Abstract
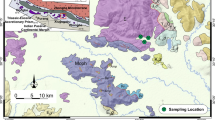
Large ultramafic bodies of the East Othris ophiolite in Central Greece consist of serpentinites, of harzburgite precursors, as well as serpentinized lherzolites, which have been intruded by thin dykes of olivine-rich and olivine-poor pyroxenites. They represent parts of partially altered upper mantle wedge rocks in a Mid-Late Jurassic intraoceanic subduction setting of the Pindos microocean, a western strand of the Tethyan oceanic realm. Serpentinization and rodingitization occurred during their exhumation toward the fore-arc oceanic region and accretionary prism through a subduction channel. Petrography and geochemistry show that protoliths of most serpentinites and serpentinized peridotites are harzburgites, while few are more fertile lherzolites. Petrogenetic modeling reveals that the former harzburgites correspond to highly depleted residual mantle peridotites, which formed after moderate degrees (~13–20 %) of hydrous partial melting, whereas lherzolites, being closely related to the ophiolitic mantle peridotites of West Othris, resulted after lower partial melting degrees (~7–10 %). Mineral chemistry and geochemical data from pyroxenites imply that they have been derived after crystallization of a subduction-related IAT hydrous magma that formed after moderate partial melting degrees (~14–19 %), quite similar to those that produced the harzburgites. Melting processes for the East Othris mantle peridotites occurred in the spinel-stability field, at estimated equilibrium temperatures ranging between 900 and 1,050 °C and pressures between 1.4 and 1.7 GPa, in a rather highly oxidized environment. It is estimated that the primary IAT magma, formed under relatively high temperatures with liquidus temperature at ~1,260 °C and mantle potential temperature at ~1,372 °C. Cooling rates of the shallow mantle beneath the Pindos oceanic basin, from its Mid-Triassic rift/drift phase and the subsequently developed Mid-Late Triassic short-lived intraoceanic subduction, to the Mid-Late Jurassic main subduction phase, are estimated at ~0.7 and ~1.6 °C/Ma, respectively, with the latter being considered as unusually high.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott D, Burgess L, Longhi J, Smith WHF (1994) An empirical thermal history of the Earth’s upper mantle. J Geophys Res 99:13835–13850
Aldanmaz E, Schmidt MW, Gourgaud A, Meisel T (2009) Mid-ocean ridge and supra-subduction geochemical signatures in spinel–peridotites from the Neotethyan ophiolites in SW Turkey: implications for upper mantle melting processes. Lithos 113:691–708
Arai S, Kadoshima K, Morishita T (2006) Widespread arc-related melting in the mantle section of the northern Oman ophiolite as inferred from detrital chromian spinels. J Geol Soc 163:869–879
Ballhaus C (1993) Redox states of lithospheric and asthenospheric upper mantle. Contrib Mineral Petrol 114:331–348
Barth M, Gluhak T (2009) Geochemistry and tectonic setting of mafic rocks from the Othris Ophiolite, Greece. Contrib Mineral Petrol 157:23–40
Barth MG, Mason PRD, Davies GR, Dijkstra AH, Drury MR (2003) Geochemistry of the Othris Ophiolite, Greece: evidence for refertilization? J Petrol 44:1759–1785
Barth MG, Mason PRD, Davies GR, Drury MR (2008) The Othris Ophiolite, Greece: a snapshot of subduction initiation at a mid-ocean ridge. Lithos 100:234–254
Batanova VG, Sobolev AV (2000) Compositional heterogeneity in subduction-related mantle peridotites, Troodos massif, Cyprus. Geology 28:55–58
