Abstract
Background
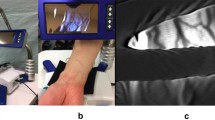
The current available literature is not unanimous in reporting the utility of short-axis and long-axis techniques for radial artery cannulation in both adults and children. This study was designed to compare short-axis out-of-plane (SA-OOP) and long-axis in-plane (LA-IP) techniques in ultrasound-guided radial artery cannulation in adults.
Methods
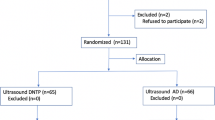
In this prospective randomized controlled trial, 150 adult patients of American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I–III aged between 18 and 70 years were included. All patients were randomized into two groups (group SA-OOP) and (group LA-IP) of 75 each undergoing ultrasound-guided radial artery cannulation. The primary outcome was successful cannulation in the first attempt. Secondary outcomes included antero-posterior arterial diameter, skin-to-artery distance, ultrasonic localization time, cannulation time, no of attempts to cannulate artery, cannula insertion failure, and vascular complications.
Results
First-attempt arterial cannulation was successful in 80 % of patients in the SA-OOP group as opposed to 82.6 % patients in the LA-IP group (p = 0.67). The time to cannulate the artery was similar between the two groups, but the time to localize artery was significantly higher in the long-axis technique (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
The first-attempt cannulation success rate and cannulation time in adult patients are similar in ultrasound-guided radial artery cannulation with both short-axis as well as long-axis techniques.
Trial registration Clinical Trial Registry of India (CTRI/2015/02/005552).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berk D, Gurkan Y, Kus A, Ulugol H, Solak M, Toker K. Ultrasound-guided radial arterial cannulation: long-axis/in-plane versus short-axis/out-of-plane approaches. J Clin Monit Comput. 2013;27:319–24.
Sandhu NS, Patel B. Use of ultrasonography as a rescue technique for failed radial artery cannulation. J Clin Anesth. 2006;18:138–41.
White L, Halpin A, Turner M, Wallace L. Ultrasound-guided radial artery cannulation in adult and paediatric populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2016;116:610–7.
Gu WJ, Wu XD, Wang F, Ma ZL, Gu XP. Ultrasound guidance facilitates radial artery catheterization: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials. Chest. 2016;149:166–79.
Ueda K, Puangsuvan S, Hove MA, Bayman EO. Ultrasound visual image-guided vs Doppler auditory-assisted radial artery cannulation in infants and small children by non-expert anaesthesiologists: a randomized prospective study. Br J Anesth. 2013;110:281–6.
Latham GJ, Veneracion ML, Joffe DC, Bosenberg AT, Flack SH, Low DK. High-frequency micro-ultrasound for vascular access in young children–a feasibility study by the high-frequency ultrasound in kids study (husky) group. Pediatr Anesth. 2013;23:529–63.
Brzezinski M, Luisetti T, London MJ. Radial artery cannulation: a comprehensive review of recent anatomic and physiologic investigations. Anesth Analg. 2009;109:1763–81.
Edanaga M, Mimura M, Azumaguchi T, Kimura M. Yamakage M [Comparison of ultrasound-guided and blindly placed radial artery catheterization]. Masui. 2012;61:221–4.
Chittoodan S, Breen D, O’Donnell BD, Iohom G. Long versus short-axis ultrasound-guided approach for internal jugular vein cannulation: a prospective randomised controlled trial. Med Ultrason. 2011;13:21–5.
Sommerkamp SK, Romaniuk VM, Witting MD, Ford DR, Allison MG, Euerle BD. A comparison of longitudinal and transverse approaches to ultrasound-guided axillary vein cannulation. Am J Emerg Med. 2013;31:478–81.
Stone MB, Moon C, Sutijono D, Blaivas M. Needle tip visualization during ultrasound-guided vascular access: short-axis vs long-axis approach. Am J Emerg Med. 2010;28:343–7.
Quan ZF, Ming T, Ping C, Cao YH, Li X, Peng KJ. Modified short-axis out-of-plane ultrasound versus conventional long-axis in-plane ultrasound to guide radial artery cannulation: a randomized controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2014;119:163–9.
Song IK, Choi JY, Lee JH, Kim EH, Kim HJ, Kim HS, Kim JT (2016) Short-axis/out-of-plane or long-axis/in-plane ultrasound-guided arterial cannulation in children: a randomised controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. [Epub ahead of print].
Stone MB, Moon C, Sutijono D, Blaivas M. Needle tip visualization during ultrasound-guided vascular access: short-axis vs long-axis approach. Am J Emerg Med. 2010;28:343–7.
Blaivas M, Brannam L, Fernandez E. Short-axis versus long-axis approaches for teaching ultrasound-guided vascular access on a new inanimate model. Acad Emerg Med. 2003;10:1307–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was conducted after approval of Institute Ethics Committee of Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (NK/1852/Res/265, dated 24.12.2014) and was prospectively registered with the Clinical Trial Registry of India (CTRI) with an assigned number of (CTRI/2015/02/005552).
About this article
Cite this article
Sethi, S., Maitra, S., Saini, V. et al. Comparison of short-axis out-of-plane versus long-axis in-plane ultrasound-guided radial arterial cannulation in adult patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Anesth 31, 89–94 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-016-2270-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-016-2270-6