Abstract
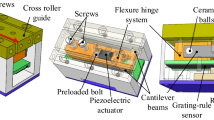
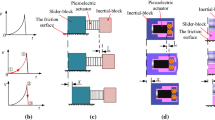
In order to achieve the nano-operation in a limited space, a precision motion platform with a cubic centimeter volume based on the principle of inertial stick–slip driving is proposed in this paper. The mechanical structure and the operating principle are discussed. Kinematic models are used to analyze the performance of the prototype. To investigate the working performance of the prototype, a series of experiments are carried out. Experimental results show that the displacement outputs is related to the parameters of the electrical signal. The maximum moving speed of the platform reaches 13.1 mm/s when the driving frequency is 3.1 kHz. The maximum single step displacement reaches 4.8 μm. Through proper driving voltage and frequency, the proposed prototype can produce a satisfactory velocity.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dsouza RD, Navin KP, Theodoridis T et al (2018) Design, fabrication and testing of a 2 DOF compliant flexural microgripper. Microsyst Technol 24(9):3867–3883
Hui X, Onal C, Régnier S et al (2011) Automated control of AFM based nanomanipulation. Atomic force microscopy based nanorobotics. Springer, Berlin
Hunstig M (2017) Piezoelectric inertia motors—a critical review of history. Concept Des Appl Perspect 2017(6):7
Jiang TY, Ng TY, Lam KY (2000) Optimization of a piezoelectric actuator actuator. Sens Actuator 84(1/2):81–94
Kudela P, Radzienski M, Ostachowicz W et al (2018) Structural Health Monitoring system based on a concept of Lamb wave focusing by the piezoelectric array. Mech Syst Signal Process 2018(108):21–32
Lee SW, Ahn KG, Ni J (2007) Development of a piezoelectric multi-axis stage based on stick-and-clamping actuation technology. Smart Mater Struct 16(6):2354–2367
Liang C, Wang F, Tian Y et al (2017) Design of a novel asymmetrical piezoelectric actuated microgripper for micromanipulation. In: IEEE international conference on manipulation, manufacturing and measurement on the nanoscale. IEEE, pp 318–322
Meyer C, Sqalli O, Lorenz H et al (2005) Slip-stick step-scanner for scanning probe microscopy. Rev Sci Instrum 76(6):965
Nah SK, Zhong ZW (2007) A microgripper using piezoelectric actuation for micro-object manipulation. Sens Actuator A Phys 133(1):218–224
Nomura Y, Aoyama H (2007) Development of inertia driven micro robot with nano tilting stage for SEM operation. Microsyst Technol 13(8–10):1347–1352
Peng Y, Cao J, Guo Z et al (2015) A linear actuator for precision positioning of dual objects. Smart Mater Struct 24(12):125039
Tang H, Li Y, Huang J (2012) Design and analysis of a dual-mode driven parallel XY micromanipulator for micro/nanomanipulations. Arch Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C J Mech Eng Sci 226(12):3043–3057
Yoshihiro N, Hisayuki A (2007) Development of inertia driven micro robot with nano tilting stage for SEM operation. Microsyst Technol 13(8–10):1347–1352
Zhang ZM, An Q, Li JW et al (2012) Piezoelectric friction–inertia actuator—a critical review and future perspective. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 2012(62):669–685
Zhong BW, Zhu J, Jin ZQ et al (2019) Improved inertial stick-slip movement performance via driving waveform optimization. Precis Eng 55:260–267
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51875378), the Jiangsu province Natural Science Foundation (No. BK20181439) and the Suzhou science and technology development project (No. SYG201720).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 2890 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, B., Liu, B., Jin, Z. et al. Cubic centimeter robot based on inertial stick–slip driving. Microsyst Technol 26, 437–445 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04557-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04557-2