Beccaluva L, Ohnestetter D, Ohnestetter M, Paupy A (1984) Two magmatic series with island arc affinities within the Vourinos ophiolites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 85:253–271
Beccaluva L, Macciotta G, Piccardo GB, Zeda O (1989) Clinopyroxene composition of ophiolite basalts as petrogenetic indicator. Chem Geol 77:165–182
Beccaluva L, Coltorti M, Saccani E, Siena F (2005) Magma generation and crustal accretion as evidenced by supra-subduction ophiolites of the Albanide: Hellenide subpelagonian zone. Island Arc 14:551–563
Berger J, Femenias O, Mercier JC, Demaiffe D (2005) Ocean-floor hydrothermal metamorphism in the Limousin ophiolites (western French Massif Central): evidence of a rare preserved Variscan oceanic marker. J Metamorphic Geol 23:795–812
Berly TJ, Hermann J, Arculus RJ, Lapierre H (2006) Supra-subduction Zone Pyroxenites from San Jorge and Santa Isabel (Solomon Islands). J Petrol 47:1531–1555
Bettison-Varga L, Schiffman P, Janecky DR (1995) Fluid-rock interaction in the hydrothermal upflow zone of the Solea graben, Troodos ophiolite, Cyprus. Geol Soc Amer Spec Pap 296:81–100
Blundy JD, Holland TJB (1990) Calcic amphibole equilibria and a new amphibole–plagioclase geothermometer. Contrib Mineral Petrol 104:208–224
Bodinier JL, Godard M (2003) Orogenic, ophiolitic, and abyssal peridotites. In: Carlson RW (ed) Treatise on geochemistry. 2. Geochemistry of the mantle and core. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 103–170
Bortolotti V, Chiari M, Marroni M, Pandolfi L, Principi G, Saccani E (2013) Geodynamic evolution of ophiolites from Albania and Greece (Dinaric-Hellenic belt): one, two, or more oceanic basins? Int J Earth Sci 102:783–811
Boschi C, Bonatti E, Ligi M, Brunelli D, Dallai L, D’Orazio M, Früh-Green GL, Tonarini S, Barnes J, Bedini R (2013) Serpentinization of mantle peridotites along an uplifted lithospheric section, Mid Atlantic Ridge at 11° N. Lithos 178:3–23
Brocker M, Enders M (1999) U-Pb zircon geochronology of unusual eclogite facies rocks from Syros and Tinos (Cyclades, Greece). Geol Mag 136:111–118
Buse B, Schumacher J, Sparks R, Field M (2010) Growth of bultfonteinite and hydrogarnet in metasomatized basalt xenoliths in the B/K9 kimberlite, Damtshaa, Botswana: insights into hydrothermal metamorphism in kimberlite pipes. Contrib Mineral Petrol 160:533–550
Campbell IH (2001) Identification of ancient mantle plumes. In: Ernst RE, Buchan KL (eds) Mantle plumes: their identification through time. Geol Soc Amer Spec Pap 352:5–21
Chen J, Zeng Z (2007) Metasomatism of the peridotites from southern Mariana fore-arc: trace element characteristics of clinopyroxene and amphibole. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 50:1005–1012
Coleman RG (1977) Ophiolites. Ancient oceanic lithosphere?. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–229
De Hoog JCM, Gall L, Cornell DH (2010) Trace-element geochemistry of mantle olivine and application to mantle petrogenesis and geothermobarometry. Chem Geol 270:196–215
Deschamps F, Guillot S, Gvel C, Andreani M, Hattori K (2010) In situ characterization of serpentinites from forearc mantle wedges: timing of serpentinization and behavior of fluid-mobile elements in subduction zones. Chem Geol 269:262–277
Dijkstra AH, Drury MR, Vissers RLM (2001) Structural petrology of plagioclase peridotites in the West Othris Mountains (Greece): melt impregnation in mantle lithosphere. J Petrol 42:5–24
