Abstract
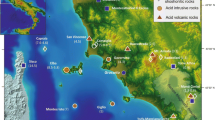
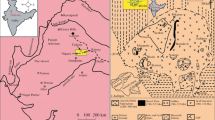
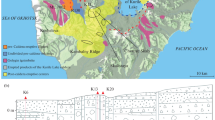
The Zafarghand Igneous Complex is composed of granite, granodiorite, diorite, and gabbro that contain many mafic microgranular enclaves. This complex was emplaced during the late Oligocene (24.6 Ma) to form part of the Urumieh–Dokhtar magmatic arc of Central Iran. The enclaves have spheroidal to elongated/lenticular shapes and are quenched mafic melts in felsic host magma as evidenced by fine-grained sinuous margins and (or) locally transitional and diffuse contacts with the host rocks, as well as having disequilibrium textures. These textures including oscillatory zoning with resorption surfaces on plagioclase, feldspar megacrysts with poikilitic and anti-rapakivi textures, mafic clots, acicular apatites, and small lath-shaped plagioclase in larger plagioclase crystals all indicate that the enclaves crystallized from mafic magma that was injected into and mixing/mingling with the host felsic magma. The studied rocks have calc-alkaline, metaluminous compositions, with an arc affinity. They are enriched in large ion lithophile elements, light rare-earth elements, and depleted in high field strength elements with significant negative Eu anomalies. The Sr–Nd isotopic data for all of the samples are similar and display ISr = 0.705123–0.705950 and εNd (24.6 Ma) = − 1.04–1.03 with TDM ~ 0.9–1.1 Ga. The host granites and enclaves are of mixed/mingled origin and most probably formed by the interaction between the juvenile lower crust with a basaltic composition and old lower or middle continental crust as a major component and lithospheric mantle as a minor component; this was followed by fractional crystallization and possibly minor crustal assimilation. The source seems to be comprised of about 90–80% of the basaltic magma and about 10–20% of lower/middle-crust-derived magma. Geochemical characteristics indicate that the intrusion of these rocks from a subduction zone setting below the Central Iran micro-continent was related to an active continental margin, although was transitional to a transtensional setting possibly due oblique convergence to slab rollback or break-off.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agard P, Omrani J, Jolivet L, Mouthereau F (2005) Convergence history across Zagros (Iran): constraints from collisional and earlier deformation. Int J Earth Sci 94:401–419
Agard P, Omrani J, Jolivet L, Whitechurch H, Vrielynck B, Spakman W, Monié P, Meyer B, Wortel R (2011) Zagros orogeny: a subduction-dominated process. Geol Mag 148:692–725
Ahmadian J, Sarjoughian F, Lentz D, Esna-Ashari A, Murata M, Ozawa H (2016) Eocene K-rich adakitic rocks in the Central Iran: implications for evaluating its Cu–Au–Mo metallogenic potential. Ore Geol Rev 72:323–342
Alavi M (1994) Tectonics of the Zagros orogenic belt of Iran; new data and interpretations. Tectonophysics 229:211–238
Alavi M, Mahdavi MA (1994) Stratigraphy and structure of the Nahavand region in western Iran and their implications for the Zagros tectonics. Geol Mag 131:43–47
Ali SA, Buckman S, Aswad KJ, Jones BG, Ismail SA, Nutman AP (2013) The tectonic evolution of a Neo-Tethyan (Eocene–Oligocene) island-arc (Walash and Naopurdan groups) in the Kurdistan region of the Northeast Iraqi Zagros Suture Zone. Isl Arc 22:104–125
Allen MB (1991) Local equilibrium of mafic enclaves and granitoids of the Turtle pluton, southeast California: mineral, chemical, and isotopic evidence. Am Miner 76:574–588
Allen MB (2009) Discussion on the Eocene bimodal Piranshahr massif of the Sanandaj-Sirjan zone, west Iran: a marker of the end of collision in the Zagros orogen. J Geol Soc Lond 166:981–982
Allen MB, Armstrong HA (2008) Arabia–Eurasia collision and the forcing of mid-Cenozoic global cooling. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 265:52–58
Annen C, Blundy JD, Sparks RSJ (2006) The genesis of intermediate and silicic magmas in deep crustal hot zones. J Petrol 47:505–539
Ao S, Xiao W, Khalatbari Jafari M, Talebian M, Chen L, Wan B, Ji W, Zhang Z (2016) U–Pb zircon ages, field geology and geochemistry of the Kermanshah ophiolite (Iran): from continental rifting at 79 Ma to oceanic core complex at ca. 36 Ma in the southern Neo-Tethys. Gondwana Res 31:305–318
Asadi S, Moore F, Zarasvandi A (2014) Discriminating productive and barren porphyry copper deposits in the southeastern part of the central Iranian volcano-plutonic belt, Kerman region, Iran: a review. Earth Sci Rev 138:25–46
