Abstract
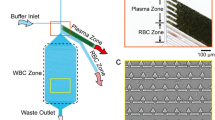
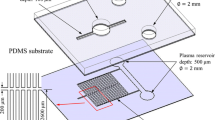
Miniaturized on-chip blood separators have a great value for point-of-care diagnosis. In our work, a combined design strategy—microfiltration, sedimentation in a retarded flow, and wetting contrast—was taken to overcome the known limitations of on-chip blood separators. Our microfluidic chip consists of a polydimethylsiloxane micropillar array and an etched glass with microchannel branches. The red blood cells are significantly slowed and gradually settled down due to micropillars and enlarged dimension of a chamber. An etched glass microchannel allows the extraction of blood plasma exclusively due to the capillary effect. The fabricated microfluidic device can separate blood plasma from a whole blood sample without any external driving force or dilution. The measured plasma separation efficiency was close to 100 % from human whole blood. Autonomous on-chip separation and collection of blood plasma was demonstrated.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campo AD, Greiner C (2007) SU-8: a photoresist for high-aspect-ratio and 3D submicron lithography. J Micromech Microeng 17:R81–R95. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/17/6/R01
Chen J, Chen D, Yuan T, Chen X, Xie Y, Fu H, Cui D, Fan X, Oo MKK (2014) Blood plasma separation microfluidic chip with gradual filtration. Microelectron Eng 128:36–41. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2014.05.032
Chua DBH, Ng HT, Li SFY (2000) Spontaneous formation of complex and ordered structures on oxygen-plasma-treated elastomeric polydimethylsiloxane. Appl Phys Lett 76:721–723. doi:10.1063/1.125873
Cripps CM (1968) Rapid method for the estimation of plasma haemoglobin levels. J Clin Pathol 21:110–112. doi:10.1136/jcp.21.1.110
Di Virgilio V, Bermejo S, Castañer L (2011) Wettability increase by “Corona” ionization. Langmuir 27:9614–9620. doi:10.1021/la2019583
Eifert A, Petit J, Baiera T, Bonaccurso E, Hardt S (2015) Inscribing wettability gradients onto polymer substrates with different stiffness using corona discharge in point-to-plane geometry. Appl Surf Sci 330:104–110. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.12.169
Fung YC (1973) Stochastic flow in capillary blood vessels. Microvas Res 5:34–48. doi:10.1016/S0026-2862(73)80005-6
Geng Z, Ju Y, Wang W, Li Z (2013) Continuous blood separation utilizing spiral filtration microchannel with gradually varied width and micro-pillar array. Sens Act B 180:122–129. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2012.06.064
Göke B, Volker K (1992) HPLC and FPLC. Int J Pancreatol 11:109–116. doi:10.1007/BF02925982
Hillborg H, Tomczak N, Olàh A, Schönherr H, Vancso GJ (2004) Nanoscale hydrophobic recovery: a chemical force microscopy study of UV/ozone-treated cross-linked poly(dimethylsiloxane). Langmuir 20:785–794. doi:10.1021/la035552k
Kang KH, Kang Y, Xuan X, Li D (2006) Continuous separation of microparticles by size with direct current-dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 27:694–702. doi:10.1002/elps.200500558
Kerhoas MK, Dhariwal R, Desmulliez MPY, Jouvet L (2010) Hydrodynamic blood plasma separation in microfluidic channels. J Microfluid Nanofluid 8:105–114. doi:10.1007/s10404-009-0450-5
Kim D (2009) Effect of microstructure on blood cell clogging in blood separators based on capillary action. Microsyst Technol 15:227–233. doi:10.1007/s00542-008-0663-7
Lee KK, Ahn CH (2013) A new on-chip whole blood/plasma separator driven by asymmetric capillary forces. Lab Chip 13:3261–3267. doi:10.1039/C3LC50370D
Lee JH, Khang G, Lee JW, Lee HB (1997) Interaction of cells on chargeable functional group gradient surfaces. Biomaterials 18:351–358. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(96)00128-7
Lee JH, Khang G, Lee JW, Lee HB (1998) Interaction of different types of cells on polymer surfaces with Wettability gradient. J Colloid Interface Sci 205:323–330. doi:10.1006/jcis.1998.5688
Lee S, Lee C, Kim B, Kim Y (2003) Quantitatively controlled nanoliter liquid manipulation using hydrophobic valving and control of surface wettability. J Micromech Microeng 13:89–97. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/13/1/313