Dijkstra AH, Barth MG, Drury MR, Mason PRD, Vissers RLM (2003) Diffuse porous melt flow and melt-rock reaction in the mantle lithosphere at a slow-spreading ridge: a structural petrology and LA-ICP-MS study of the Othris Peridotite Massif (Greece). Geochem Geophys Geosys 4:8613
Dilek Y, Furnes H (2009) Structure and geochemistry of Tethyan ophiolites and their petrogenesis in subduction rollback systems. Lithos 113:1–20
Dilek Y, Furnes H, Shallo M (2008) Geochemistry of the Jurassic Mirdita Ophiolite (Albania) and the MORB to SSZ evolution of a marginal basin oceanic crust. Lithos 100:174–209
Downes H (2001) Formation and modification of the shallow sub-continental lithospheric mantle: a review of geochemical evidence from ultramafic xenolith suites and tectonically emplaced ultramafic massifs of western and central Europe. J Petrol 42:233–250
Dungan MA (1979) Bastite pseudomorphs after orthopyroxene, clinopyroxene and tremolite. Can Mineral 17:729–740
Economou EM, Naldrett AJ (1984) Sulfides associated with podiform bodies of chromite at Tsagli, Eretria, Greece. Miner Deposita 19:289–297
Evans BW (1977) Metamorphism of alpine peridotite and serpentinite. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci Lett 5:397–447
Fabriès J (1979) Spinel-olivine geothermometry in peridotites from ultramafic complexes. Contrib Mineral Petrol 69:329–336
Fang N, Niu Y (2003) Late palaeozoic ultramafic Lavas in Yunnan, SW China, and their Geodynamic Significance. J Petrol 44:141–158
Ferrière J (1982) Paleogeopraphie et tectoniques superposées dans les Hellénides internes: les massifs de l’Othrys et du Pélion (Grèce septentrional). Thése, sciences Univ. Lille- Societe Géologique Du Nord 8:1–970
Ferrière J, Chanier F, Ditbanjong P (2012) The Hellenic ophiolites: eastward or westward obduction of the Maliac Ocean, a discussion. Int J Earth Sci 101:1559–1580
Frost BR (1975) Contact metamorphism of serpentinite, chloritic blackwall, and rodingite at Paddy-Go-Easy Pass, Central Cascades, Washington. J Petrol 16:272–313
Frost BR, Beard JS (2007) On silica activity and serpentinization. J Petrol 48:1351–1368
Garfunkel Z (2006) Neotethyan ophiolites: formation and obduction within the life cycle of the host basins. In: Robertson AHF, Mountrakis D (eds) Tectonic development of the eastern mediterranean region. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 260:301–326
Gillis KM, Robinson PT (1988) Distribution of alteration zones in the upper oceanic crust. Geology 16:262–266
Gysi AP, Jagoutz O, Schmidt MW, Targuisti K (2011) Petrogenesis of pyroxenites and melt infiltrations in the ultramafic complex of Beni Bousera, Northern Morocco. J Petrol 52:1679–1735
Hellebrand E, Snow JE, Dick HJB, Hofmann AW (2001) Coupled major and Trace elements as indicators of the extent of melting in mid-ocean-ridge peridotites. Nature 410:677–681
Herzberg CT (1993) Lithosphere peridotites of the Kaapvaal craton. Earth Planet Sci Lett 120:13–29
Herzberg C, Asimow PD (2008) Petrology of some oceanic island basalts: PRIMELT2.XLS software for primary magma calculation. Geochem Geophys Geosys 9. doi:10.1029/2008GC002057
Herzberg C, Gazel E (2009) Petrological evidence for secular cooling in mantle plumes. Nature 458:619–622
Herzberg C, Asimow PD, Arndt N, Niu Y, Lesher CM, Fitton JG, Cheadle MJ, Saunders AD (2007) Temperatures in ambient mantle and plumes: Constraints from basalts, picrites, and komatiites. Geochem Geophys Geosys 8. doi:10.1029/2006GC001390
Herzberg C, Condie K, Korenaga J (2010) Thermal history of the Earth and its petrological expression. Earth Planet Sci Lett 292:79–88
