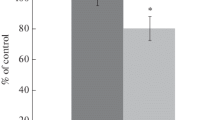
Abstract
Background
Nitrite-derived NO protects against middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. We developed a new mouse model of global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion (GCI/R) involving reversible occlusion of the major vessels from the aortic arch supplying the brain, and investigated neuroprotection with dietary sodium nitrite supplementation against GCI/R injury.
Methods
Mice received drinking water with (nitrite group) or without (control group) sodium nitrite (2 mM) for 5 days and underwent 3-min GCI/R by reversible occlusion of major vessels from the aortic arch (i.e., brachiocephalic, left common carotid, and left subclavian artery). Survival rates and neurological function scores were evaluated for up to 5 days after GCI/R. Histopathological studies were performed to detect neurological degeneration and caspase-3 activation in serial hippocampal sections.
Results
In the control group, 17/30 mice (57 %) survived 5 days after 3-min GCI/R, whereas in the nitrite group 25/30 mice (83 %) survived (p < 0.05). The neurological score at 5 days after GCI in control group was significantly higher than in the nitrite group. Cerebral blood flow (CBF) during GCI was significantly higher in the nitrite group than in the control group, while MABP did not differ significantly between groups. Degenerative changes and caspase-3 activation in hippocampal sections after GCI were observed in the control group but not in the nitrite group. Pretreatment with the NO scavenger c-PTIO abolished the neuroprotective effects of sodium nitrite.
Conclusions
Sodium nitrite supplementation attenuated mortality and neurological impairment after 3-min GCI in mice; an effect likely mediated via vascular mechanisms involving NO.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cosby K, Partovi KS, Crawford JH, Patel RP, Reiter CD, Martyr S, Yang BK, Waclawiw MA, Zalos G, Xu X, Huang KT, Shields H, Kim-Shapiro DB, Schechter AN, Cannon IIIRO, Gladwin MT. Nitrite reduction to nitric oxide by deoxyhemoglobin vasodilates the human circulation. Nat Med. 2003;9:1498–505.
Dimmeler S, Zeiher AM. Nitric oxide-an endothelial cell survival factor. Cell Death Differ. 1999;6:964–8.
Contestabile A, Ciani E. Role of nitric oxide in the regulation of neuronal proliferation, survival and differentiation. Neurochem Int. 2004;45:903–14.
Radomski MW, Palmer RMJ, Moncada S. Endogenous nitric oxide inhibits human platelet adhesion to vascular endothelium. Lancet. 1987;2:1057–8.
Jung KH, Chu K, Ko SY, Lee ST, Sinn DI, Park DK, Kim JM, Song EC, Kim M, Roh JK. Early intravenous infusion of sodium nitrite protects brain against in vivo ischemia-reperfusion injury. Stroke. 2006;37:2744–50.
Brown GC. Nitric oxide and mitochondrial respiration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1411:351–69.
Duranski MR, Greer JJM, Dejam A, Jaganmohan S, Hogg N, Langston W, Patel RP, Yet SF, Wang X, Kevil CG, Gladwin MT, Lefer DJ. Cytoprotective effects of nitrite during in vivo ischemia-reperfusion of the heart and liver. J Clinical Investigation. 2005;115:1232–40.
Lu P, Liu F, Yao Z, Wang CY, Chen DD, Tian Y, Zhang JH, Wu YH. Nitrite-derived nitric oxide by xanthine oxidoreductase protects the liver against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2005;4:350–5.
Webb A, Bond R, McLean P, Uppal R, Benjamin N, Ahluwalia A. Reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide during ischemia protects against myocardial ischemia–reperfusion damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:2–7.
Baker JE, Su J, Fu X, Hsu A, Gross GJ, Tweddell JS, Hogg N. Nitrite confers protection against myocardial infarction: role of xanthine oxidoreductase, NADPH oxidase and K(ATP) channels. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;43:437–44.
Tripatara P, Patel NSA, Webb A, Rathod K, Lecomte FMJ, Mazzon E, Cuzzocrea S, Yaqoob MM, Ahluwalia A, Thiemermann C. Nitrite-derived nitric oxide protects the rat kidney against ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo: role for xanthine oxidoreductase. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:570–80.
Dezfulian C, Shiva S, Alekseyenko A, Pendyal A, Beiser DG, Munasinghe JP, Anderson SA, Chesley CF, Vanden Hoek TL, Gladwin MT. Nitrite therapy after cardiac arrest reduces reactive oxygen species generation, improves cardiac and neurological function, and enhances survival via reversible inhibition of mitochondrial complex I. Circulation. 2009;120:897–905.
