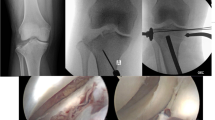
Abstract
Purpose
To determine if the type of approach used for treatment of lateral split-depression tibial plateau fractures affects clinical outcome and complications rate.
Methods
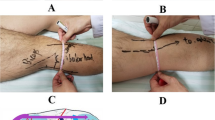
This is a retrospective review of 169 patients who presented between 01/2005 and 12/2020 to a Level-I trauma center for operative management of an isolated lateral Schatzker II tibial plateau fractures (AO/OTA Type 41B3.1) treated through a single anterolateral approach: a 90-degree “L” (L), longitudinal vertical (V), or “lazy S” (S). Postoperative radiographic, clinical, and functional outcomes were assessed at 3, 6, 12 months, and beyond.
Results
Average time to radiographic healing was longer in the S incision cohort (p < 0.05). Furthermore, patients within the S incision cohort developed more postoperative wound complications at follow-up when compared to those within the L and V incision cohorts (p < 0.05). Additionally, reoperation rates were greater in the S incision cohort (p < 0.05). Lastly, on physical examination of the knee, patients within the S incision cohort had significantly poorer knee range of motion (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Our study demonstrates that skin incision type in the anterolateral approach to the proximal tibia has an association with outcomes following operative repair of tibial plateau fractures. The information from this study can be used to inform surgeons about the potential complications and long-term outcomes that patients may experience when undergoing operative repair of a tibial plateau fracture through a specific incision type.
Level of evidence
III.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Egol KA, Koval KJ, Zuckerman JD. (2019) Handbook of fractures. Wolters Kluwers Health, Philadelphia, PA, pp. 525-533.
Tscherne H, Lobenhoffer P (1993) Tibial plateau fractures. Management and expected results. Clin Orthop Relat Res 292:87–100 (PMID: 8519141)
Kugelman D, Qatu A, Haglin J et al (2017) Complications and unplanned outcomes following operative treatment of tibial plateau fractures. Injury 48(10):2221–2229
Colman M, Wright A, Gruen G et al (2013) Prolonged operative time increases infection rate in tibial plateau fractures. Injury 44(2):249–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2012.10.032
Berkson EM, Virkus WW (2006) High-energy tibial plateau fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 14(1):20–31. https://doi.org/10.5435/00124635-200601000-00005
Schatzker J, McBroom R, Bruce D (1979) The tibial plateau fracture. The Toronto experience 1968–1975. Clin Orthop Relat Res 138:94–104
Luo CF, Sun H, Zhang B, Zeng BF (2010) Three-column fixation for complex tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma 24(11):683–692. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181d436f3 (PMID: 20881634)
Meinberg EG, Agel J, Roberts CS et al (2018) Fracture and dislocation classification compendium. J. Orthop Trauma 32(1):S1–S170
Cruess RL, Dumont J (1975) Fracture healing. Can J Surg 18(5):403–413 (PMID: 1175109)
Rademakers MV, Kerkhoffs GM, Sierevelt IN et al (2007) Operative treatment of 109 tibial plateau fractures: five- to 27-year follow-up results. J Orthop Trauma 21(1):5–10. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e31802c5b51
Ma Y, Meng X, Su Y, Yan Z, Shao Q, Chen Y (2021) Evaluation of a modified spoon-shaped 363 medial incision in the surgical repair of a chronic achilles tendon rupture. J Foot Ankle Surg, 364 60(4):729–732. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2020.11.007. Epub 2021 Mar 5. PMID: 365 33773920.
Shetty VD, Shetty GM (2009) Anterolateral incision in total knee arthroplasty: is there a role for a longer incision in this day-and-age of minimal invasive surgery? Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 19:327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-009-0436-8
Momaya AM, Hlavacek J, Etier B et al (2016) Risk factors for infection after operative fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Injury 47(7):1501–1505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2016.04.011
Lin S, Mauffrey C, Hammerberg EM et al (2014) Surgical site infection after open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24:797–803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-013-1252-8
Ma Y, Meng X, Su Y, Yan Z, Shao Q, Chen Y (2021) Evaluation of a modified spoon-shaped medial incision in the surgical repair of a chronic Achilles tendon rupture. J Foot Ankle Surg. 60(4):729–732. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2020.11.007. Epub 2021 Mar 5. PMID: 33773920.
Hunt TK, Hopf H, Hussain Z (2000) Physiology of wound healing. Adv Skin Wound Care. 13(2 Suppl):6–11 (PMID: 11074996)
Young MJ, Barrack RL (1994) Complications of internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Rev 23(2):149–154
Chen HW, Luo CF (2015) Extended anterolateral approach for treatment of posterolateral tibial plateau fractures improves operative procedure and patient prognosis. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(8):13708–13715
Haller JM, Holt DC, McFadden ML et al (2015) Arthrofibrosis of the knee following a fracture of the tibial plateau. Bone Joint J 97-B(1):109–14. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.97B1.34195
Egol KA, Tejwani NC, Capla EL, et al. (2005) Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures (OTA types 41): the results of a prospective, standardized protocol. J Orthop Trauma, 19(7):448–55. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.bot.0000171881.11205.80. Discussion 456.
Kugelman DN, Qatu AM, Strauss EJ et al (2018) Knee stiffness after tibial plateau fractures: predictors and outcomes (OTA-41). J Orthop Trauma 32(11):e421–e427. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000001304
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Dr. Andrew Bi for his contributions to this manuscript.
Funding
This study did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All conflicts of interest are unrelated to this work.
Ethical approval
This is an institutional review board-approved study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deemer, A.R., Jejurikar, N., Konda, S. et al. Approach variation affects outcomes after operative repair of lateral tibial plateau fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 33, 1705–1711 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-022-03343-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-022-03343-7