Abstract
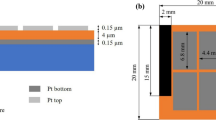
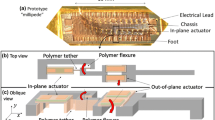
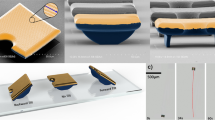
We have developed a piezoelectric-driven millimeter-scale robot with a simple structure. This millimeter-scale robot, which consists of a titanium (Ti) body and front/back legs integrated with a Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 (PZT) piezoelectric thin film actuator, is driven by using mechanical resonance. To simply fabricate the millimeter-scale robot, the PZT thin film was directly deposited on an H-shaped Ti substrate by radio frequency magnetron sputtering and the shape of the robot was completed by plastic deformation of the monolithic Ti substrate. We obtained the transverse piezoelectric coefficient d 31 of the deposited PZT thin film was −21.3 pm/V, which was sufficient for driving the fabricated millimeter-scale robot with a low driving voltage ≤10 V. We also evaluated the resonant characteristics of the fabricated robot and confirmed that the front/back legs of robot were oscillated in primary and secondary resonance modes at around 4.5 and 11 kHz, respectively. We demonstrated that the millimeter-scale robot with asymmetric structure in the front-back direction was controlled by changing driving voltage conditions and a bending angle formed by the front/back legs. The moving speed of the millimeter-scale robot was 13.6 cm/s by applying negative unipolar voltage of 10 Vpp at 10.6 kHz when the bending angle was set to 109°. We experimentally confirmed that the millimeter-scale robot can be driven forward and backward by optimizing the shape of the robot and mechanical resonant modes.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott JJ, Nagy Z, Beyeler F, Nelson BJ (2007) Robotics in the small part 1 IEEE robot. Autom Mag 14:92–103
Berlincourt DA, Cmolik C, Jaffe H (1960) Piezoelectric properties of polycrystalline lead titanate zirconate compositions. Proc IRE 48:220–229
Dario P, Hannaford B, Menciassi A (2003) Smart surgical tools and augmenting devices. IEEE Trans Robot Autom 19:782–792
Donald BR, Levey CG, McGray CG, Paprotny I, Rus D (2006) An untethered, electrostatic, globally controllable MEMS micro-robot. J Microelectromechanical Syst 15:1–15
Gokdel YD, Sarioglu B, Mutlu S, Yalcinkaya AD (2009) Design and fabrication of two-axis micromachined steel scanners. J Micro Mech Microeng 19:075001
Jing W, Cappelleri D (2014) A magnetic microrobot with in situ force sensing capabilities. Robotics 3:106–119
Kanda K, Kanno I, Kotera H, Wasa K (2009) Simple fabrication of metal-based piezoelectric MEMS by direct deposition of Pb(Zr, Ti) O3 thin films on titanium substrates. J Microelectromechanical Syst 18:610–615
Kanno I, Kotera H, Wasa K (2003) Measurement of transverse piezoelectric properties of PZT thin films. Sens Actuators A 107:68–74
Karpelson M, Wei GY, Wood RJ (2012) Driving high voltage piezoelectric actuators in microrobotic applications. Sens Actuators A Phys 176:78–89
Khalil ISM, Dijkslag HC, Abelmann L, Misra S (2014) MagnetoSperm: a microrobot that navigates using weak magnetic fields. Appl Phys Lett 104:223701
Kobayashi T, Tsaur J, Maeda R (2005) Fabrication of optical micro scanner driven by PZT actuators. Jpn J Appl Phys 44:7078–7082
Koh KH, Kobayashi T, Hsiao FL, Lee C (2010) Characterization of piezoelectric PZT beam actuators for driving 2D scanning micromirrors. Sens Actuators A 162:336–347
Matsushita S, Kanno I, Adachi K, Yokokawa R, Kotera H (2012) Metal-based piezoelectric microelectromechanical systems scanner composed of Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 thin film on titanium substrate. Microsyst Technol 18:765–771
Pan CL, Ma YT, Yin J, Kong FR, Feng ZH (2010) Miniature orthogonal optical scanning mirror excited by torsional piezo- electric fiber actuator. Sens Actuators A 165:329–337
Park JH, Akedo J, Sato H (2007) High-speed metal-based optical microscanners using stainless-steel substrate and piezoelectric thick films prepared by aerosol deposition method. Sens Actuators A 135:86–91
Pham PH, Dang LB, Vu HN (2010) Micro robot system with moving micro-car driven by electrostatic comb-drive actuators. Microsyst Technol 16:505–510
Ponsky JL (2006) Endoluminal surgery: past, present and future. Surg Endosc Other Interv Tech 20:500–502
Shackelford JF, Alexander W (2000) CRC Materials science and engineering handbook, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Suzuki T, Kanno I, Loverich JJ, Kotera H, Wasa K (2006) Characterization of Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 thin films deposited on stainless steel substrates by RF-magnetron sputtering for MEMS appli- cations. Sens Actuators A 125:382–386
Tomioka K, Kurokawa F, Yokokawa R, Kotera H, Adachi K, Kanno I (2012) Composition dependence of piezoelectric properties of Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 films prepared by combinatorial sputtering. Jpn J Appl Phys 51:9S1
Wang J, Jiao N, Tung S, Liu L (2014) Magnetic microrobot and its application in a microfluidic system. Robot Biomimetics 1:1–8
Wolf RA, Trolier-McKinstry S (2004) Temperature dependence of the piezoelectric response in lead zirconate titanate films. J Appl Phys 95:1397–1406
Wood RJ (2007) Liftoff of a 60 mg flapping-wing MAV. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intel- ligent Robots and Systems 1889–1894
Yasuda Y, Akamatsu M, Tani M, Iijima T, Toshiyoshi H (2005) Piezoelectric 2D-optical micro scanners with PZT thick films. Integr Ferroelectr 76:81–91
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hida, H., Morita, Y., Kurokawa, F. et al. Simple millimeter-scale robot using Pb(Zr, Ti) piezoelectric thin film actuator on titanium substrate. Microsyst Technol 22, 1429–1436 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-2882-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-2882-7