Bacon CR (1986) Magmatic inclusions in silicic and intermediate rocks. J Geophys Res 81:6091–6112
Baker DR (1989) Tracer versus trace element diffusion: diffusional decoupling of Sr concentration from Sr isotope composition. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 53:3015–3023
Ballato P, Uba CE, Landgraf A, Strecker MR, Sudo M, Stockli DF, Friedrich A, Tabatabaei SH (2011) Arabia–Eurasia continental collision: insights from late tertiary foreland-basin evolution in the Alborz Mountains, northern Iran. Geol Soc Am Bull 123:106–131
Barbarin B (2005) Mafic magmatic enclaves and mafic rocks associated with some granitoids of the central Sierra Nevada batholith, California: nature, origin, and relations with the hosts. Lithos 88:155–177
Barbarin B, Didier J (1992) Genesis and evolution of mafic microgranular enclaves through various types of interaction between coexisting felsic and mafic magmas. T Roy Soc Edin Earth 83:145–153
Berberian F, Berberian M (1981) Tectono-plutonic episodes in Iran. In: Gupta HK, Delany FM (eds) Zagros-Hindu Kush-Himalaya geodynamic evolution, vol 3. Am Geophys Union Geodynamics Series, Washington, DC, pp 5–32
Berberian M, King GCP (1981) Towards a paleogeography and tectonic evolution of Iran. Can J Earth Sci 18:210–265
Berzina AP, Berzina AN, Gimon VO (2014) Geochemical and Sr–Pb–Nd isotopic characteristics of the Shakhtama porphyry Mo–Cu system (Eastern Transbaikalia, Russia). J Asian Earth Sci 79:655–665
Beydoun ZR, Hughes Clarke MW, Stoneley R (1992) Petroleum in the Zagros Basin; a Late Tertiary foreland basin overprinted onto the outer edge of a vast hydrocarbon-rich Paleozoic-Mesozoic passive-margin shelf. AAPG Mem 55:309–339
Blundy JD, Sparks RSJ (1992) Petrogenesis of mafic inclusions in granitoids of the Adamelo Massif, Italy. J Petrol 33:1039–1104
Bonin B (2004) Do coeval mafic and felsic magmas in post-collisional to within-plate regimes necessarily imply two constrasting, mantle and crust, sources? a review. Lithos 78:1–24
Campbell IH, Turner JS (1985) Turbolent mixing between fluids with different viscosities. Nature 313:39–42
Campbell IH, Turner JS (1986) The influence of viscosity on fountains in magma chambers. J Petrol 27:1–30
Carmichael ISE (2002) The andesite aqueduct: perspectives on the evolution of intermediate magmatism in west–central (105–99°W) Mexico. Contrib Miner Petrol 143:641–663
Chappell BW (1999) Aluminium saturation in I- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites. Lithos 46:535–551
Chappell BW (2004) Towards a unified model of granite genesis. T Royal Soc Edin Earth 95:1–10
Chappell BW, White AJR (1991) Restite enclaves and the restite model. In: Didier J, Barbarin B (eds) Developments in petrology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 375–381
Chappell BW, White AJR, Williams IS, Wyborn D, Wyborn LAI (2000) Lachlan Fold Belt granites revisited: high- and low-temperature granites and their implications. Aust Earth Sci 47:123–138
Chen B, Jahn BM, Wei C (2002) Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids in the Dabie UHP complex, Central China: trace element and Nd–Sr isotope evidence. Lithos 60:67–88
Cheng Y, Spandler C, Mao J, Rusk BG (2012) Granite, gabbro and mafic microgranular enclaves in the Gejiu area, Yunnan Province, China: a case of two-stage mixing of crust- and mantle-derived magmas. Contrib Miner Petrol 164:659–676
Chiu HY, Chung SL, Zarrinkoub MH, Mohammadi SS (2013) Zircon U–Pb age constraints from Iran on the magmatic evolution related to Neotethyan subduction and Zagros orogeny. Lithos 162–163:70–87
Christiansen EH, Keith JD (1996) Trace-element systematics in silicic magmas: a metallogenic perspective. In: Wyman DA (ed) Trace element geochemistry of volcanic rocks: applications for massive sulfide exploration, vol 12. Geological Association of Canada, Short Course Notes, pp 115–151
Chung SL, Chu MF, Ji J, O’Reilly SY, Pearson NJ, Liu D, Lee TY, Lo CH (2009) The nature and timing of crustal thickening in southern Tibet: geochemical and zircon Hf isotopic constraints from postcollisional adakites. Tectonophysics 477:36–48
Clarke DB (1992) Granitoid rocks. Chapman and Hall, London
Çolakoğlu AR, Arehart GB (2010) The petrogenesis of Sarıçimen (Çaldıran-Van) quartz monzodiorite: implication for initiation of magmatism (Late Medial Miocene) in the east Anatolian collision zone. Turk Lithos 119:607–620
Dahlquist JA (2002) Mafic microgranular enclaves: early segregation from metaluminous magma (Sierra de Chepes), Pampean Ranges, NW Argentina. J S Am Earth Sci 15:643–655