Hubbard MS (1996) Ductile shear as a cause of inverted metamorphism: example from the Nepal Himalaya. J Geol 104:493–499
Ishizuka H (1985) Prograde metamorphism of the Horokanai ophiolite in the Kamuikotan Zone, Hokkaido, Japan. J Petrol 26:391–417
Jochum KP, Arndt PNT, Hofmann AW (1991) Nb-Ta-La in komatiites and basalts: constraints on komatiite petrogenesis and mantle evolution. Earth Planet Sci Lett 107:272–289
Johnson A, Schwab B (2004) Constrainst on clinopyroxene/melt partitioning REE, Rb, Sr, Ti, Cr, Zr, and Nb during mantle melting: first insights from direct peridotite melting experiments at 1.0 GPa. Geochim et Cosmochim Acta 68:4949–4962. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2004.06.009
Jones G, Robertson AHF (1991) Tectono-stratigraphy and evolution of the Mesozoic Pindos ophiolite and related units, northwestern Greece. J Geol Soc London 148:267–288
Kamenetsky VS, Crawford AJ, Meffre S (2001) Factors controlling chemistry of magmatic spinel: an empirical study of associated olivine, Cr-spinel and melt inclusions from primitive rocks. J Petrol 42:655–671
Katsikatsos G (1992) Geology of Greece. University of Patras, pp 1–451
Katzir Y, Avigad D, Matthews A, Garfunkel Z, Evans BW (1999) Origin and metamorphism of ultrabasic rocks associated with a subducted continental margin, Naxos (Cyclades, Greece). J Met Geol 17:301–318
Keiter M, Piepjohn K, Ballhaus C, Lagos M, Bode M (2004) Structural development of high-pressure metamorphic rocks on Syros island (Cyclades, Greece). J Struct Geol 26:1433–1445
Kelley KA, Cottrell E (2009) Water and the oxidation state of subduction zone magmas. Science 325:605–607
Kerrich R, Polat A, Wyman D, Hollings P (1999) Trace element systematics of Mg-, to Fe-tholeiitic basalt suits of the Superior Province: implications for Archean mantle reservoirs and greenstone belt genesis. Lithos 46:163–187
Kilias A, Frisch W, Avgerinas A, Dunkl I, Falalakis G, Gawlick HJ (2010) Alpine architecture and kinematics of deformation of the northern Pelagonian nappe pile in the Hellenides. Aust J Earth Sci 103:4–28
Koutsovitis P (2012) Gabbroic rocks in ophiolitic occurrences from East Othris, Greece: petrogenetic processes and geotectonic environment implications. Mineral Petrol 104:249–265. doi:10.1007/s00710-011-0191-5
Koutsovitis P, Magganas A (2010) The geochemistry and petrogenesis of volcanic rocks within ophiolitic formations at the northeast Othris region, Greece. In: Proceedings of the XIX congress of the carpathian-balkan geological association, special vol 99, pp 263–227
Koutsovitis P, Magganas A, Katerinopoulos A (2009) Calc-alkaline volcanic rocks in mélange formations from the South Othris region, Greece: petrogenetic and geotectonic implications. Geochem Mineral Petrol 47:79–95
Koutsovitis P, Magganas A, Ntaflos T (2012) Rift and intra-oceanic subduction signatures in the Western Tethys during the Triassic: the case of ultramafic lavas as part of an unusual ultramafic–mafic–felsic suite in Othris, Greece. Lithos 144–145:177–193. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.03.018
Koutsovitis P, Magganas A, Pomonis P, Ntaflos T (2013) Subduction-related rodingites from East Othris, Greece: mineral reactions and physicochemical conditions of formation. Lithos 172–173:139–157. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.04.009
Lacassin R, Arnaud N, Leloup PH, Armijo R, Meyer B (2007) Syn- and post-orogenic exhumation of metamorphic rocks in North Aegean. eEarth 2:51–63
