. N Engl J Med 369(3):224–232
Seaquist ER, Anderson J, Childs B, Cryer P, Dagogo-Jack S et al (2013) Hypoglycemia and diabetes: a report of a workgroup of the American Diabetes Association and the Endocrine Society. Diabetes Care 36(5):1384–1395
Acknowledgments
This study was organized and funded by the AMD Foundation Rome, with an unrestricted grant from Novo Nordisk.
Conflict of interest
Carlo B Giorda, Alessandro Ozzello, Sandro Gentile, Alberto Aglialoro, Anna Chiambretti, Fabio Baccetti, Francesco M. Gentile, Giuseppe Lucisano, Antonio Nicolucci and Maria Chiara Rossi declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
This study was approved by Institutional Interdipartimental Ethics Committee S. Luigi Hospital of Orbassano, Italy.
Human and animal rights
All procedures were carried out in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 [5].
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Managed by Massimo Federici.
Please refer the “Appendix” section for HYPOS-1 Study Group of AMD investigators list.
Appendix: HYPOS-1 study group of AMD investigators
Appendix: HYPOS-1 study group of AMD investigators
R. Fornengo—Chivasso(TO), A. Alessiato—Chieri (TO), A. Ozzello—Pinerolo (TO), L. Sciangula—Mariano Comense (CO), N. Musacchio—Cusano Milanino (MI), G. Marelli—Desio (MB), A. Corsi—Sanpierdarena (GE), F. Baccetti—Massa (MS), V. Paciotti—Avezzano (AQ), R. Iannarelli L’Aquila (AQ), D. Antenucci—Lanciano (CH), F. Chiaramonte—Roma, S. Leotta—Roma, S. Gentile- Napoli, V. Armentano—Napoli, F.M. Gentile—Rutigliano (BA), F. Mastinu—Oristano (OR) and D. Cucinotta—Messina.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giorda, C.B., Ozzello, A., Gentile, S. et al. Incidence and risk factors for severe and symptomatic hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Results of the HYPOS-1 study. Acta Diabetol 52, 845–853 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-015-0713-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-015-0713-4