Davidson J, Turner S, Handley H, Macpherson C, Dosseto A (2007) Amphibole “sponge” in arc crust? Geology 35:787–790
De la Roche H, Leterrier J, Grandclaude P, Marchal M (1980) A classification of volcanic and plutonic rocks using R1R2 diagram and major-element analyses—its relationships with current nomenclature. Chem Geol 29:183–210
Debon F (1991) Comparative major element chemistry in various “microgranular enclave–plutonic host” pairs. In: Didier J, Barbarin B (eds) Enclaves and granite petrology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 293–312
Defant MJ, Drummond MS (1990) Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature 347:662–665
Didier J (1987) Granites and their enclaves. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Dilek Y, Imamverdiyev N, Altunkaynak S (2010) Geochemistry and tectonics of Cenozoic volcanism in the Lesser Caucasus (Azerbaijan) and the peri-Arabian region: collision-induced mantle dynamics and its magmatic fingerprint. Inter Geol Rev 52:536–578
Domenick MA, Kistler RE, Dodge FCW, Tatsumoto M (1983) Nd and Sr isotopic study of crustal and mantle inclusions from the Sierra Nevada and implications for batholith petrogenesis. Geol Soc Am Bull 94:713–719
Donaire T, Pascual E, Pin C, Duthou JL (2005) Microgranular enclaves as evidence of rapid cooling in granitoid rocks: the case of the Los Pedroches granodiorite, Iberian Massif, Spain. Contrib Miner Petrol 149:247–265
Dorais MJ, Whitney JA, Roden MF (1990) Origin of mafic enclaves in the Dinkey Creek Pluton, Central Sierra Neveda Batholith, California. J Petrol 31:853–881
Drake MJ, Weill DF (1975) Partition of Sr, Ba, Ca, Y, Eu2+, Eu3+ and other REE between plagioclase feldspar and magmatic liquid: an experimental study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 39:689–712
Ebertz GW, Nicholls IA, Maas R, McCulloch MT, Whitford DJ (1990) The Nd and Sr isotopic composition of I-type microgranitoid enclaves and their host rocks from the Swifts Creek pluton, southeast Australia. Chem Geol 85:119–134
Eichelberger JC (1975) Origin of andesite and dacite: evidence of mixing at Glass Mountain in California and other circum Pacific volcanoes. Geol Soc Am Bull 86:1381–1391
El-Bialy MZ, Omar MM (2015) Spatial association of Neoproterozoic continental arc I-type and post-collision A-type granitoids in the Arabian–Nubian Shield: the Wadi Al-Baroud older and younger granites, north eastern desert, Egypt. J Afr Earth Sci 103:1–29
Erdmann S, Clarke DB (2007) The contamination of granitic magma by metasedimentary country-rock material: an experimental study. Can Miner 45:43–61
Feng SJ, Zhao KD, Ling HF, Chen PR, Chen WF, Sun T, Jiang SY, Pu W (2014) Geochronology, elemental and Nd–Hf isotopic geochemistry of Devonian A-type granites in central Jiangxi, South China: constraints on petrogenesis and post-collisional extension of the Wuyi–Yunkai orogeny. Lithos 206–207:1–18
Fernandez A, Barbarin B (1991) Relative rheology of coeval mafic and felsic magmas: nature of resulting interaction processes and shape and mineral fabrics of mafic microgranular enclaves. In: Didier J, Barbarin B (eds) Enclaves and granite petrology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 63–275
Fershtater GB, Borodina NS (1977) Petrology of autoliths in granitic rocks. Inter Geol Rev 19:458–468
Flood RH, Shaw SE (2014) Microgranitoid enclaves in the felsic Looanga monzogranite, New England Batholith, Australia: pressure quench cumulates. Lithos 198–199:92–102
Frost TP, Mahood GA (1987) Field, chemical and physical constraints on mafic-felsic magma interaction in the Lamark granodiorite, Sierra Nevada, California. Geol Soc Am Bull 99:272–291
Frost BR, Barnes CG, Collins WJ, Arculus RJ, Ellis DJ, Frost CD (2001) A geochemical classification for granitic rocks. J Petrol 41:2033–2048
Furman T, Spera FJ (1985) Co-mingling of acid and basic magma with implications for the origin of I-type xenoliths: field and petrochemical relations of an unusual dike complex at Eagle Lake, Sequoia National Park. J Volcanol Geoth Res 24:151–178
Gao Y, Hou Z, Kamber BS, Wei R, Meng X, Zhao R (2007) Adakite-like porphyries from the southern Tibetan continental collision zones: evidence for slab melt metasomatism. Contrib Miner Petrol 153:105–120
Geng HY, Sun M, Yuan C, Xiao WJ, Xian WS, Zhao GC, Zhang LF, Wong K, Wu FY (2009) Geochemical, Sr–Nd and zircon U–Pb–Hf isotopic studies of Late Carboniferous magmatism in the West Junggar, Xinjiang: implications for ridge subduction? Chem Geol 266:373–398