Lassiter JC (2006) Constraints on the coupled thermal evolution of the Earth’s core and mantle, the age of the inner core, and the origin of the 186Os/188Os “core signal” in plume-derived lavas. Earth Plan Sci Lett 250:306–317. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.07.044
Leblanc M, Lbouabi M (1988) Native silver mineralization along a rodingite tectonic contact between serpentine and quartz diorite (Bou Azzer, Morocco). Econ Geol 83:1379–1391
Lee C-TA, Brandon AD, Norman M (2003) Vanadium in peridotites as a proxy of paleo-fO 2 during partial melting: prospects, limitations and implications. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67:3045–3064
Li XP, Rahn M, Bucher K (2004) Metamorphic Processes in Rodingites of the Zermatt-Saas Ophiolites. Inter Geol Rev 46:28–51
Li XP, Rahn M, Bucher K (2008) Eclogite facies metarodingites: phase relations in the system SiO2–Al2O3–Fe2O3–FeO–MgO–CaO–CO2–H2O: an example from the Zermatt-Saas ophiolite. J Metam Geol 26:347–364
Liou JG, Maruyama S, Cho M (1985) Phase equilibria and mineral parageneses of metabasites in low grade metamorphism. Miner Mag 49:321–333
Lips ALW, Wijbrans JR, White SH (1999) New insights from 40Ar/39Ar laserprobe dating of white mica fabrics from the Pelion Massif, Pelagonian Zone, Internal Hellenides, Greece: implications for the timing of metamorphic episodes and tectonic events in the Aegean region. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 156:457–474
Magganas Α (2002) Constraints on the petrogenesis of Evros ophiolite extrusives, NE Greece. Lithos 65:165–182
Magganas A, Economou M (1988) On the chemical composition of chromite ores from the ophiolitic complex of Soufli, NE Greece. Ofioliti 13:15–28
Manning CE, Bird DK (1995) Porosity, permeability and basalt metamorphism. In: Schiffman P, Day HW (eds) Low-grade metamorphism of mafic rocks. Geol Soc Amer Spec Pap 296:123–140
Marchesi C, Garrido C, Godard M, Proenza J, Gervilla F, Blanco-Moreno J (2006) Petrogenesis of highly depleted peridotites and gabbroic rocks from the Mayarí-Baracoa Ophiolitic Belt (eastern Cuba). Contrib Mineral Petrol 151:717–736
Mcdonough WF, Sun SS (1995) The composition of the Earth. Chem Geol 120:223–253
McKenzie DP, O’Nions RK (1991) Partial melt distribution from inversion of rare earth element concentrations. J Petrol 32:1021–1991
Migiros G, Hatzipanagiotou K, Pavlopoulos A, Moulas I, Tsagalidis A (1997) Les roches métabasiques d’Erétria (Othrys du Nord, Grèce Centrale): un nouvel épisode magmatique de type MORB au Crétacé? Annales de la Societe geologique du Nord 5:59–67
Mogessie A, Rammlmair D (1994) Occurrence of zoned uvarovite-grossular garnet in a rodingite from the vumba schist belt, Botswana, Africa: implications for the Origin of Rodingites. Mineral Mag 58:375–386
Morimoto N (1988) Nomenclature of pyroxenes. Mineral Mag 52:535–550
Morishita T, Dilek Y, Shallo M, Tamura A, Arai S (2011) Insight into the uppermost mantle section of a maturing arc: the Eastern Mirdita ophiolite, Albania. Lithos 124:215–226
Nakagawa T, Tackley PJ (2012) Influence of magmatism on mantle cooling, surface heat flow and Urey ratio. Earth Plan Sci Lett 329–330:1–10
Nisbet EG, Cheadle MJ, Arndt NT, Bickle MJ (1993) Constraining the potential temperature of the Archaean mantle: a review of the evidence from komatiites. Lithos 30:291–307
Niu Y (1997) Mantle melting and melt extraction processes beneath ocean ridges: evidence from abyssal peridotites. J Petrol 38:1047–1074
Niu Y (2004) Bulk-rock major and trace element compositions of abyssal peridotites: implications for mantle melting, melt extraction and post-melting processes beneath mid-ocean ridges. J Petrol 45:2423–2458
