Abstract
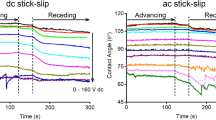
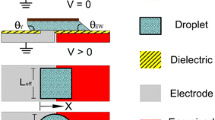
Electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD) with atypical liquid-substrate combinations has growing utility for a range of microfluidic devices. However, there are challenges to understanding and utilizing the EWOD behavior on rougher substrates with potentially heterogeneous wetting conditions that cause high contact angle (CA) hysteresis. Accurate and consistent EWOD responses can be obtained for these substrates by measuring advancing and receding CAs at constant applied potential. This method was used to characterize the EWOD (DC) responses of two ionic liquids and an aqueous solution on several conductive polyimide and silicon substrates coated with Parylene C/Teflon AF. The results showed Lippmann–Young behavior with liquid-dependent zero-voltage CAs and 13°–40° control authority, 11° average hysteresis, and CA saturation at approximately 80° for all liquids and substrates. Surface roughness and substrate material had little effect on EWOD response and CA hysteresis. The hysteresis was surprisingly high for a Teflon AF-coated substrate. O2 plasma etching of the Parylene prior to Teflon coating may have contributed to the high hysteresis conditions by forming Teflon AF islands or embedding charges into the substrate that affected wetting through the thin Teflon AF layer. CA “ratcheting” was observed during advance corresponding to stick–slip of the droplet triple-line. The stick–slip behavior occurred with all liquid-substrate combinations at sufficiently high voltages and on previously polarized surfaces at lower voltages. Experiments with smooth (“ideal”) Si substrates showed ratcheting only at saturation-level voltages suggesting a link between ratcheting and saturation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry S, Kedzierski J, Abedian B (2006) Low voltage electrowetting using thin fluoroploymer films. J Colloid Interface Sci 303:517–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2006.08.004
Charipar KM, Charipar NA, Bellemare JV, Peak JE, Pique A (2015) Electrowetting displays utilizing bistable, multi-color pixels via laser processing. J Disp Technol 11:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1109/Jdt.2014.2364189
Dubois P et al (2006) Ionic liquid droplet as e-microreactor. Anal Chem 78:4909–4917. https://doi.org/10.1021/Ac060481q
Fair RB (2007) Digital microfluidics: is a true lab-on-a-chip possible? Microfluid Nanofluid 3:245–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-007-0161-8
Gołda M, Brzychczy-Włoch M, Faryna M, Engvall K, Kotarba A (2013) Oxygen plasma functionalization of Parylene C coating for implants surface: nanotopography and active sites for drug anchoring. Mater Sci Eng, C 33:4221–4227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2013.06.014
Hsu TH, Manakasettharn S, Taylor JA, Krupenkin T (2015) Bubbler: a novel ultra-high power density energy harvesting method based on reverse electrowetting. Sci Rep 5:16537. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16537
Jones TB (2005) An electromechanical interpretation of electrowetting. J Micromech Microeng 15:1184–1187. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/15/6/008
Kedzierski J, Meng K, Thorsen T, Cabrera R, Berry S (2016) Microhydraulic electrowetting actuators. J Microelectromech Syst 25:394–400. https://doi.org/10.1109/Jmems.2016.2521439
Ko YH, Kim YH, Park J, Nam KT, Park JH, Yoo PJ (2011) Electric-field-assisted layer-by-layer assembly of weakly charged polyelectrolyte multilayers. Macromolecules 44:2866–2872. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma102112a
Kontziampasis D, Trantidou T, Regoutz A, Humphrey EJ, Carta D, Terracciano CM, Prodromakis T (2016) Effects of Ar and O-2 plasma etching on Parylene C: topography versus surface chemistry and the impact on cell viability. Plasma Process Polym 13:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppap.201500053
Li F, Mugele F (2008) How to make sticky surfaces slippery: contact angle hysteresis in electrowetting with alternating voltage. Appl Phys Lett 92:244108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2945803
Liu H, Dharmatilleke S, Maurya DK, Tay AAO (2009) Dielectric materials for electrowetting-on-dielectric actuation. Microsyst Technol 16:449–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-009-0933-z
Marmur A (2009) Solid-surface characterization by wetting. Annu Rev Mater Sci 39:473–498. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.matsci.38.060407.132425
Meng E, Li PY, Tai YC (2008) Plasma removal of parylene C. J Micromech Microeng 18. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/18/4/045004
Merrill MH, Thomas JP, Auyeung RCY, Piqué A (2014) Electrowetting actuation methods for surface morphology control of multifunctional composites. In: Paper presented at the American Society for Composites—29th technical conference, La Jolla