Geshi N (2000) Fractionation and magma mixing within intruding dike swarm: evidence from the Miocene Shitara-Otoge igneous complex, central Japan. J Volcanol Geoth Res 98:127–152
Golkaram S, Rashidnejad–Omran N, Azizi H, Asahara Y, Buchsd DM, McDonald I, Santose FJ (2016) Petrogenesis and geodynamic evolution of the Kajan Neogene subvolcanic rocks, Nain, Central Iran. Chem Erde 76:567–578
Green TH, Pearson NJ (1985) Experimental determination of REE partition coefficients between amphibole and basaltic to andesitic liquids at high pressure. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 49:1465–1468
Guo F, Fan W, Li Ch, Gao X, Miao L (2009) Early Cretaceous highly positive εNd felsic volcanic rocks from the Hinggan Mountains, NE China: origin and implications for Phanerozoic crustal growth. Int J Earth Sci 98:1395–1411
Hafkenscheid E, Wortel MJR, Spakman W (2006) Subduction history of the Tethyan region derived from seismic tomography and tectonic reconstructions. J Geophys Res 111:B08401
Hanson GN (1980) Rare earth elements in petrogenetic studies of igneous systems. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 8:371–406
Haschke M, Ahmadian J, Murata M, McDonald I (2010) Copper mineralization prevented by arc-root delamination during Alpine–Himalayan collision in Central Iran. Econ Geol 105:855–865
Hassanzadeh J, Wernicke BP (2016) The Neotethyan Sanandaj-Sirjan zone of Iran as an archetype for passive margin-arc transitions. Tectonics 35:586–621
Hatzfeld D, Molnar P (2010) Comparisons of the kinematics and deep structures of the Zagros and Himalaya and of the Iranian and Tibetan plateaus and geodynamic implications. Rev Geophys 48:1–48
Hempton MR (1987) Constraints on Arabian Plate motion and extensional history of the Red Sea. Tectonics 6:687–705
Hildreth W, Moorbath S (1988) Crustal contributions to arc magmatism in the Andes of Central Chile. Contrib Miner Petrol 98:455–489
Hofmann A (1980) Diffusion in silicate melts. In: Hargraves RB (ed) Physics of magmatic processes. Princeton University Press, New York, pp 385–417
Holden P, Halliday AN, Stephens WE, Henney PJ (1991) Chemical and isotopic evidence for major mass transfer between mafic enclaves and felsic magma. Chem Geol 92:135–152
Holten T, Jamtveit B, Meakin P (2000) Noise and oscillatory zoning of minerals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:893–1904
Honarmand M, Rashidnejad Omran N, Neubauer F, Emami MH, Nabatiand G, Liu X, Dong Y, Quadt A, Cheng B (2014) Laser-ICP-MS U–Pb zircon ages and geochemical and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic compositions of the Niyasar plutonic complex, Iran: constraints on petrogenesis and tectonic evolution. Inter Geol Rev 56:104–132
Hooper RJ, Baron I, Hatcher RD, Agah S (1994) The development of the southern Tethyanmargin in Iran after the break-up of Gondwana-implications for the Zagros hydrocarbon province. Geoscience 4:72–85
Hou ZQ, Guo YF, Qu XM, Rui ZY, Mo XX (2004) Origin of adakitic intrusives generated during mid-Miocene east–west extension in southern Tibet. Earth Planet Sci Lett 220:139–155
Jahn BM, Wu F, Lo DH, Tsai CH (1999) Crust–mantle interaction induced by deep subduction of the continental crust: geochemical and Sr–Nd isotopic evidence from post-collisional mafic–ultramafic intrusions of the northern Dabie complex, central China. Chem Geol 157:119–146
Jahn BM, Wu F, Chen B (2000) Massive granitoid generation in Central Asia: Nd isotope evidence and implication for continental growth in the Phanerozoic. Episodes 23:82–92
Jahn BM, Valui G, Kruk N, Gonevchuk V, Usuki M, Wu JTJ (2015) Emplacement ages, geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic characterization of Mesozoic to early Cenozoic granitoids of the Sikhote-Alin orogenic belt, Russian far east: crustal growth and regional tectonic evolution. J Asian Earth Sci 111:872–918
Kananian A, Sarjoughian F, Nadimi AR, Ahmadian J, Ling W (2014) Geochemical characteristics of the Kuh-e Dom intrusion, Urumieh–Dokhtar Magmatic Arc (Iran): implications for source regions and magmatic evolution. J Asian Earth Sci 90:137–148
Karagaranbafghi F, Foeken JPT, Guest B, Stuart FM (2012) Cooling history of the Chapedony metamorphic core complex, Central Iran: implications for the Eurasia–Arabia collision. Tectonophysics 524–525:100–107
Karsli O, Chen B, Aydin F, Sen C (2007) Geochemical and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic compositions of the Eocene Dolek and Saricicek plutons, Eastern Turkey: implications for magma interaction in the genesis of high-K calc-alkaline granitoids in a post-collision extensional setting. Lithos 98:67–96