Thal SC, Thal SE, Plesnila N. Characterization of a 3-vessel occlusion model for the induction of complete global cerebral ischemia in mice. J Neurosci Methods. 2010;192:219–27.
Zivin J, Waud DR. Quantal bioassay and stroke. Stroke. 1992;23:767–73.
Kleinbongard P, Dejam A, Lauer T, Rassaf T, Schindler A, Picker O, Scheeren T, Godecke A, Schrader J, Schulz R, Heusch G, Schaub GA, Bryan NS, Feelisch M, Kelm M. Plasma nitrite reflects constitutive nitric oxide synthase activity in mammals. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003;35:790–6.
Bryan NS. Nitrite in nitric oxide biology: cause or consequence? A systems-based review. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;41:691–701.
Kleinbongard P, Dejam A, Lauer T, Jax T, Kerber S, Gharini P, Balzer J, Zotz RB, Scharf RE, Willers R, Schechter AN, Feelisch M, Kelm M. Plasma nitrite concentrations reflect the degree of endothelial dysfunction in humans. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;40:295–302.
Raat NJH, Noguchi AC, Liu VB, Raghavachari N, Liu D, Xu X, Shiva S, Munson PJ, Gladwin MT. Dietary nitrate and nitrite modulate blood and organ nitrite and the cellular ischemic stress response. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009;47:510–7.
Zuckerbraun BS, Shiva S, Ifedigbo E, Mathier MA, Mollen KP, Rao J, Bauer PM, Choi JJW, Curtis E, Choi AMK, Gladwin MT. Nitrite potently inhibits hypoxic and inflammatory pulmonary arterial hypertension and smooth muscle proliferation via xanthine oxidoreductase-dependent nitric oxide generation. Circulation. 2010;121:98–109.
Gonzalez FM, Shiva S, Vincent PS, Ringwood LA, Hsu LY, Hon YY, Aletras AH, Cannon IIIRO, Gladwin MT, Arai AE. Nitrite anion provides potent cytoprotective and antiapoptotic effects as adjunctive therapy to reperfusion for acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2008;117:2986–94.
Kumar D, Branch BG, Pattillo CB, Hood J, Thoma S, Simpson S, Illum S, Arora N, Chidlow JH, Lagston W, Teng X, Lefer DJ, Patel RP, Kevil CG. Chronic sodium nitrite therapy augments ischemia-induced angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:7540–5.
Raat NJH, Shiva S, Gladwin MT. Effects of nitrite on modulating ROS generation following ischemia and reperfusion. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61:339–50.
Pluta RM, Dejam A, Grimes G, Gladwin MT, Oldfield EH. Nitrite infusions to prevent delayed cerebral vasospasm in a primate model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. JAMA. 2005;293:1477–84.
Fukuyama N, Takizawa S, Ishida H, Hoshiai K, Shinohara Y, Nakazawa H. Peroxynitrite formation in focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats occurs predominantly in the peri-infarct region. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996;18:123–9.
Dawson VL, Dawson TM, London ED, Bredt DS, Snyder SH. Nitric oxide mediates glutamate neurotoxicity in primary cortical cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:6368–71.
Nishida T, Yu JD, Minamishima S, Sips PY, Searles RJ, Buys ES, Janssens S, Brouckaert P, Bloch KD, Ichinose F. Protective effects of nitric oxide synthase 3 and soluble guanylate cyclase on the outcome of cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation in mice. Crit Care Med. 2009;37:256–62.
Acknowledgments
We thank Masato Tsutsui MD, Ph.D and Mayuko Sakanashi Ph.D for technical assistance for measuring cGMP level.
Financial Disclosure Statement
This work was supported by a Grant-in-aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education of JAPAN (B) 25293329 to M. K. and Grant-in-aid for challenging exploratory research JAPAN 25670559 to M. K.
Conflict of interest
Takasuke Fukuda, Manabu Kakinohana, Chitoshi Takayama, Masayuki Matsushita, and Kazuhiro Sugahara have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Fukuda, T., Kakinohana, M., Takayama, C. et al. Dietary supplementation with sodium nitrite can exert neuroprotective effects on global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in mice. J Anesth 29, 609–617 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-014-1968-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-014-1968-6