Abstract
Purpose
To detect the associations between the degree of the endplate (EP) lesions with the presence of risk factors, biochemical and genetic markers previously observed in low back pain (LBP) patients with EP defects in comparison with hernia/discopathy patients and healthy controls.
Methods
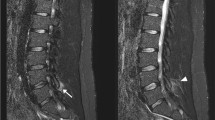
In this observational retrospective study, T2-weighted sagittal MRI images (n = 223 LBP patients) were scored for EP lesions by two independent observers. Total MRI score and number of affected levels (L1/L2–L5/S1) have been considered for the correlation with demographic, behavioral, clinical, biochemical (25(OH)D, CTx-I and CTx-II levels, n = 69 males) and VDR variables.
Results
Males showed higher BMI and total MRI score than females. Patients bearing TT compared to tt VDR genotypes showed significant higher total MRI scores. Among males (n = 125), TT, bb and aa genotypes showed increased total MRI scores. Higher total MRI score directly correlates with higher levels of CTx-I and CTx-II (n = 69 males).
Conclusions
The markers previously identified as associated with the presence of EP lesions have been confirmed as related to their severity and could be used to follow the pathology progression.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data are available at: https://osf.io/uhqf3/?view_only=6568d660a2f74e78995db57108d25509.
References
Moore RJ (2006) The vertebral endplate: disc degeneration, disc regeneration. Eur Spine J 15(Suppl 3):S333-337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-006-0170-4
Roberts S, Menage J, Urban JP (1989) Biochemical and structural properties of the cartilage end-plate and its relation to the intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila PA 1976) 14:166–174. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-198902000-00005
Lesoin F, Leys D, Rousseaux M, Dubois F, Villette L, Pruvo JP, Petit H, Jomin M (1987) Thoracic disk herniation and Scheuermann’s disease. Eur Neurol 26:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1159/000116327
Fields AJ, Ballatori A, Liebenberg EC, Lotz JC (2018) Contribution of the endplates to disc degeneration. Curr Mol Biol Rep 4:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40610-018-0105-y
Wang Y, Videman T, Battie MC (2012) ISSLS prize winner: Lumbar vertebral endplate lesions: associations with disc degeneration and back pain history. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 37:1490–1496. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182608ac4
Rajasekaran S, Venkatadass K, Naresh Babu J, Ganesh K, Shetty AP (2008) Pharmacological enhancement of disc diffusion and differentiation of healthy, ageing and degenerated discs: results from in-vivo serial post-contrast MRI studies in 365 human lumbar discs. Eur Spine J 17:626–643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-008-0645-6
Brayda-Bruno M, Albano D, Cannella G, Galbusera F, Zerbi A (2018) Endplate lesions in the lumbar spine: a novel MRI-based classification scheme and epidemiology in low back pain patients. Eur Spine J 27:2854–2861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-018-5787-6
Cauci S, Vigano M, de Girolamo L, De Luca P, Orfei CP, Banfi G, Lombardi G, Brayda-Bruno M, Colombini A (2017) High levels of circulating type II collagen degradation marker (CTx-Ii) are associated with specific VDR polymorphisms in patients with adult vertebral osteochondrosis. Int J Mol Sci 18:2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/Ijms18102073
Colombini A, Brayda-Bruno M, Ferino L, Lombardi G, Maione V, Banfi G, Cauci S (2015) Gender differences in the VDR-FokI polymorphism and conventional non-genetic risk factors in association with lumbar spine pathologies in an Italian case–control study. Int J Mol Sci 16:3722–3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16023722
Zehra U, Flower L, Robson-Brown K, Adams MA, Dolan P (2017) Defects of the vertebral end plate: implications for disc degeneration depend on size. Spine J 17:727–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2017.01.007
Brayda-Bruno M, Vigano M, Cauci S, Vitale JA, de Girolamo L, De Luca P, Lombardi G, Banfi G, Colombini A (2017) Plasma vitamin D and osteo-cartilaginous markers in Italian males affected by intervertebral disc degeneration: focus on seasonal and pathological trend of type II collagen degradation. Clin Chim Acta 471:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2017.05.028