Niu Y, Gilmore T, Mackie S, Greig A, Bach W (2002) Mineral chemistry, whole-rock compositions and petrogenesis of ODP Leg 176 gabbros: data and discussion (on line). Proc Ocean Drill Prog Sci Results 176:1–60
Ntaflos T, Tschegg C, Coltorti M, Akinin VV, Kosler J (2008) Asthenospheric signature in fertile spinel lherzolites from the Viliga Volcanic Field in NE Russia. Geological Society, London, Special Publications 293:57–81
O’Hanley DS (1996). Serpentinites: records of tectonic and petrological history. Oxford monographs on geology and geophysics. Oxford University Press, pp 1–277
O’Reilly SY, Griffin WL, Ryan CG (1997) Minor elements in olivine from spinel lherzolite xenoliths; implications for thermobarometry. Mineral Mag 61:257–269
Papanikolaou D (2009) Timing of tectonic emplacement of the ophiolites and terrane paleogeography in the Hellenides. Lithos 108:262–280
Parkinson IJ, Pearce JA (1998) Peridotites from the Izu-Bonin-Mariana forearc (ODP leg 125): Evidence for mantle melting and melt-mantle interaction in a supra-subduction zone setting. J Petrol 39:1577–1618
Parkinson IJ, Pearce JA, Thirlwall MF, Johnson KTM, Ingram G (1992) Trace element geochemistry of peridotites from the Izu–Bonin–Mariana forearc, Leg 125. In: Fryer P, Pearce JA, Stokking LB, et al (eds) Proceedings of the ocean drilling program scientific results, 125. Ocean Drilling Program, College Station, pp 487–506
Parman SW, Dann JC, Grove TL, de Wit MJ (1997) Emplacement conditions of komatiite magmas from the 3.49 Ga Komati Formation. Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa: Earth Planet Sci Lett 150:303–323
Paulick H, Bach W, Godard M, De Hoog JCM, Suhr G, Harvey J (2006) Geochemistry of abyssal peridotites (Mid-Atlantic Ridge, 15°20′N, ODP Leg 209): implications for fluid/rock interaction in slow spreading environments. Chem Geol 234:179–210
Peacock SM (2013) Thermal structure and metamorphic evolution of subducting slabs. In: Inside the subduction factory. Amer Geoph Union 7–22 doi:10.1029/138GM02
Pearce JA, Peate DW (1995) Tectonic implications of the composition of volcanic ARC magmas. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 23:251–285
Pearce JA, Barker PF, Edwards SJ, Parkinson IJ, Leat PT (2000) Geochemistry and tectonic significance of peridotites from the South Sandwich arc-basin system, South Atlantic. Contrib Mineral Petrol 139:36–53
Pelletier L, Vils F, Kalt A, Gméling K (2008) Li, B and Be contents of harzburgites from the dramala complex (Pindos Ophiolite, Greece): evidence for a MOR-type mantle in a supra-subduction zone environment. J Petrol 49:2043–2080
Pe-Piper G, Piper DJW (2002) The igneous rocks of Greece. Borntraeger, Stuttgart, pp 1–645
Pe-Piper G, Tsikouras B, Hatzipanagiotou K (2004) Evolution of boninites and island-arc tholeiites in the Pindos Ophiolite, Greece. Geol Mag 141:455–469
Perraki M, Hoinkes G, Mposkos E, Thoeni M (2003) Early Cretaceous and Tertiary metamorphic events of the Pelagonian Zone in the E. Thessaly area, Greece. Geophys Res Abstracts 5:04438
Pinsent RH, Hirst DM (1977) The metamorphism of the Blue River ultramafic body, Cassiar, British Columbia, Canada. J Petrol 18:567–594
Pomonis P, Tsikouras B, Hatzipanagiotou K (2007) Petrogenetic evolution of the Koziakas ophiolite complex (W. Thessaly, Greece). Mineral Petrol 89:77–111
Putirka K (2008) Thermometers and barometers for volcanic systems. In: Putirka K, Tepley F (eds) Minerals, inclusions and volcanic processes, reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry. Mineral Soc Amer 69:61–120
