Abstract
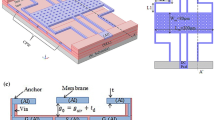
This paper presents a novel design, optimization and analysis of capacitive radio frequency (RF) micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) switch. The design incorporates a novel membrane and beams’ structure with two short high-impedance transmission-line (T-line) sections added on either side of the switch (namely T-match switch) to improve its RF performance, while maintaining low-actuation voltage. The short high-impedance T-line section has narrower width and higher impedance than the coplanar waveguide (CPW)’s signal line, behaves as series inductor to compensate the switch’s up-state capacitance and provides excellent matching at the design frequency. This high-impedance T-line section was designed, simulated and optimized using finite-element-modelling (FEM) tool of electromagnetic (EM) simulator of AWR Design EnvironmentTM. The optimized T-line section’s width and length is 10 µm and 70 µm, respectively. The RF-MEMS switch is actuated by electrostatic force with low-actuation voltage of 2.9 V, has maximum von Mises stress of 13.208 MPa which is less than aluminium’s yield stress and can be operated in robust conditions. Compared to the normal capacitive RF-MEMS switch, this T-match capacitive RF-MEMS switch with two sections of optimized high-impedance T line has improved the performance of return loss and insertion loss, at switch-on state, by 45.83% and 55.35%, respectively; while at the switch-off state, the isolation is increased by 24.05%; only the switch-off return loss is degraded by 11.7% but the value (− 0.5519 dB) is still located in the range of design specifications. The RF-MEMS switch’s actuation time was simulated to be ~ 27 µs with amplitude of 5 V up-step voltage.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afrang S, Abbaspour-Sani E (2006) A low voltage MEMS structure for RF capacitive switches. Prog Electromagn Res 65:157–167. doi:10.2528/PIER06093001
Badia MFB, Buitrago E, Ionescu AM (2012) RF MEMS shunt capacitive switches using AlN compared to dielectric. J Microelectromech Syst 21(5):1229–1240. doi:10.1109/JMEMS.2012.2203101
Balaraman D, Bhattacharya SK, Ayazi F, Papapolymerou J (2002) Low-cost low actuation voltage copper RF MEMS switches. In: 2002 IEEE MTT-S international microwave symposium digest, vol 2, pp 1225–1228. doi:10.1109/MWSYM.2002.1011879
Bartolucci G, Angelis GD, Lucibello A, Marcelli R, Proietti E (2012) Analytic modelling of RF MEMS shunt connected capacitive switches. J Electromagn Waves Appl 26(8–9):1168–1179. doi:10.1080/09205071.2012.710564
Dai CL, Chen JH (2006) Low voltage actuated RF micromechanical switches fabricated using CMOS-MEMS technique. Microsyst Technol 12(12):1143–1151. doi:10.1007/s00542-006-0243-7
Dai CL, Chen YL (2007) Modelling and manufacturing of micromechanical RF switch with inductors. Sensors 7(11):2660–2670. doi:10.3390/s7112670
Deng Z, Wei H, Fan S, Gan J (2016) Design and analysis a novel RF MEMS switched capacitor for low pull-in voltage application. Microsyst Technol 22(8):2141–2149. doi:10.1007/s00542-015-2604-6
Fernández-Bolaños M, Perruisseau-Carrier J, Dainesi P, Ionescu AM (2008) RF MEMS capacitive switch on semi-suspended CPW using low-loss high-resistivity silicon substrate. Microelectron Eng 85(5):1039–1042. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2008.01.093
Fouladi S, Mansour RR (2010) Capacitive RF MEMS switches fabricated in standard 0.35-CMOS technology. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 58(2):478–486. doi:10.1109/TMTT.2009.2038446
Guo FM, Zhu ZQ, Long YF, Wang WM, Zhu SZ, Lai ZS, Lu W (2003) Study on low voltage actuated MEMS rf capacitive switches. Sens Actuators A 108(1):128–133. doi:10.1016/S0924-4247(03)00372-8
Kim CH (2012) Mechanically coupled low-voltage electrostatic resistive RF multithrow switch. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 59(2):1114–1122. doi:10.1109/TIE.2011.2159694
Kim JM, Lee S, Park JH, Baek CW, Kwon Y, Kim YK (2010) Electrostatically driven low-voltage micromechanical RF switches using robust single-crystal silicon actuators. J Micromech Microeng 20(9):095007. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/20/9/095007
Ma LY, Nordin AN, Soin N (2016a) Design, optimization and simulation of a low-voltage shunt capacitive RF-MEMS switch. Microsyst Technol 22(3):537–549. doi:10.1007/s00542-015-2585-5
Ma LY, Soin N, Nordin AN (2016) A novel design of low-voltage low-loss K-band RF-MEMS capacitive switch. In: 2016 IEEE symposium on design, test, integration and packaging of MEMS/MOEMS (DTIP), pp 1–5. doi:10.1109/DTIP.2016.7514827
Mahameed R, Rebeiz GM (2011) RF MEMS capacitive switches for wide temperature range applications using a standard thin-film process. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 59(7):1746–1752. doi:10.1109/TMTT.2011.2135376
Peroulis D, Pacheco SP, Sarabandi K, Katehi LP (2003) Electromechanical considerations in developing low-voltage RF MEMS switches. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 51(1):259–270. doi:10.1109/TMTT.2002.806514
Persano A, Quaranta F, Martucci MC, Siciliano P, Cola A (2015) On the electrostatic actuation of capacitive RF MEMS switches on GaAs substrate. Sens Actuators A 232:202–207. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2015.05.008
Rebeiz GM (2003) RF MEMS. Theory, design, and technology. Wiley, Hoboken, p 6 (pp. 92, 228, 66)
Reddy BL, Shanmuganantham T (2014) Design of novel capacitive RF MEMS shunt switch with aluminum nitride (AlN) dielectric. Proc Mater Sci 6:692–700. doi:10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.085
Wang Z, Liu Z, Li X (2010) A Ka-band 3-bit RF MEMS switched line phase shifter implemented in coplanar waveguide. In: 2010 10th IEEE international conference on solid-state and integrated circuit technology (ICSICT), pp 1450–1452. doi:10.1109/ICSICT.2010.5667567
Ya ML, Soin N, Nordin AN (2014) Novel low-voltage RF-MEMS switch: design and simulation. In: 2014 IEEE international conference on semiconductor electronics (ICSE), pp 142–145. doi:10.1109/SMELEC.2014.6920816
Acknowledgements
The research is collaborative effort between University of Malaya and International Islamic University Malaysia. All authors would like to thank the financial support by the RACE fund (RACE12-006-0006), UM CR 004-2013, and University Malaya High Impact Research Grant (UM.C/HIR/MOHE/ENG/19).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, LY., Nordin, A.N. & Soin, N. A novel design of a low-voltage low-loss T-match RF-MEMS capacitive switch. Microsyst Technol 24, 561–574 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3577-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3577-4