Kaygusuz A, Siebel W, Sen C, Satir M (2008) Petrochemistry and petrology of I-type granitoids in an arc setting: the composite Torul pluton, Eastern Pontides, NE Turkey. Inter Geol Earth Sci 97:739–764
Kaygusuz A, Arslan M, Siebel W, Sipahi F, İlbeyli N, Temizel İ (2014) LA-ICP MS zircon dating, whole-rock and Sr–Nd–Pb–O isotope geochemistry of the Camiboğazı pluton, Eastern Pontides, NE Turkey: implications for lithospheric mantle and lower crustal sources in arc-related I-type magmatism. Lithos 192–195:271–290
Keay S, Collins WJ, McCulloch MT (1997) A three-component Sr-Nd isotopic mixing model for granitoid genesis, Lachlan fold belt, eastern Australia. Geology 25:307–310
Kim JS, Shin KC, Lee JD (2002) Petrographical study on the Yucheon granite and its enclaves. Geosci J 6:289–302
Laumonier M, Scaillet B, Arbaret L, Champallier R (2014a) Experimental simulation of magma mixing at high pressure. Lithos 196:281–300
Laumonier M, Scaillet B, Pichavant M, Champallier R, Andujar J, Arbaret L (2014b) On the conditions of magma mixing and its bearing on andesite production in the crust. Nat Commun 5:5607
Lee CTA, Lee TC, Wu CT (2014) Modeling the compositional evolution of recharging, evacuating, and fractionating (REFC) magma chambers: Implications for differentiation of arc magmas. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 143:8–22
Lesher CE (1990) Decoupling of chemical and isotopic exchange during magma mixing. Nature 344:235–237
Lesher CE (1994) Kinetics of Sr and Nd exchange in silicate liquids: theory, experiments, and applications to uphill diffusion, isotopic equilibration, and irreversible mixing of magmas. J Geophys Res 99:9585–9604
Lesher CE (2010) Self-diffusion in silicate melts: theory, observations and applications to magmatic systems. Rev Miner Geochem 72:269–309
Li C, Li X, Li Q, Guo J, Li X, Yang Y (2012a) Rapid and precise determination of Sr and Nd isotopic ratios in geological samples from the same filament loading by thermal ionization mass spectrometry employing a single-step separation scheme. Anal Chim Acta 727:54–60
Li C, Li X, Li Q, Guo J, Li X, Feng L, Chu Z (2012b) Simultaneous determination of 143Nd/144Nd and 147Sm/144Nd ratios and Sm-Nd contents from the same filament loaded with purified Sm-Nd aliquot from geological samples by isotope dilution thermal ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 84:6040–6047
Li ZZ, Qin KZ, Li GM, Ishihara S, Jin LY, Song GX, Meng ZJ (2014) Formation of the giant Chalukou porphyry Mo deposit in northern Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Partial melting of the juvenile lower crust in intra-plate extensional environment. Lithos 202–203:138–156
Liu Z, Jiang YH, Jia RY, Zhao P, Zhou Q (2015) Origin of Late Triassic high-K calc-alkaline granitoids and their potassic microgranular enclaves from the western Tibet Plateau, northwest China: implications for Paleo-Tethys evolution. Gondwana Res 27:326–341
Maas R, Nicholls IA, Legg C (1997) Igneous and metamorphic enclaves in the S-type Deddick granodiorite, Lachlan Fold Belt, SE Australia: petrographic, geochemical and Nd-Sr isotopic evidence for crustal melting and magma mixing. J Petrol 38:815–841
Macpherson CG (2008) Lithosphere erosion and crustal growth in subduction zones: insights from initiation of the nascent East Philippine Arc. Geology 36:311–314
Macpherson CG, Dreher ST, Thirlwall MF (2006) Adakites without slab melting: high pressure differentiation of island arc magma, Mindanao, the Philippines. Earth Planet Sci Lett 243:581–593
Maniar PD, Piccoli PM (1989) Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. Geol Soc Am Bull 101:635–643
Martin VM, Holness MB, Pyle DM (2006) The role of crystal frameworks in the preservation of enclaves during magma mixing. Earth Planet Sci Lett 248:787–799
McBirney AR (1980) Mixing and unmixing of magmas. J Volcanol Geoth Res 7:357–371
McKenzie D, O’Nions RK (1991) Partial melt distributions from inversion of rare earth element concentrations. J Petrol 32:1021–1091
McQuarrie N, van Hinsbergen D (2013) Retrodeforming the Arabia-Eurasia collision zone: age of collision versus magnitude of continental subduction. Geology 41:315–318
McQuarrie N, Stock JM, Verdel C, Wernicke BP (2003) Cenozoic evolution of Neotethys and implications for the causes of plate motions. Geophysl Res Lett 30:1–4
Mo X, Niu Y, Dong G, Zhao Z, Hou Z, Zhou S, Ke S (2008) Contribution of syncollisional felsic magmatism to continental crust growth: a case study of the Paleogene Linzizong volcanic Succession in southern Tibet. Chem Geol 250:49–67
