Abstract
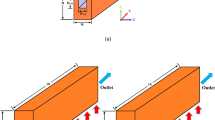
Three-dimensional simulations are performed numerically to investigate the influence of inlet/outlet positions (Z-, I-, and C-type) and header forms (rectangular, symmetric trapezoidal, and triangular) on the flow and thermal performance in microchannel heat sinks. The conjugated heat transfer model is solved based on finite element method. A good agreement is found between the numerical results and theoretical data. A detailed analysis of flow and pressure distributions is proposed to explain the flow or heat transfer performance of different geometric structures. Results indicate that the performance of I-type with a rectangular header in terms of flow velocity uniformity and heat transfer is better than others under the same pumping power consumption.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c p :
-
Special heat capacity kJ/(kg K)
- f app :
-
Friction factor
- k f :
-
Thermal conductivity of fluid W/(m K)
- k s :
-
Thermal conductivity of solid W/(m K)
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- \(\Delta {\text{p}}\) :
-
Pressure drop Pa
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- q in :
-
Mass flow rate kg/min
- q w :
-
Heat flux W/m2
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- R T :
-
Thermal resistance K/W
- T :
-
Temperature °C
- ρ:
-
Density kg/m3
- μ:
-
Dynamic viscosity kg/(m s)
- Ω:
-
Pumping power W
- V :
-
Velocity m/s
- V q :
-
Volume flow rate m3/s Subscript
- ave :
-
Average
- in :
-
Inlet
- max :
-
Maximum
- min :
-
Minimum
- out :
-
Outlet
- STD :
-
Standard deviation
- s :
-
Solid
- f :
-
Fluid
References
Abubakar SB, Sidik NAC (2015) Numerical prediction of laminar nanofluid flow in rectangular microchannel heat sink. J Adv Res Fluid Mech Therm Sci 7:29–38
Abubakar S, Nor Azwadi CS, Ahmad A (2016) The use of Fe3O4–H2O4 nanofluid for heat transfer enhancement in rectangular microchannel heatsink. J Adv Res Mater Sci 23:15–24
Chai L, Xia G, Wang L et al (2013) Heat transfer enhancement in microchannel heat sinks with periodic expansion–constriction cross-sections. J Int J Heat Mass Transf 62(1):741–751
Chang SW, Lees AW (2010) Endwall heat transfer and pressure drop in scale-roughened pin-fin channels. J. Int J Therm Sci 49(4):702–713
Chein R, Chen J (2009) Numerical study of the inlet/outlet arrangement effect on microchannel heat sink performance. J. Int J Therm Sci 48(8):1627–1638
Choi SH, Shin S, Cho YI (1993a) The effects of the Reynolds number and width ratio on the flow distribution in manifolds of liquid cooling modules for electronic packaging. J Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 20(5):607–617
Choi SH, Shin S, Cho YI (1993b) The effect of area ratio on the flow distribution in liquid cooling module manifolds for electronic packaging. J Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 20(2):221–234
Dong L, Jiang B, Minghou Liu et al (2012) Effect of inlet/outlet types on the flow distribution and heat transfer in mini-channels. J Chin J Lasers 39(10):1003005–1003502
Elperin T, Rudin G (2016) Thermal stresses in a coating–substrate assembly caused by internal heat source. J Therm Stress 39(1):90–102
Foong AJL, Ramesh N, Chandratilleke TT (2009) Laminar convective heat transfer in a microchannel with internal longitudinal fins. J. Int J Therm Sci 48(10):1908–1913
Ghani IA, Kamaruzaman N, Sidik NAC (2017a) Heat transfer augmentation in a microchannel heat sink with sinusoidal cavities and rectangular ribs. J Int J Heat Mass Transf 108:1969–1981
Ghani IA, Sidik NAC, Mamat R et al (2017b) Heat transfer enhancement in microchannel heat sink using hybrid technique of ribs and secondary channels [J]. Int J Heat Mass Transf 114:640–655
Guo J, Xu M, Cheng L (2011) Second law analysis of curved rectangular channels. J. Int J Therm Sci 50(5):760–768
Hong F, Cheng P (2009) Three dimensional numerical analyses and optimization of offset strip-fin microchannel heat sinks. J Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 36(7):651–656
Kumaran RM, Kumaraguruparan G, Sornakumar T (2013) Experimental and numerical studies of header design and inlet/outlet configurations on flow mal-distribution in parallel micro-channels. J Appl Therm Eng 58(s 1–2):205–216
Lee PS, Garimella SV (2006) Thermally developing flow and heat transfer in rectangular microchannels of different aspect ratios [J]. Int J Heat Mass Transf 49(17):3060–3067
Lu MC, Wang CC (2006) Effect of the inlet location on the performance of parallel-channel cold-plate. J IEEE Trans Compon Packag Technol 29(1):30–38
Noh NM, Fazeli A, Sidik NAC (2014) Numerical simulation of nanofluids for cooling efficiency in microchannel heat sink. J Adv Res Fluid Mech Therm Sci 4:13–23
Peles Y, Koşar A, Mishra C et al (2005) Forced convective heat transfer across a pin fin micro heat sink. J Int J Heat Mass Transf 48(17):3615–3627
Sidik NAC, Muhamad MNAW, Wan MAAJ et al (2017) An overview of passive techniques for heat transfer augmentation in microchannel heat sink [J]. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 88:74–83
Steinke ME, Kandlikar SG (2006) Single-phase liquid friction factors in microchannels [J]. Int J Therm Sci 45(11):1073–1083
Suhir Ephraim (2013) Thermal stress failures in electronics and photonics: physics, modeling, prevention. J Therm Stress 36(6):537–563
Tuckerman DB, Pease RFW (1981) High-performance heat sinking for VLSI. J IEEE Electron Device Lett 2(5):126–129
Xia GD, Jiang J, Wang J et al (2015) Effects of different geometric structures on fluid flow and heat transfer performance in microchannel heat sinks. J Int J Heat Mass Transf 80:439–447
Xie G, Liu J, Liu Y, Sunden B, Zhang W (2013) Comparative study of thermal performance of longitudinal and transversal-wavy microchannel heat sinks for electronic cooling. J Electron Packag 135:021008
Xu JL, Gan YH, Zhang DC et al (2005) Microscale heat transfer enhancement using thermal boundary layer redeveloping concept. J Int J Heat Mass Transf 48(9):1662–1674
Xu J, Song Y, Zhang W et al (2008) Numerical simulations of interrupted and conventional microchannel heat sinks. J Int J Heat Mass Transf 51(25):5906–5917
Acknowledgements
The project was financially supported by the Scientific Research Project of Beijing Educational Committee (Grant no. 004000546315527) and Scientific Research Project of Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Future Internet Technology. The authors are grateful for the support of these sponsors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, S., Zhao, Y., Diao, Y. et al. Effects of various inlet/outlet positions and header forms on flow distribution and thermal performance in microchannel heat sink. Microsyst Technol 24, 2485–2497 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3688-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3688-y