Abstract
Music genre is one of the conventional ways to describe music content, and also is one of the important labels of music information retrieval. Therefore, the effective and precise music genre classification method becomes an urgent need for realizing automatic organization of large music archives. Inspired by the fact that humans have a better automatic recognizing music genre ability, which may attribute to our auditory system, even for the participants with little musical literacy. In this paper, a novel classification framework incorporating the auditory image feature with traditional acoustic features and spectral feature is proposed to improve the classification accuracy. In detail, auditory image feature is extracted based on the auditory image model which simulates the auditory system of the human ear and has also been successfully used in other fields apart from music genre classification to our best knowledge. Moreover, the logarithmic frequency spectrogram rather than linear is adopted to extract the spectral feature to capture the information about the low-frequency part adequately. These above two features and the traditional acoustic feature are evaluated, compared, respectively, and fused finally based on the GTZAN, GTZAN-NEW, ISMIR2004 and Homburg datasets. Experimental results show that the proposed method owns the higher classification accuracy and the better stability than many state-of-the-art classification methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allamy, S., Koerich, A.L.: 1D CNN Architectures for Music Genre Classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:210507302 (2021)
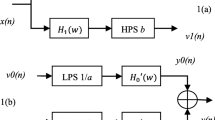
Bleeck, S., Ives, T., Patterson, R.: Aim-mat: the auditory image model in matlab. Acta Acust. Acust. 90, 781–787 (2004)
Boser, B.E., Guyon, I.M., Vapnik, V.N.: A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In: Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Workshop on Computational Learning Theory, pp 144–152 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1145/130385.130401
Cano, P., Gômez, E., Gouyon, F., Herrera, P., Koppenberger, M., Ong, B., Serra, X., Streich, S., Wack, N.: ISMIR 2004 Audio Description Contest. Technical Report. Music Technology Group, Bracelona (2006)
Castillo, J.R., Flores, M.J.: Web-based music genre classification for timeline song visualization and analysis. IEEE Access 9, 18801–18816 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3053864
Chaki, J.: Pattern analysis based acoustic signal processing: a survey of the state-of-art. Int. J. Speech Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-020-09681-3
Chan, W.C., Liang, P.H., Shih, Y.P., Yang, U.C., Chang Lin, W., Hsu, C.N.: Learning to predict expression efficacy of vectors in recombinant protein production. BMC Bioinform. 11(1), 1–12 (2010)
Çoban, Ö., Özyer, G.T.: Music genre classification from turkish lyrics. In: 2016 24th Signal Processing and Communication Application Conference (SIU), pp 101–104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/SIU.2016.7495686
Çoban, Ö.: Turkish music genre classification using audio and lyrics features. Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü Dergisi 21(2), 322–331 (2017)
Corrêa, D.C., Rodrigues, F.A.: A survey on symbolic data-based music genre classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 60, 190–210 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.04.008
Costa, Y., Oliveira, L., Koerich, A., Gouyon, F.: Music genre recognition using spectrograms. In: 2011 18th International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing, pp 1–4 (2011)
Costa, C.H.L., Valle, J.D., Koerich, A.L., Koerich, R.L.: Automatic classification of audio data. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybernet. 1, 562–567 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSMC.2004.1398359
Costa, Y., Oliveira, L., Koerich, A., Gouyon, F., Martins, J.: Music genre classification using lbp textural features. Signal Process. 92(11), 2723–2737 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2012.04.023
Costa, Y., Oliveira, L., Koerich, A., Gouyon, F.: Music genre recognition using gabor filters and lpq texture descriptors. Progress Pattern Recogn. Image Anal. Comput. Vis. Appl. 8259, 67–74 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41827-3_9
Cover, T., Hart, P.: Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 13(1), 21–27 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.1967.1053964
Foleis, J.H., Tavares, T.F.: Texture selection for automatic music genre classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 89, 106–127 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106127
Fu, Z., Lu, G., Ting, K., Zhang, D.: On feature combination for music classification. In: Structural, Syntactic, and Statistical Pattern Recognition, pp 453–462 (2010)
Fu, Z., Lu, G., Ting, K.M., Zhang, D.: A survey of audio-based music classification and annotation. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 13(2), 303–319 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2010.2098858