Mohajjel M, Fergusson CL (2014) Jurassic to Cenozoic tectonics of the zagros orogen in northwestern Iran. Int Geol Rev 56:263–287
Mohajjel M, Fergusson CL, Sahandi MR (2003) Cretaceous–Tertiary convergence and continental collision Sanandaj–Sirjan zone Western Iran. J Asian Earth Sci 21:397–412
Moita P, Santos JF, Pereira MF, Costa M, Corfu F (2015) The quartz-dioritic Hospitais intrusion (SW Iberian Massif) and its mafic microgranular enclaves—evidence for mineral clustering. Lithos 224–225:78–100
Moore JG, Sisson TW (2008) Igneous phenocrystic origin of K-feldspar megacrysts in granitic rocks from the Sierra Nevada batholith. Geosphere 4:387–400
Murphy JB (2007) Igneous rock associations 8. Arc magmatism II: geo-chemical and isotopic characteristics. J Geol assoc Can 34:7–36
Nicolae I, Saccani E (2003) Petrology and geochemistry of the Late Jurassic calcalkaline series associated to Middle Jurassic ophiolites in the South Apuseni Mountains (Romania). Schweiz Miner Petrog Mitt 83:81–96
Nittmann J, Daccord G, Stanley HE (1985) Fractal growth of viscous fingers: quantitative characterization of a fluid instability phenomenon. Nature 314:141–145
Omrani J, Agard P, Whitechurch H, Benoit M, Prouteau G, Jolivet L (2008) Arc-magmatism and subduction history beneath the Zagros Mountains, Iran: a new report of adakites and geodynamic consequences. Lithos 106:380–398
Osterhus L, Jung S, Berndt J, Hauff F (2014) Geochronology, geochemistry and Nd, Sr and Pb isotopes of syn-orogenic granodiorites and granites (Damara orogen, Namibia)—arc-related plutonism or melting of mafic crustal sources? Lithos 200–201:386–401
Pankhurst MJ, Vernon RH, Turner SP, Schaefer BF, Foden JD (2011) Contrasting Sr and Nd isotopic behaviour during magma mingling; new insights from the Mannum A-type granite. Lithos 126:135–146
Pearce JA, Norry MJ (1979) Petrogenetic implications of Ti, Zr, Y, and Nb variations in volcanic rocks. Contrib Miner Petrol 69:33–47
Pearce JA, Harris NBW, Tindle AG (1984) Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. J Petrol 25:956–983
Perugini D, Poli G, Christofides G, Eleftheriadis G (2003) Magma mixing in the Sithonia plutonic complex, Greece: evidence from mafic microgranular enclaves. Miner Petrol 78:173–200
Perugini D, Ventura G, Petrelli M, Poli G (2004) Kinematic significance of morphological structures generated by mixing of magmas: a case study from Salina Island (southern Italy). Earth Planet Sci Lett 222:1051–1066
Petford N, Atherton A (1996) Na-rich partial melts from newly underplated basaltic crust: The Cordillera Blanca Batholith, Peru. J Petrol 37:1491–1521
Philpotts AR, Shi J, Brustman C (1998) Role of plagioclase crystal chains in the differentiation of partly crystallized basaltic magma. Nature 395:343–346
Piccoli PM, Candela PA (2002) Apatite in igneous system. Rev Miner Geochem 48:255–292
Pin C, Binon M, Belin J, Barbarin B, Clemens JD (1990) Origin of microgranular enclaves in granitoids: equivocal Sr–Nd evidence from Hercynian rocks in the Massif Central (France). J Geophys Res 95:17821–17828
Piochi M, Civetta L, Orsi G (1999) Mingling in the magmatic system of Ischia (Italy) in the past 5 ka. Miner Petrol 66:227–258
Poli G (1992) Geochemistry of Tuscan Archipelago Granitoids, Central Italy: the role of hybridization processes in their genesis. J Geol 100:41–56
Poli G, Tommasini S (1990) Model for the origin and significance of microgranular enclaves in calc-alkaline granitoids. J Petrol 32:657–666
Poli G, Tommasini S, Halliday AN (1996) Trace element and isotopic exchange during acid-basic magma interaction processes. T Roy Soc Edin Earth 87:225–232
Radfar J, Amini Jehragh MR, Emami MH (1999) Geological map of Ardestan, scale 1:100000. Geological Survey of Iran, Iran
Rapp RP, Watson EB (1995) Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8–32 kbar: implications for continental growth and crust–mantle recycling. J Petrol 36:891–931
Rezaei-Kahkhaei M, Galindo C, Pankhurst RJ, Esmaeily D (2011) Magmatic differentiation in the calc-alkaline Khalkhab–Neshveh pluton, Central Iran. J Asian Earth Sci 42:499–514
Richards JP (2015) Tectonic, magmatic, and metallogenic evolution of the Tethyan orogen: from subduction to collision. Ore Geol Rev 70:323–345
Richards JP, Spell T, Rameh E, Razique A, Fletcher T (2012) High Sr/Y magmas reflect arc maturity, high magmatic water content, and porphyry Cu ± Mo ± Au potential: examples from the Tethyan arcs of Central and Eastern Iran and Western Pakistan. Econ Geol 107:295–332
