Abstract
Objective
To compare the ablation ability of nucleus pulposus after 1,064 nm Nd:YAG laser and 980 nm diode laser radiation.
Methods
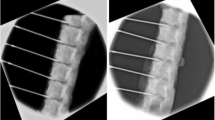
Goat spine specimen (GSS) was radiated using Nd:YAG laser and 980 nm diode laser and then divided into five groups based on the final energy—200, 400, 600, 800 and 1,000 J groups. The ablation quality of nucleus pulposus after radiation was recorded.
Results
The ablation quality of GSS was greater at higher radiation energies in both lasers. When compared at the same energy level, the ablation quality of GSS was greater in 980 nm diode laser than in 1,064 nm Nd:YAG laser. Statistical significance was observed in 200 and 400 J groups (P < 0.05) and in 600, 800 and 1,000 J groups (P < 0.01).
Conclusion
Radiation with 980 nm diode laser showed better ablation ability than 1,064 nm Nd:YAG laser.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choy DS, Case RB, Fielding W et al (1987) Percutaneous laser nucleolysis of lumbar discs. N Engl J Med 317:771–772
Choy DS, Hellinger J, Hellinger S et al (2009) 23rd Anniversary of percutaneous laser disc decompression (PLDD). Photomed Laser Surg 27:535–538
Choy DS (2004) Percutaneous laser disc decompression: a 17-year experience. Photomed Laser Surg 22:407–410
Ren Longxi, Guo Han, Zhang Tongtong et al (2013) Efficacy evaluation of percutaneous laser disc decompression in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation. Photomed Laser Surg 31:174–178
Gevargez A, Groenemeyer DWH, Czerwinski F (2000) CT-guided percutaneous laser disc decompression with Ceralas D a diode laser with 980-nm wavelength and 200-um fiber optics. Eur Radiol 10:1239–1241
Wang Shengli, Li Jihai (2006) Percutaneous laser disc decompression on treatment of 286 patients with disc herniation using 980 nm diode laser. Chin J Rehabil Theory Prac 12:632
Ren L, Guo B, Zhang J et al (2013) Mid-term efficacy of percutaneous laser disc decompression for treatment of cervical vertigo. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol [Epub ahead of print]
Ren L, Han Z, Zhang T et al (2013) Efficacy of percutaneous laser disc decompression on lumbar spinal stenosis. Lasers Med Sci [Epub ahead of print]
Nikfarjam M, Malcontenti-Wilson C, Christophi C (2005) Comparision of 980-and 1,064-nm wavelengths for interstitial laser thermotherapy of the liver [J]. Photomed Laser Surg 23:284–288
Gong Z, Wang M, Gao M (2003) Heating-solidified effect to albumin with GaAlAs diode laser—InGaAs diode laser and Nd:YAG laser: a comparison[J]. Chin J Laser Med Surg 12:100–102
Jayasree RS, Gupta AK, Bodhey NK et al (2009) Effect of 980-nm Diode Laser and 1,064-nm Nd:YAG Laser on the Intervertebral Disc—In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Photomed Laser Surg 27:547–552
Conflict of interest
Nil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, J., Han, Z., Guo, B. et al. Comparison of the ablation ability of nucleus pulposus after 1,064 nm Nd:YAG laser and 980 nm diode laser radiation. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 25 (Suppl 1), 59–62 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-014-1514-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-014-1514-0