Millefiorini S, Tkaczyk AH, Sedev R, Efthimiadis J, Ralston J (2006) Electrowetting of ionic liquids. J Am Chem Soc 128:3098–3101. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja057606d
Moon H, Cho SK, Garrell RL, Kim CJ (2002) Low voltage electrowetting-on-dielectric. J Appl Phys 92:4080–4087. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1504171
Mugele F, Baret JC (2005) Electrowetting: from basics to applications. J Phys: Condens Matter 17:R705–R774. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/17/28/R01
Murade CU, van der Ende D, Mugele F (2012) High speed adaptive liquid microlens array. Opt Express 20:18180–18187. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.20.018180
Nanayakkara YS, Moon H, Payagala T, Wijeratne AB, Crank JA, Sharma PS, Armstrong DW (2008) A fundamental study on electrowetting by traditional and multifunctional ionic liquids: possible use in electrowetting on dielectric-based microfluidic applications. Anal Chem 80:7690–7698. https://doi.org/10.1021/Ac8009802
Nanayakkara YS, Perera S, Bindiganavale S, Wanigasekara E, Moon H, Armstrong DW (2010) The effect of AC frequency on the electrowetting behavior of ionic liquids. Anal Chem 82:3146–3154. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac9021852
Nelson WC, Kim C-JC (2012) Droplet actuation by electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD): a review. J Adhes Sci Technol 26:1747–1771. https://doi.org/10.1163/156856111x599562
Paneru M, Priest C, Sedev R, Ralston J (2010) Static and dynamic electrowetting of an ionic liquid in a solid/liquid/liquid system. J Am Chem Soc 132:8301–8308. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja9106397
Park J, Hammond PT (2005) Polyelectrolyte multilayer formation on neutral hydrophobic surfaces. Macromolecules 38:10542–10550. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma051158c
Prins MWJ, Welters WJJ, Weekamp JW (2001) Fluid control in multichannel structures by electrocapillary pressure. Science 291:277–280
Reid RC, Thomas JP, Merrill MH (2017) Advances in poro-vascular composites: toward non-mechanical surface roughness control. In: Paper presented at the 21st international conference on composite materials (ICCM-21), Xi’an
Restolho J, Mata JL, Saramago B (2009) Electrowetting of ionic liquids: contact angle saturation and irreversibility. J Phys Chem C 113:9321–9327. https://doi.org/10.1021/Jp902393r
Ricks-Laskoski HL, Buckley MA, Snow AW (2008) EWOD-driven translational movement of a liquid polyelectrolyte droplet. J Appl Polym Sci 110:3865–3870. https://doi.org/10.1002/App.28880
Shapiro B, Moon H, Garrell RL, Kim CJ (2003) Equilibrium behavior of sessile drops under surface tension, applied external fields, and material variations. J Appl Phys 93:5794–5811. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1563828
Smith NR, Hou L, Zhang J, Heikenfeld J (2009) Fabrication and demonstration of EWOD liquid lens arrays. J Disp Technol 5:411–413. https://doi.org/10.1109/JDT.2009.2027036
Steckl AJ, You H, Kim DY (2011) Flexible electrowetting and electrowetting on flexible substrates. In: Paper presented at the proceedings of SPIE, San Francisco
Woodward RP (1999) Contact angle measurements using the drop shape method. First Ten Angstroms, Inc. http://www.firsttenangstroms.com/pdfdocs/CAPaper.pdf. Accessed 6 Jan 2017
You H, Steckl AJ (2010) Three-color electrowetting display device for electronic paper. Appl Phys Lett 97:023514. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3464963
Zhou K, Heikenfeld J, Dean KA, Howard EM, Johnson MR (2009) A full description of a simple and scalable fabrication process for electrowetting displays. J Micromech Microeng 19:065029. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/19/6/065029
Zimmermann R, Dukhin S, Werner C (2001) Electrokinetic measurements reveal interfacial charge at polymer films caused by simple electrolyte ions. J Phys Chem B 105:8544–8549. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp004051u
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (MIPR F4FGA05239G001) and by the Office of Naval Research through the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory’s Basic Research Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supporting information (*.pdf file) contains a property table for the liquids used, scanning electron images of Kapton XC before and after coating with Parylene C and Teflon AF, a full series of CP-EWOD on one substrate, CV-EWOD data for IL4 on Kapton RS, and CA hysteresis over all liquid-substrate combinations. Detailed explanation of the calculations and averaging schemes used as well as the algorithm for fitting the Lippmann–Young equation are also included.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merrill, M.H., Reid, R.C., Gogotsi, N. et al. Electrowetting on polyimide and silicon substrates with high hysteresis. Microsyst Technol 24, 4847–4854 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-3896-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-3896-0