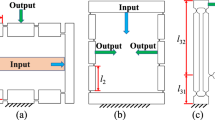
Abstract
This paper presents a novel piezo-driven microgripper for micromanipulation. A two-grade amplification mechanism is introduced to enlarge the jaw displacement of the microgripper driven by a piezoelectric actuator (PEA). The design adopts a hybrid flexure structure that integrates flexure hinge and flexure beam to combine their advantages to further improve the microgripper performance. The mechanical designs of two microgrippers with different output manners are first described, one of which is selected to conduct the detailed modeling and analysis. Subsequently, the finite element analysis (FEA) is performed to verify the microgripper performance and the effectiveness of the established models for the investigation of optimum structure parameters. Finally, after the prototype is fabricated, the experimental results show that the developed microgripper possesses the high-precision grasping capacity for different shaped and sized microobjects. Moreover, a large jaw displacement of 150.8 μm corresponding to the 100 V drive voltage and a high amplification ratio of 16.4 can be obtained.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassan HS, Patel RV, Moallem M (2009) A novel manipulator for percutaneous needle insertion: design and experimentation. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 14:746–761
Butefisch S, Seidemann V, Buttgenbach S (2002) Novel micro-pneumatic actuator for MEMS. Sens Actuator A Phys 97–98:638–645
Chang H, Zhao H, Ye F, Yuan G, Xie J, Kraft M, Yuan W (2014) A rotary comb-actuated microgripper with a large displacement range. Microsyst Technol 20:119–126
Chen WJ, Lin W (2008) Fiber assembly of MEMS optical switches with U-groove channels. IEEE Trans Automat Sci Eng 5:207–215
Chen T, Chen L, Sun L, Li X (2009) Design and fabrication of a four-arm-structure MEMS gripper. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 56:996–1004
Choi KB, Kim DH (2006) Monolithic parallel linear compliant mechanism for two axes ultraprecision linear motion. Rev Sci Instrum 77:065106
Howell LL (2001) Compliant mechanism. Wiley, New York
Kim DH, Lee MG, Kim B, Sun Y (2005) A superelastic alloy microgripper with embedded electromagnetic actuators and piezoelectric force sensors: a numerical and experimental study. Smart Mater Struct 14:1265–1272
Kim K, Liu X, Zhang Y, Sun Y (2008) Nanonewton force-controlled manipulation of biological cells using a monolithic MEMS microgripper with two-axis force feedback. J Micromech Microeng 18:055013
Kim BS, Park JS, Kang BH, Moon C (2012a) Fabrication and property analysis of a MEMS micro-gripper for robotic micro-manipulation. Bobot Com Int Manuf 28:50–56
Kim K, Ahn D, Gweon D (2012b) Optimal design of a 1-rotational DOF flexure joint of a 3-DOF H-type stage. Mechatronics 22:24–32
Li Y, Xu Q (2009) Design and analysis of a totally decoupled flexure-based XY parallel micromanipulator. IEEE Trans Robot 25:645–657
Nah SK, Zhong ZW (2007) A microgripper using piezoelectric actuation for micro-object manipulation. Sensor Actuator A Phys 133:218–224
Ouyang PR, Zhang WJ, Gupta MM, Zhao W (2007) Overview of the development of a visual based automated bio-micromanipulation system. Mechatronics 17:578–588
Paros JM, Weisbord L (1965) How to design flexure hinges. Mach Des 37:151–156
Raghavendra MRA, Kumar AS, Jagdish BN (2010) Design and analysis of flexure-based parameter in microgripper. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 49:1185–1193
Sun X, Chen W, Zhou R, Chen W, Zhang J (2013) A force-decoupled compound parallel alignment stage for nanoimprint lithography. Rev Sci Instrum 84:125002
Tang X, Chen I, Li Q (2006) Design and nonlinear modeling of a large-displacement XYZ flexure parallel mechanism with decoupled kinematic structure. Rev Sci Instrum 77:115101
Tian Y, Shirinzadeh B, Zhang D (2009) A flexure-based mechanism and control methodology for ultra-precision turning operation. Precis Eng 33:160–166
Tian Y, Shirinzadeh B, Zhang D (2010) Design and dynamics of a 3-DOF flexure-based parallel mechanism for micro/nano manipulation. Microelectron Eng 87:230–241
Tsui K, Geisberger AA, Ellis M, Skidmore GD (2004) Micromachined end-effector and techniques for directed MEMS assembly. J Micromech Microeng 14:542–549
Volland BE, Heerlein H, Rangelow IW (2002) Electrostatically driven microgripper. Microelectron Eng 61–62:1015–1023
Zesch W, Brunner M, Weber A (1997) Vacuum tool for handling microobjects with a nanorobot. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Albuquerque, New Mexico, pp 1761–1766
Zhang Y, Chen BK, Liu X, Sun Y (2010) Autonomous robotic pick-and-place of microobjects. IEEE Trans Robot 26:200–207
Zhang R, Chu J, Wang H, Chen Z (2013) A multipurpose electrothermal microgripper for biological micro-manipulation. Microsyst Technol 19:89–97
Zhong ZW, Yeong CK (2006) Development of a gripper using SMA wire. Sensor Actuator A Phys 126:375–381
Zubir MNM, Shirinzadeh B (2009) Development of a high precision flexure-based microgripper. Precis Eng 33:362–370
Zubir MNM, Shirinzadeh B, Tian Y (2009) A new design of piezoelectric driven compliant-based microgripper for micromanipulation. Mech Mach Theory 44:2248–2264
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 51275018, Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China under Grant No. 20131102110010 and Innovation Foundation of BUAA for PhD Graduates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Chen, W., Fatikow, S. et al. A novel piezo-driven microgripper with a large jaw displacement. Microsyst Technol 21, 931–942 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2199-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2199-3