Robertson AHF (2000) Mesozoic-Tertiary tectonicsedimentary evolution of a south Tethyan oceanic basin and its margins in southern Turkey. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 173:97–138
Robertson A, Parlak O, Ustaömer T (2009) Melange genesis and ophiolite emplacement related to subduction of the northern margin of the Tauride? Anatolide continent, central and western Turkey. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 311:9–55
Rogers NW, Hawkesworth CJ, Ormerod DS (1989) Late Cenozoic basaltic magmatism in the Western Great Basin California and Nevada. J Geophys Res 100:10287–10301
Rollinson H (1993) Using geochemical data: evolution, presentation, interpretation. Longman Scientific and Technical, UK
Ross PS, Bedard JH (2009) Magmatic affinity of modern and ancient subalkaline volcanic rocks determined from trace-element discriminant diagrams. Can J Earth Sci 46:823–839
Rudnick RL, Gao S (2003) Composition of the continental crust. In: Holland HD, Turekian KK (eds) Treatise on geochemistry. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 1–64
Sadeghian M, Ghaffary M (2011) The petrogenesis of Zafarghand granitoid pluton (SE of Ardestan). Petrology 2:47–70 (Persian with English Abstract)
Sajona FG, Maury RC, Bellon H, Cotton J, Defant M (1996) High field strength elements of Pliocene–Pleistocene island-arc basalts Zamboanga Peninsula, Western Mindanao (Philippines). J Petrol 37:693–726
Sarjoughian F, Kananian A (2017) Zircon U-Pb geochronology and emplacement history of intrusive rocks in the Ardestan section, Central Iran. Geol Acta 15:25–36
Sarjoughian F, Kananian A, Haschke M, Ahmadian J, Ling W, Zong K (2012) Magma mingling and hybridization in the Kuh-e Dom pluton, Central Iran. J Asian Earth Sci 54–55:49–63
Saunders AD, Tarney J (1984) Geochemical characteristics of basaltic volcanism in back-arc basins. In Kokelaar BP, Howells MF (eds) Marginal basin geology: volcanic and associated sedimentary and tectonic processes in modern and ancient marginal basins, vol 16. Geol Soc London, London, pp 59–76
Schonenberger J, Marks M, Wagner T, Markl G (2006) Fluid-rock interaction in autoliths of agpaitic nepheline syenites in the Ilimaussaq intrusion, South Greenland. Lithos 91:331–351
Shafiei B, Haschke M, Shahabpour J (2009) Recycling of orogenic arc crust triggers porphyry Cu mineralization in Kerman Cenozoic arc rocks, southeastern Iran. Miner Depos 44:265–283
Sisson TW, Layne GD (1993) H2O in basalt and basaltic andesite glass inclusions from four subduction-related volcanoes. Earth Planet Sci Lett 117:619–635
Sparks RSJ, Marshall LA (1986) Thermal and mechanical constraints on mixing between mafic and silicic magmas. J Volcanol Geoth Res 29:99–124
Sun SS, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotope systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol Soc 42:313–345
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1995) The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev Geophys 33:241–265
Thieblemont D, Tegyey M (1994) Geocchemical discrimination of differentiated magmatic rocks attesting for the variable origin and tectonic setting of calc-alkaline magmas. C R Acad Sci II 319:87–94
Vernon RH (1984) Microgranitoid enclaves: globules of hybrid magma quenched in a plutonic environment. Nature 304:438–439
Vernon RH (1990) Crystallization and hybridism in microgranitoid enclave magmas: microstructural evidence. J Geophys Res 95:17849–71859
Vernon RH (1991) Interpretation of microstructures of microgranitoid enclaves. In: Didier J, Barbarin B (eds) Enclaves and granite petrology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 277–291
Vernon RH, Etheridge ME, Wall VJ (1988) Shape and microstructure of microgranitoid enclaves: indicators of magma mingling and flow. Lithos 22:1–11
Vernon RH, Johnson SE, Melis EA (2004) Emplacement-related microstructures in the margin of a deformed tonalite pluton: the San José pluton, Baja California, México. J Struct Geol 26:1845–1865
Waight TE, Maas R, Nicholls IA (2000) Fingerprinting feldspar phenocrysts using crystal isotopic composition stratigraphy: implications for crystal transfer and magma mingling in S-type granites. Contrib Miner Petrol 139:227–239
Watson EB (1982) Basalt contamination by continental crust: some experiments and models. Contrib Miner Petrol 80:73–87
Weaver BL, Tarney J (1984) Estimating the composition of the continental crust: an empirical approach. Nature 310:575–577