Rampone E, Piccardo GB (2000) The ophiolite-oceanic lithosphere analogue: new insights from the Northern Apennines (Italy). In: Dilek Y, Moores EM, Elthon D, Nicolas A (eds) Ophiolites and oceanic crust: New insights from field studies and ocean drilling program. Geol Soc Amer Bull 349:21–34
Rasse P (1974) Al and Ti contents of hornblende, indicators of pressure and temperature of regional metamorphism. Contrib Mineral Petrol 45:231–236
Rassios Α (1990) Geology and copper mineralization of the Vrinera area, east Othris ophiolite, Greece. Ofioliti 15:287–304
Renner R (1989) Cooling and crystallisation of komatiite flows from Zimbabwe. Ph.D. thesis, University of Cambridge, pp 1–162
Ridolfi F, Renzulli A, Puerini M (2010) Stability and chemical equilibrium of amphibole in calc-alkaline magmas: an overview, new thermobarometric formulations and application to subduction-related volcanoes. Contrib Mineral Petrol 160:45–66
Robertson AHF (2002) Overview of the genesis and emplacement of Mesozoic ophiolites in the Eastern Mediterranean Tethyan region. Lithos 65:1–67
Robertson AHF (2004) Development of concepts concerning the genesis and emplacement of Tethyan ophiolites in the Eastern Mediterranean and Oman regions. Earth Sci Rev 66:331–387
Robertson AHF (2012) Late Palaeozoic-Cenozoic tectonic development of Greece and Albania in the context of alternative reconstructions of Tethys in the Eastern Mediterranean region. Inter Geol Rev 54:373–454
Robertson AHF, Clift PD, Degnan PJ, Jones G (1991) Palaeogeographic and palaeotectonic evolution of the Eastern Mediterranean Neotethys. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclim Palaeoeco 87:289–343
Robertson AHF, Dixon JE, Brown S, Collins A, Morris A, Pickett E, Sharp I, Ustaomer T (1996) Alternative tectonic models for the Late Paleozoic: Early Tertiary development of Tethys in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 105:239–263
Ross JV, Zimmerman J (1996) Comparison of evolution and tectonic significance of the Pindos and Vourinos ophiolite suites, northern Greece. Tectonophysics 256:1–15
Saccani E, Photiades A (2004) Mid-ocean ridge and supra-subduction affinities in the Pindos ophiolites (Greece): implications for magma genesis in a forearc setting. Lithos 73:229–253
Saccani E, Photiades A (2005) Petrogenesis and tectono-magmatic significance of volcanic and subvolcanic rocks in the Albanide-Hellenide ophiolitic mélanges. Island Arc 14(4):494–516
Saccani E, Photiades A, Beccaluva L (2008) Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of IAT magma-types in the Hellenide ophiolites as deduced from the Rhodiani ophiolites (Pelagonian zone, Greece). Lithos 104:71–84
Sharp IR, Robertson AHF (2006) Tectonic-sedimentary evolution of the western margin of the Mesozoic Vardar Ocean: evidence from the Pelagonian and Almopias zones, northern Greece. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 260:373–412
Shaw DM (1970) Trace element fractionation during anatexis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 34:237–243
Shimizu H, Sangen K, Masuda A (1982) Experimental study on rare-earth element partitioning in olivine and clinopyroxene formed at 10 and 20 kb for basaltic systems. Geochem J 16:107–117
Smith AG (1979) Othris, Pindos and Vourinos ophiolites and the Pelagonian zone. Institute of Geological Mining Research, Athens, Greece. In: 6th Colloquium on the geology of the Aegean region 3:1369–1374
