Abstract
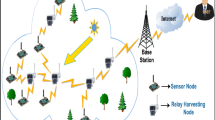
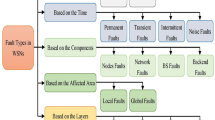
Wireless sensor network being a dominant prerequisite in the modern pervasive environment has nodes connected with multi-hop to transmit and reinforce continuous monitoring with real-time updates from the field environment. To achieve pervasiveness integrating wireless and physical devices is unavoidable. Numerous self-organized tiny sensor nodes cooperate with each other to form the clusters and the most prominent node act as cluster head (CH). The cluster head pioneered based on its battery forte whose failure affects rest of the communications. In this paper, we discuss on the essential of idle resource sharing using participatory devices as relay nodes along with node failure rate and node density to achieve reliable communication. The earlier performances are observed and results are revealed. Hence we concentrate on minimizing the task of CH using relay nodes such as participatory devices and the faulty nodes are identified over Poisson distribution which observes the failure probability without affecting communication and reduced resource consumption.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz IF, Lo BF, Balakrishnan R (2011) Cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks a survey. Phys Commun 4(1):40–62
Bhatti S, Xu J, Memon M (2010) Clustering and fault tolerance for target tracking using wireless sensor networks. IET Wirel Sens Syst 1(2):66–73
Chen S, Fang Y, Xia Y (2007) Lexicographic maxmin fairness for data collection in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 6(7):762–776
Choi J, Sethuraman S, Venkataramani SC (2015) A scaling limit for the degree distribution in sublinear preferential attachment schemes. Random Structures & Algorithms, Wiley
Clouqueur T, Saluja KK, Ramanathan P (2004) Fault tolerance in collaborative sensor networks for target detection. IEEE Trans Comput 53(3):320–333
Costan A, Dobre C, Pop F, Leordeanu C, Cristea V (2010) A fault tolerance approach for distributed systems using monitoring based replication. In: Proceedings of the IEEE, Romania, pp 451–458
Eris C, Saimler M, Gungor VC, Fadel E, Akyildiz IF (2014) Lifetime analysis of wireless sensor nodes in different smart grid environments. Wirel Netw 20(7):2053–2062
Hull B, Jamieson K, Balakrishnan H (2004) Mitigating congestion in wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the ACM, USA, pp 134–147
Prabakaran N, Naresh K, Kannan RJ (2014) Fusion centric decision making for node level congestion in wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the CSI, India, pp 321–329
Sankarasubramaniam Y, Akan ÖB, Akyildiz IF (2003) ESRT: event-to-sink reliable transport in wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the ACM, USA, pp 177–188
Shih E, Cho SH, Ickes N, Min R, Sinha A, Wang A, Chandrakasan A (2001) Physical layer driven protocol and algorithm design for energy-efficient wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the ACM, USA, pp 272–287
Vivek HJ, Sutar DS (2010) EDCAM early detection congestion avoidance mechanism for wireless sensor network. Int J Comput Appl 7(2):11–14
Wang Q, Zhang T (2010) Fair energy allocation in wireless sensor networks theory and practice. In: Proceedings of the IEEE, USA, pp 1–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prabakaran, N., Kannan, R.J. Sustainable life-span of WSN nodes using participatory devices in pervasive environment. Microsyst Technol 23, 651–657 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3117-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3117-7