Lee D, Sukumar P, Mahyuddin A, Choolani M, Xu G (2010) Separation of model mixtures of epsilon-globin positive fetal nucleated red blood cells and anucleate erythrocytes using a microfluidic device. J Chromatogr A 1217:1862–1866. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2010.01.065
Park JB, Bronzino JD (2003) Biomaterials: principles and applications. CRC Press, USA
Psychogios N, Hau DD, Peng J, Guo AC, Mandal R, Bouatra S, Sinelnikov I, Krishnamurthy R, Eisner R, Gautam B, Young N, Xia J, Knox C, Dong E, Huang P, Hollander Z, Pedersen TL, Smith SR, Bamforth F, Greiner R, McManus B, Newman JW, Goodfriend T, Wishart DS (2011) The human serum metabolome. PLoS One 6:e16957. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016957
Sakamoto H, Hatsuda R, Miyamura K, Sugiyama S (2012) Plasma separation PMMA device driven by capillary force controlling surface wettability. Micro Nano Lett 7:64–67. doi:10.1049/mnl.2011.0627
Sathyakumar SK, Ali Asgar SB, Girish K, Papautsky I (2009) Inertial microfluidics for continuous particle separation in spiral microchannels. Lab Chip 9:2973–2980. doi:10.1039/B908271A
Sheehan D, O’Sullivan SM (2004) Fast protein liquid chromatography in protein purification protocols. In: Cutler P (ed) Methods in molecular biology series, 2nd edn. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 253–258
Shim JS, Ahn CH (2012) An on-chip whole blood/plasma separator using hetero-packed beads at the inlet of a microchannel. Lab Chip 12:863–866. doi:10.1039/C2LC21009F
Sun M, Khan ZS, Vanapalli SA (2012) Blood plasma separation in a long two-phase plug flowing through disposable tubing. Lab Chip 12:5225–5230. doi:10.1039/C2LC40544J
Svanes K, Zweifach BW (1968) Variations in small blood vessel hematocrits produced in hypothermic rats by micro-occlusion. Microvas Res 1:210–220. doi:10.1016/0026-2862(68)90019-8
Tachi T, Kaji N, Tokeshi M, Baba Y (2009) Simultaneous separation, metering, and dilution of plasma from human whole blood in a microfluidic system. Anal Chem 81:3194–3198. doi:10.1021/ac802434z
Tamada Y, Ikada Y (1993) Cell adhesion to plasma-treated polymer surfaces. Polymer 34:2208–2212. doi:10.1016/0032-3861(93)90752-V
Tanaka T, Ishikawa T, Numayama-Tsuruta K, Imai Y, Ueno H, Matsuki N, Yamaguchi T (2012) Separation of cancer cells from a red blood cell suspension using inertial force. Lab Chip 12:4336–4343. doi:10.1039/C2LC40354D
Thorslund S, Klett O, Nikolajeff F, Markides K, Bergquist J (2006) A hybrid poly (dimethylsiloxane) microsystem for on-chip whole blood filtration optimized for steroid screening. Biomed Microdevices 8:73–79. doi:10.1007/s10544-006-6385-7
Tsutsui H, Kawano T (2013) Blood plasma separator using Micro pillars arranged like a labyrinth. In: 17th International Conference Miniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences, pp 1810–1812
Van Wachem PB, Hogt AH, Beugeling T, Feijen J, Bantjes A, Detmers JP, Van Aken WG (1987) Adhesion of cultured human endothelial cells onto methacrylate polymers with varying surface wettability and charge. Biomaterials 8:323–328. doi:10.1016/0142-9612(87)90001-9
VanDelinder V, Groisman A (2006) Separation of plasma from whole human blood in a continuous cross-flow in a molded microfluidic device. Anal Chem 78:3765–3771. doi:10.1021/ac060042r
Verbeke K, Verbruggen A (1996) Usefulness of fast protein liquid chromatography as an alternative to high performance liquid chromatography of 99mTc-labelled human serum albumin preparations. J Pharm Biomed Anal 14:1209–1213. doi:10.1016/S0731-7085(95)01755-0
Wintrobe MM, Greer JP (2009) Wintrobe’s clinical hematology. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia
Yang S, Undar A, Zahn JD (2006) A microfluidic device for continuous, real time blood plasma separation. Lab Chip 6:871–880. doi:10.1039/B516401J
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute Primary Research Program through the Korea Research Council for Industrial Science and Technology funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (No. 13-12-N0201-07), and Namjeong Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S., Shabani, R., Schumacher, M. et al. On-chip whole blood plasma separator based on microfiltration, sedimentation and wetting contrast. Microsyst Technol 22, 2077–2085 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2656-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2656-7