Smith AG (1993) Tectonic significance of the Hellenic-Dinaric ophiolites. In: Prichard HM, Alabaster T, Harris NBW, Neary CR (eds) Magmatic processes and plate tectonics. Geol Soc Spl Publ 76:213–243
Smith AG, Rassios A (2003) The evolution of ideas for the origin and emplacement of the western Hellenic ophiolites, In: Dilek Y, Newcomb S (eds) Ophiolite concept and the evolution of geological thought. Geol Soc Amer Spec Pap 373:337–350
Smith AG, Hynes AJ, Menzies M, Nisbet EG, Price I, Welland MJ, Ferrière J (1975) The stratigraphy of the Othris Mountains, eastern central Greece: a deformed Mesozoic continental margin sequence. Eclogue Geol Helv 68:463–481
Snow JE, Dick HJB (1995) Pervasive magnesium loss by marine weathering of peridotite. Geochim et Cosmochim Acta 59:4219–4235
Spear FS (1993) Metamorphic phase equilibria and pressure-temperature-time paths. Mineral. Soc. Am. Mon. Ser.,Washington, DC, pp 1–799
Stampfli G, Vavassis I, De Bono A, Rosselet F, Matti B, Bellini M (2003) Remnants of the Paleotethys oceanic suture-zone in the western Tethys area. Bolletino della Societa Geologica Italiana Special 2:1–23
Streckeisen AL (1976) To each plutonic rock its proper name. Earth Sci Rev 12:1–33
Tribuzio R, Tiepolo M, Vannucci R, Bottazzi P (1999) Trace element distribution within olivine-bearing gabbros from the Northern Apennine ophiolites (Italy): evidence for post-cumulus crystallization in MOR-type gabbroic rocks. Contrib Mineral Petrol 134:123–133
Welland MJP (1972) The stratigraphy and structure of part of the eastern Ohris mountains, Greece. PhD Dissertation. Cambridge Univ, pp 1–156
Wells PRA (1977) Pyroxene thermometry in simple and complex systems. Contrib Mineral Petrol 62:129–139
Whattam SA, Stern RJ (2011) The ‘subduction initiation rule’: a key for linking ophiolites, intra-oceanic forearcs and subduction initiation. Contrib Mineral Petrol 162:1031–1045
Wicks FJ, Plant AG (1979) Electron-microprobe and x-ray-microbeam studies of serpentine textures. Can Mineral 17:785–830
Witt-Eickschen GE, Seck HA (1991) Solubility of Ca and Al in orthopyroxene from spinel peridotite: an improved version of an empirical geothermometer. Contrib Mineral Petrol 106:431–439
Workman RK, Hart SR (2005) Major and trace element composition of the depleted MORB mantle (DMM). Earth Planet Sci Lett 231:53–72
Zindler A, Hart S (1986) Chemical geodynamics. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 14:493-571
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincerest thanks to Prof. Nikolay Bonev, to an anonymous reviewer and to the Editor in Chief Prof. Wolf-Christian Dullo for their constructive reviews, suggestions and critical comments, which significantly helped us to improve this paper. We gratefully acknowledge Prof. Theodoros Ntaflos (University of Vienna) for assisting with the use of electron microprobe facility and for beneficial discussions. We would like to express our appreciation to SARG (University of Athens) for covering part of field work expenses. Panagiotis A. Chrisanthopoulos (alumnus of Drexel University, PA, USA) is also acknowledged for aiding to improve the English text in the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magganas, A., Koutsovitis, P. Composition, melting and evolution of the upper mantle beneath the Jurassic Pindos ocean inferred by ophiolitic ultramafic rocks in East Othris, Greece. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 104, 1185–1207 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-014-1137-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-014-1137-z