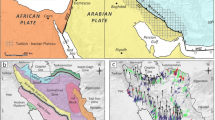
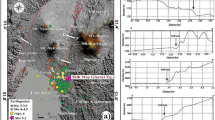
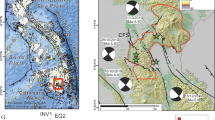
Abstract
A significant amount of work has been conducted in the Japanese islands on high-precision positioning, surveying, natural disaster mitigation, reference frame, and datum definitions; however, there is substantial scope for exploring the current seismotectonic activity of Japan, which would provide further awareness of disaster management. The short recurrence time of great inter-plate earthquakes and well-recorded geodetic observations provide one of the best examples to analyze the combination of contemporary deformation and seismic intensity in Southwest (SW) Japan. In the current study, we analyzed three districts of SW Japan which include mainly Kyushu district and parts of Chugoku and Shikoku districts. We predicted Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) measurements based on Amurian-fixed reference frame (AREF) velocities with the help of singular spectrum analysis (SSA) method and examined the regional deformation from April 01, 2010 to December 31, 2018. In addition, we analyzed the earthquakes clustered calculated by the nearest neighborhood distance method, which showed prominently bimodal seismicity of SW Japan and revealed the existence of two statistically distinct earthquake populations. The events inside a cluster were normally close to their nearest neighbors, whereas events from distinct clusters were comparatively aloof from each other. Finally, the paper provides the spatial strain and rotational rate variation for selected seismotectonic districts that are in relatively good agreement with the seismic deformation inferred from earthquake focal mechanisms. We believe that our integrated approaches would provide a better insight into the active deformation of SW Japan.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando M (1975) Source mechanisms and tectonic significance of historical earthquakes along the Nankai trough, Japan. Tectonophysics 27:119–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(75)90102-X
Ansari K (2018) Crustal deformation and strain analysis in Nepal from GPS time-series measurement and modeling by ARMA method. Int J Earth Sci 107(8):2895–2905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-018-1633-7
Ansari K, Park KD (2018) Multi constellation GNSS precise point positioning and prediction of propagation errors using singular spectrum analysis. Astrophys Space Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-018-3479-7
Ansari K, Corumluoglu O, Sharma SK (2017) Numerical simulation of crustal strain in Turkey from continuous GNSS measurements in the interval 2009–2017. J Geodetic Sci 7(1):113–129. https://doi.org/10.1515/jogs-2017-0013
Baiesi M, Paczuski M (2004) Scale-free networks of earthquakes and aftershocks. Phys Rev E 69(6):066106. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.69.066106
Barnes GL (2003) Origins of the Japanese Islands: The New” Big Picture”. Nichibunken Japan Review, 3–50; https://www.jstor.org/stable/25791268
Bautista J (2011) Nearest-neighbor analysis of marked point fields with applications to cluster analysis of seismicity. Undergraduate Honors Thesis, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Nevada, Reno, May 2011
Cook DB, Fujita K, McMullen CA (1986) Present day plate interactions in northeast Asia: North American, Eurasian, and Okhotsk plates. J Geodyn 6:33–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/0264-3707(86)90031-1
El-Fiky G, Kato T (2006) Secular crustal deformation and interplate coupling of the Japanese Islands as deduced from continuous GPS array, 1996-2001. Tectonophysics 422(1–4):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2006.04.021
El-Fiky GS, Kato T, Oware EN (1999) Crustal deformation and interplate coupling in the Shikoku district, Japan, as seen from continuous GPS observation. Tectonophysics 314(4):387–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00226-7
Ghil M, Allen MR, Dettinger MD, Ide K, Kondrashov D, Mann ME, Robertson AW, Saunders A, Tian Y, Varadi F, Yiou P (2002) Advanced spectral methods for climatic time series. Rev Geophys 40(1):3-1. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000RG000092