Glasberg, B., Moore, B.: Derivation of auditory filter shapes from notched-noise data. Hear. Res. 47(1), 103–138 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5955(90)90170-T
Glasberg, B., Moore, B.: Frequency selectivity as a function of level and frequency measured with uniformly exciting notched noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 108(5), 2318–2328 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1315291
Glasberg, B., Moore, B.: A model of loudness applicable to time-varying sounds. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 50, 331–342 (2002)
Gogate, M., Dashtipour, K., Hussain, A.: Visual Speech In Real Noisy Environments (VISION): A Novel Benchmark Dataset and Deep Learning-Based Baseline System. In: Proceeding Interspeech 2020, pp 4521–4525 (2020b). https://doi.org/10.21437/Interspeech.2020-2935
Gogate, M., Dashtipour, K., Adeel, A., Hussain, A.: Cochleanet: a robust language-independent audio-visual model for speech enhancement. Inf. Fus. 63, 273–285 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2020.04.001
Homburg, H., Mierswa, I., Möller, B., Morik, K., Wurst, M.: A benchmark dataset for audio classification and clustering. ISMIR 2005, 528–531 (2005)
Hyder, R., Ghaffarzadegan, S., Feng, Z., Hansen, J., Hasan, T.: Acoustic Scene Classification using a CNN-Supervector System Trained with Auditory and Spectrogram Image Features. pp. 3073–3077 (2017). https://doi.org/10.21437/Interspeech.2017-431
Irino, T., Patterson, R.: A dynamic compressive gammachirp auditory filterbank. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 14(6), 2222–2232 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2006.874669
Kittler, J., Hatef, M., Duin, R.P.W., Matas, J.: On combining classifiers. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 20(3), 226–239 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1109/34.667881
Lee, C.H., Shih, J.L., Yu, K.M., Lin, H.S.: Automatic music genre classification based on modulation spectral analysis of spectral and cepstral features. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 11, 670–682 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2009.2017635
Li, T.L., Chan, A.B.: Genre classification and the invariance of mfcc features to key and tempo. In: International Conference on MultiMedia Modeling, Springer, pp 317–327 (2011)
Li, T., Ogihara, M.: Toward intelligent music information retrieval. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 8(3), 564–574 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2006.870730
Lidy, T., Rauber, A.: Evaluation of feature extractors and psycho-acoustic transformations for music genre classification. In: Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Music Information Retrieval (ISMIR 2005), pp 34–41 (2005)
Lim, S., Lee, J., Jang, S., Lee, S., Kim, M.Y.: Music-genre classification system based on spectro-temporal features and feature selection. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 58(4), 1262–1268 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2012.6414994
Martens, J.P., Leman, M., Baets, B., Meyer, H.: A comparison of human and automatic musical genre classification. IEEE Int. Conf. Acoustics Speech Signal Process. 4, 233–236 (2004)
McKay, C., Fujinaga, I.: Improving automatic music classification performance by extracting features from different types of data. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Information Retrieval. pp. 257–266 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1145/1743384.1743430
Mitrović, D., Zeppelzauer, M., Breiteneder, C.: Features for content-based audio retrieval. In: Advances in Computers: Improving the Web, vol 78, Elsevier. pp .71–150 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2458(10)78003-7
Muller, F., Mertins, A.: On using the auditory image model and invariant-integration for noise robust automatic speech recognition. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). pp. 4905–4908 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2012.6289019
Munkong, R., Juang, B.: Auditory perception and cognition. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 25(3), 98–117 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2008.918418
Nanni, L., Costa, Y., Lumini, A., Kim, M.Y., Baek, S.R.: Combining visual and acoustic features for music genre classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 45, 108–117 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.09.018
Nanni, L., Costa, Y., Lucio, D., Silla, C., Brahnam, S.: Combining visual and acoustic features for audio classification tasks. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 88, 49–56 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2017.01.013
Nonaka, R., Emoto, T., Abeyratne, U.R., Jinnouchi, O., Kawata, I., Ohnishi, H., Akutagawa, M., Konaka, S., Kinouchi, Y.: Automatic snore sound extraction from sleep sound recordings via auditory image modeling. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 27, 7–14 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2015.12.009