Weinberg RF, Sial AN, Pessoa RR (2001) Magma flow within the traverse pluton, northeastern Brazil: compositional and thermal convection. Geol Soc Am Bull 113:508–520
White AJR, Chappell BW (1977) Ultrametamorphism and granitoid genesis. Tectonophysics 43:7–22
White AJR, Chappell BW, Wyborn D (1999) Application of the restite model to the Deddick Granodiorite and its enclaves—a reinterpretation of the observations and data of Maas et al. (1997). J Petrol 40:413–421
Whitechurch H, Omrani J, Agard P, Humbert F, Montigny R, Jolivet L (2013) Evidence for Paleocene–Eocene evolution of the foot of the Eurasian margin (Kermanshah ophiolite, SW Iran) from back-arc to arc: implications for regional geodynamics and obduction. Lithos 182–183:11–32
Wu FY, Jahn BM, Lin Q (1998) Isotopic characteristics of the post-orogenic granite in orogenic belt of northern China and their implications in crustal growth. Chin Sci Bull 43:420–424
Wu FY, Jahn BM, Wilde SA, Sun DY (2000) Phanerozoic crustal growth: U-Pb and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from the granites in northeastern China. Tectonophysics 328:89–113
Wu RX, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Zhao ZF, Zhang SB, Liu X, Wu FY (2006) Reworking of juvenile crust: element and isotope evidence from Neoproterozoic granodiorite in South China. Precambrian Res 146:179–212
Yang JH, Wu FY, Wilde S, Xie LW, Yang YH, Liu XM (2007) Tracing magma mixing in granite genesis: in situ U–Pb dating and Hf-isotope analysis of zircons. Contrib Miner Petrol 153:177–190
Yang XM, Lentz DR, Chi G, Thorne KG (2008) Geochemical characteristics of gold-related granitoids in southwestern New Brunswick, Canada. Lithos 104:355–377
Yang YH, Zhang HF, Chu ZY, Xie LW, Wu FY (2010) Combined chemical separation of Lu, Hf, Rb, Sr, Sm and Nd from a single rock digest and precise and accurate isotope determinations of Lu–Hf, Rb–Sr and Sm–Nd isotope systems using Multi-Collector ICP-MS and TIMS. Int J Mass Spectrom 290:120–126
Yang H, Ge WC, Zhao GC, Dong Y, Xu WL, Ji Z, Yu JJ (2015a) Late Triassic intrusive complex in the Jidong region, Jiamusi–Khanka Block, NE China: Geochemistry, zircon U–Pb ages, Lu–Hf isotopes, and implications for magma mingling and mixing. Lithos 224–225:143–159
Yang LQ, Deng J, Qiu KF, Ji XZ, Santosh M, Song KR, Song YH, Geng JZ, Zhang C, Hua B (2015b) Magma mixing and crust–mantle interaction in the Triassic monzogranites of Bikou Terrane, central China: Constraints from petrology, geochemistry, and zircon U–Pb–Hf isotopic systematics. J Asian Earth Sci 98:320–341
Yilmaz Sahin S (2008) Geochemistry of mafic microgranular enclaves in the Tamdere Quartz Monzonite, south of Dereli/Giresun, Eastern Pontides, Turkey. Chem Erde Geochem 68:81–92
Zhang Y, Ni H, Chen Y (2010) Diffusion data in silicate melts. Rev Miner Geochem 72:311–408
Zhang X, Yuan L, Wilde SA (2014a) Crust/mantle interaction during the construction of an extensional magmatic dome: middle to Late Jurassic plutonic complex from western Liaoning, North China Craton. Lithos 205:185–207
Zhang J, Ma C, Xiong F, Liu B, Li J, Pan Y (2014b) Early Paleozoic high-Mg diorite-granodiorite in the eastern Kunlun Orogen, western China: response to continental collision and slab break-off. Lithos 210–211:129–146
Zhang Y, Sun M, Yuan C, Xu Y, Long X, Tomurhuu D, Wang CY, He B (2015) Magma mixing origin for high Ba–Sr granitic pluton in the Bayankhongor area, central Mongolia: response to slab roll-back. J Asian Earth Sci 113:353–368
Acknowledgements
Thanks go to the University of Kurdistan for supporting this project under grants provided by the research council (number: 4.64500; date: 3/11/2015). This study was also financially supported by the “National Natural Science Foundation of China (41472192)", and the State Key Laboratory of Lithosphere Evolution (11232240). DL is supported by a NSERC Discovery grant. This is a contribution to IGCP 592. We acknowledge Prof. Dr. Wolf-Christian Dullo, Prof. Greg Shellnutt, Prof. Saskia Erdmann, and anonymous reviewer for their constructive comments leading to important improvements in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarjoughian, F., Lentz, D., Kananian, A. et al. Geochemical and isotopic constraints on the role of juvenile crust and magma mixing in the UDMA magmatism, Iran: evidence from mafic microgranular enclaves and cogenetic granitoids in the Zafarghand igneous complex. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 107, 1127–1151 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-017-1548-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-017-1548-8