Hashimoto C, Noda A, Sagiya T, Matsu’ura M (2009) Interplate seismogenic zones along the Kuril-Japan trench inferred from GPS data inversion. Nat. Geosci 2,141–144, https://www.nature.com/articles/ngeo421. Accessed 30 June 2019
Hassani H (2007) Singular spectrum analysis: methodology and comparison, J Data Sci 4991, 239-257. https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/4991/. Accessed 30 June 2019
Hassani H, Heravi S, Zhigljavsky A (2009) Forecasting European industrial production with singular spectrum analysis. Int J Forecast 25(1):103–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijforecast.2008.09.007
Herring TA, King RW, McClusky SC (2010) Introduction to GAMIT/GLOBK. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Massachusetts
Hicks, A. (2011), Clustering in multidimensional spaces with applications to statistical analysis of earthquake clustering, MSc Thesis, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Nevada, Reno, August 2011
Hoshizumi H, Ozaki M, Miyazaki K, Matsuura H, Toshimitsu S, Uto K et al (2004) Geologic map of Japan 1:200,000. Geological Survey of Japan, AIST, Kumamoto
Huang Z, Wang L, Zhao D, Mi N, Xu M (2011) Seismic anisotropy and mantle dynamics beneath China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 306(1–2):105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2011.03.038
Ide S (2013) The proportionality between relative plate velocity and seismicity in subduction zones. Nat Geosci 6, 780-784, https://www.nature.com/articles/ngeo1901
Ito T (2004) Spatiotemporal distribution of interplate coupling in southwest Japan from inversion of geodetic data. J Geophys Res 109:B02315–B02335. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JB002358
Loveless JP, Meade BJ (2010) Geodetic imaging of plate motions, slip rates, and partitioning of deformation in Japan. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JB006248
Maruyama S, Isozaki Y, Kimura G, Terabayashi M (1997) Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands: plate tectonic synthesis from 750 Ma to the present. Island Arc 6(1):121–142. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1738.1997.tb00043.x
Mukul M, Jade S, Ansari K, Matin A (2014) Seismotectonic implications of strike-slip earthquakes in the Darjeeling-Sikkim Himalaya. Curr Sci 106 (2): 198-210; https://www.currentscience.ac.in/cs/Volumes/106/02/0198.pdf
Mukul M, Jade S, Ansari K, Matin A, Joshi V (2018) Structural insights from geodetic Global Positioning System measurements in the Darjiling-Sikkim Himalaya. J Struct Geol 114:346–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2018.03.007
Sagiya T (1995) Crustal deformation cycle and interplate coupling in Shikoku, Southwest Japan, Ph. D. Thesis, Univ. of Tokyo, 164 pp
Sagiya T, Miyazaki S, Tada T (2000) Continuous GPS array and present-day crustal deformation of Japan. Pure Appl. Geophys 157(11–12):2303–2322. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00022507
Sella GF, Dixon TH, Mao A (2002) REVEL: a model for Recent plate velocities from space geodesy. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JB000033
Seno T (1999) Syntheses of the regional stress fields of the Japanese islands. Island Arc 8:66–79. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1738.1999.00225.x
Seno T, Stein S, Gripp AE (1993) A model for the motion of the Philippine Sea plate consistent with NUVEL-1 and geological data. J Geophys Res 98:17941–17948. https://doi.org/10.1029/93JB00782
Seno T, Sakurai T, Stein S (1996) Can the Okhotsk plate be discriminated from the North American plate? J Geophys Res 101:27957–27980. https://doi.org/10.1029/96JB00532
Shiono K, Mikumo T, Ishikawa Y (1980) Tectonics of the Kyushu-Ryukyu arc as evidenced from seismicity and focal mechanism of shallow to intermediate-depth earthquakes. J. Phys. Earth 28:17–43. https://doi.org/10.4294/jpe1952.28.17
Simons M, Minson SE, Sladen A, Ortega F, Jiang J, Owen SE, Meng L, Ampuero JP, Wei S, Chu R, Helmberger DV (2011) The 2011 magnitude 9.0 Tohoku-Oki earthquake Mosaicking the megathrust from seconds to centuries. Science 332(6036):1421–1425. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.l206731
Sun A, Zhao D, Ikeda M, Chen Y, Chen Q (2008) Seismic imaging of southwest Japan using P and PmP data: implications for arc magmatism and seismotectonics. Gondwana Res. 14:535–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2008.04.004