Nosaka, R., Suryanto, C.H., Fukui, K.: Rotation invariant co-occurrence among adjacent lbps. In: Park, J.I., Kim, J. (eds.) Computer Vision - ACCV 2012 Workshops, pp. 15–25. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Ojala, T., Pietikainen, M., Maenpaa, T.: Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(7), 971–987 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2002.1017623
Ojansivu, V., Heikkilä, J.: Blur insensitive texture classification using local phase quantization. In: Elmoataz, A., Lezoray, O., Nouboud, F., Mammass, D. (eds.) Image and Signal Processing, pp. 236–243. Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Panagakis, Y., Kotropoulos, C.L., Arce, G.R.: Music genre classification using locality preserving non-negative tensor factorization and sparse representations. In: ISMIR, pp 249–254 (2009)
Panagakis, Y., Kotropoulos, C.L., Arce, G.R.: Music genre classification via joint sparse low-rank representation of audio features. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Language Process. 22(12), 1905–1917 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASLP.2014.2355774
Patterson, R., Robinson, K., Holdsworth, J., McKeown, D., Zhang, C., Allerhand, M.: Complex sounds and auditory images. In: Cazals, Y., Horner, K., Demany, L. (eds) Auditory Physiology and Perception, Pergamon. pp. 429–446 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-041847-6.50054-X
Patterson, R.D., Allerhand, M.H., Giguère, C.: Time-domain modeling of peripheral auditory processing: a modular architecture and a software platform. Acoust. Soc. Am. J. 98(4), 1890–1894 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1121/1.414456
Perrot, D., Gjerdigen, R.: Scanning the dial: an exploration of factors in the identification of musical style. In: Proceedings of the 1999 Society for Music Perception and Cognition, p 88 (1999)
Qiu, L., Li, S., Sung, Y.: 3D-DCDAE: Unsupervised music latent representations learning method based on a deep 3d convolutional denoising autoencoder for music genre classification. Mathematics 9(18), 2274 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/math9182274
Qiu, L., Li, S., Sung, Y.: DBTMPE: Deep bidirectional transformers-based masked predictive encoder approach for music genre classification. Mathematics 9(5), 530 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/math9050530
Schindler, A., Rauber, A.: An audio-visual approach to music genre classification through affective color features. In: Hanbury A, Kazai G, Rauber A, Fuhr N (eds) Advances in Information Retrieval. pp. 61–67 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16354-3_8
Sturm, B.L.: The GTZAN dataset: its contents, its faults, their effects on evaluation, and its future use. CoRR abs/1306.1461:1–29 (2013)
Tsaptsinos, A.: Lyrics-based music genre classification using a hierarchical attention network. CoRR abs/1707.04678 (2017)
Tzanetakis, G., Cook, P.: Musical genre classification of audio signals. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 10(5), 293–302 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSA.2002.800560
Wright, J., Yang, A.Y., Ganesh, A., Sastry, S.S., Ma, Y.: Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 31(2), 210–227 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2008.79
Wu, M., Chen, Z., Jang, J.R., Ren, J., Li, Y., Lu, C.: Combining visual and acoustic features for music genre classification. In: 2011 10th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications and Workshops, vol 2, pp. 124–129 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMLA.2011.48
Yang, H., Zhang, W.Q.: Music genre classification using duplicated convolutional layers in neural networks. In: Proc. Interspeech 2019, pp. 3382–3386 (2019). https://doi.org/10.21437/Interspeech.2019-1298
Ylioinas, J., Hadid, A., Guo, Y., Pietikäinen, M.: Efficient image appearance description using dense sampling based local binary patterns. In: Lee, K.M., Matsushita, Y., Rehg, J.M., Hu, Z. (eds.) Computer Vision - ACCV 2012, pp. 375–388. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Yu, Y., Luo, S., Liu, S., Qiao, H., Liu, Y., Feng, L.: Deep attention based music genre classification. Neurocomputing 372, 84–91 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.09.054
Zhao, G., Ahonen, T., Matas, J., Pietikainen, M.: Rotation-invariant image and video description with local binary pattern features. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(4), 1465–1477 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2011.2175739
Acknowledgements
We thank all the referees and the editorial board members for their insightful comments and suggestions, which improved our paper significantly. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Grants No. 11501351.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Pala.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, X., Zhang, H. Music genre classification based on auditory image, spectral and acoustic features. Multimedia Systems 28, 779–791 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-021-00886-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-021-00886-3