Colombini A, Brayda-Bruno M, Lombardi G, Croiset SJ, Ceriani C, Buligan C, Barbina M, Banfi G, Cauci S (2016) BsmI, ApaI and TaqI Polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) and association with lumbar spine pathologies: an Italian case–control study. PLoS ONE 11:e0155004. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155004
Colombini A, Brayda-Bruno M, Lombardi G, Croiset SJ, Vrech V, Maione V, Banfi G, Cauci S (2014) FokI polymorphism in the vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) and its association with lumbar spine pathologies in the Italian population: a case–control study. PLoS ONE 9:e97027. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097027
Chen L, Zhao S, Niu F, Bi GB (2017) Association between vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and intervertebral disc degeneration: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Sci 22:184–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jos.2016.11.009
Colombini A, Cauci S, Lombardi G, Lanteri P, Croiset S, Brayda-Bruno M, Banfi G (2013) Relationship between vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) polymorphisms, vitamin D status, osteoarthritis and intervertebral disc degeneration. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 138:24–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.03.001
Jiang H, Qin ZL, Zong SH, He ML, Zhan XL, Xiao ZM, Wei QJ (2017) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and lumbar disc degeneration: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J 26:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4771-2
Antoniou J, Goudsouzian NM, Heathfield TF, Winterbottom N, Steffen T, Poole AR, Aebi M, Alini M (1996) The human lumbar endplate. Evidence of changes in biosynthesis and denaturation of the extracellular matrix with growth, maturation, aging, and degeneration. Spine (Phila PA 1976) 21:1153–1161. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-199605150-00006
Colombini A, Lanteri P, Lombardi G, Grasso D, Recordati C, Lovi A, Banfi G, Bassani R, Brayda-Bruno M (2012) Metabolic effects of vitamin D active metabolites in monolayer and micromass cultures of nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus cells isolated from human intervertebral disc. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:1019–1030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2012.03.012
De Luca P, de Girolamo L, Perucca Orfei C, Vigano M, Cecchinato R, Brayda-Bruno M, Colombini A (2018) Vitamin D’s effect on the proliferation and inflammation of human intervertebral disc cells in relation to the functional vitamin D receptor gene FokI polymorphism. Int J Mol Sci 19:2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072002
Gruber HE, Hoelscher G, Ingram JA, Chow Y, Loeffler B, Hanley EN Jr (2008) 1,25(OH)2-vitamin D3 inhibits proliferation and decreases production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, thrombopoietin, VEGF, and angiogenin by human annulus cells in vitro. Spine (Phila PA 1976) 33:755–765. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181695d59
La Marra F, Stinco G, Buligan C, Chiriaco G, Serraino D, Di Loreto C, Cauci S (2017) Immunohistochemical evaluation of vitamin D receptor (VDR) expression in cutaneous melanoma tissues and four VDR gene polymorphisms. Cancer Biol Med 14:162–175. https://doi.org/10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2017.0020
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Italian Ministry of Health, “Ricerca Corrente”.
Funding
This research was funded by the Italian Ministry of Health, “Ricerca Corrente”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization was done by Alessandra Colombini, Fabio Galbusera. Methodology was done by Maria Cristina Cortese, Enrico Gallazzi, Domenico Albano, and formal analysis and investigation were done by Alessandra Colombini, Marco Viganò. Writing—original draft preparation was done by Alessandra Colombini, Fabio Galbusera. Writing—review and editing was done by Sabina Cauci, Luca Maria Sconfienza, Marco Brayda Bruno. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
Patients had signed a written informed consent to participate to this study.
Consent for publication
Patients had signed a written informed consent for data publication.
Ethics approval
The protocol GENODISC01 of this study was approved by the Institutional Review Board ASL Città di Milano. The study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colombini, A., Galbusera, F., Cortese, M.C. et al. Classification of endplate lesions in the lumbar spine and association with risk factors, biochemistry, and genetics. Eur Spine J 30, 2231–2237 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-021-06719-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-021-06719-1