Tabei T, Adachi M, Miyazaki SI, Watanabe T, Kato S (2007) Inter-seismic deformation of the Nankai subduction zone, southwest Japan, inferred from three-dimensional crustal velocity fields. Earth, Planets and Space 59(10):1073–1082. https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352050
Tada T (1984) Spreading of the Okinawa Trough and its relation to the crustal deformation in Kyushu. Zishin 37, 407–415 (in Japanese); https://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10007640556/
Takayama H, Yoshida A (2007) Crustal deformation in Kyushu derived from GEONET data. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JB004690
Teza G, Galgaro A (2008) Grid_strain and grid_strain3: software packages for strain field computation in 2D and 3D environment. Comput. Geosci 34(9):1142–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2007.07.006
Tsuji H, Miyagawa K, Yamaguchi K, Yahagi T, Oshima K, Yamao H, Furuya T (2013), Modernization of GEONET from GPS to GNSS. Bulletin of the Geospatial Information Authority of Japan, 61(12), 9–20; https://web1.gsi.go.jp/common/000085715.pdf
Umeda K, Asamori K, Negi T, Kusano T (2011) A large intraplate earthquake triggered by latent magmatism. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 116:B01207. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JB007963
Vautard R, Yiou P, Ghil M (1992) Singular-spectrum analysis: a toolkit for short, noisy chaotic signal. Physica D 58:95–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2789(92)90103-T
Wakita K (2013) Geology and tectonics of Japanese islands: a review–the key to understanding the geology of Asia. J Asian Earth Sci 72:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.04.014
Wei D, Seno T (1998) Determination of the Amurian plate motion in mantle dynamics and plate interactions in East Asia. In: Flower M et al. (ed), Geodyn. Series, vol. 27, pp. 337–346, 10.1029/GD027p0337
Yamasaki T, Seno T (2005) High strain rate zone in central Honshu resulting from the viscosity heterogeneities in the crust and mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett 232:13–27. https://doi.org/10.1029/GD027p0337
Zabalza J, Ren J, Zheng J, Han J, Zhao H, Li S, Marshall S (2015) Novel two-dimensional singular spectrum analysis for effective feature extraction and data classification in hyperspectral imaging. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 53(8):4418–4433. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2015.2398468
Zaliapin I, Gabrielov A, Keilis-Borok V, Wong H (2008) Clustering analysis of seismicity and aftershock identification. Phys Rev Low-frequency earthquakes and tomography in western Japan: insight into fluid and magmatic activity 101(1):018501. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.018501
Zhao D, Wei W, Nishizono Y, Inakura H (2011) Low-frequency earthquakes and tomography in western Japan: insight into fluid and magmatic activity. J. Asian Earth Sci. 42:1381–1393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.08.003
Zhao D, Fujisawa M, Toyokuni G (2017) Tomography of the subducting Pacific slab and the 2015 Bonin deepest earthquake (Mw 7.9). Scientific reports 7:44487. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44487
Zonenshain LP, Savostin A (1981) Geodynamics of the Baikal Rift zone and plate tectonics of Asia. Tectonophysics 76:1–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(81)90251-1
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2016R1D1A1B01009872). The authors appreciate the GNSS Earth Observation Network (GEONET) for establishing and maintaining the GNSS stations in Japan. This GNSS data are available at the Geospatial Information Authority of Japan (GSI) website (http://terras.gsi.go.jp). The author also thanks Prof. Bob King from MIT for providing the GAMIT-GLOBK software and helping to resolve the issues related to the software. Our sincere thanks to Prof. G. Teza for giving the strain analysis software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ansari, K., Park, KD. Contemporary deformation and seismicity analysis in Southwest Japan during 2010–2018 based on GNSS measurements. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 108, 2373–2390 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-019-01768-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-019-01768-w