Abstract
With the introduction of ChatGPT, the public’s perception of AI-generated content has begun to reshape. Artificial intelligence has significantly reduced the barrier to entry for non-professionals in creative endeavors, enhancing the efficiency of content creation. Recent advancements have seen significant improvements in the quality of symbolic music generation, which is enabled by the use of modern generative algorithms to extract patterns implicit in a piece of music based on rule constraints or a musical corpus. Nevertheless, existing literature reviews tend to present a conventional and conservative perspective on future development trajectories, with a notable absence of thorough benchmarking of generative models. This paper provides a survey and analysis of recent intelligent music generation techniques, outlining their respective characteristics and discussing existing methods for evaluation. Additionally, the paper compares the different characteristics of music generation techniques in the East and West as well as analysing the field’s development prospects.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Agres K, Forth J, Wiggins GA (2016) Evaluation of musical creativity and musical metacreation systems. Comput Entertain CIE 14(3):1–33 (Publisher: ACM New York, NY, USA)
Avdeeff M (2019) Artificial intelligence and popular music: SKYGGE, flow machines, and the audio uncanny valley. In: Arts, volume 8, page 130. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute. Issue: 4
Berthelot D, Schumm T, Metz L (2017) Began: Boundary equilibrium generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.10717
Briot J-P, Hadjeres G, Pachet F-D (2020) Deep learning techniques for music generation. Springer International Publishing, Cham, Computational Synthesis and Creative Systems
Brunner G, Konrad A, Wang Y, Wattenhofer R (2018) MIDI-VAE: Modeling dynamics and instrumentation of music with applications to style transfer. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.07600
Brunner G, Wang Y, Wattenhofer R, Wiesendanger J (2017) JamBot: music theory aware chord based generation of polyphonic music with LSTMs. In: 2017 IEEE 29th international conference on tools with artificial intelligence (ICTAI), pp 519–526, Boston, MA. IEEE
Brunner G, Wang Y, Wattenhofer R, Zhao S (2018) Symbolic music genre transfer with CycleGAN. arXiv:1809.07575 [cs, eess, stat]
Budzianowski P, Vuli I (2019) Hello, It’s GPT-2—How can i help you? Towards the use of pretrained language models for task-oriented dialogue systems
Carnovalini F, Rodà A (2020) Computational creativity and music generation systems: an introduction to the state of the art. Front Artif Intell 3:14
Chen K, Zhang W, Dubnov S, Xia G, Li W (2019) The effect of explicit structure encoding of deep neural networks for symbolic music generation. In: 2019 International workshop on multilayer music representation and processing (MMRP), pp 77–84. IEEE
Choi K, Hawthorne C, Simon I, Dinculescu M, Engel J (2020) Encoding musical style with transformer autoencoders. In: International conference on machine learning, pp 1899–1908. PMLR
Chu H, Urtasun R, Fidler S (2016) Song From PI: a musically plausible network for pop music generation. arXiv:1611.03477 [cs]
De Prisco R, Zaccagnino G, Zaccagnino R (2020) EvoComposer: an evolutionary algorithm for 4-voice music compositions. Evolution Comput 28(3):489–530 (Publisher: MIT Press One Rogers Street, Cambridge, MA 02142-1209, USA journals-info)
Dhariwal P, Jun H, Payne C, Kim JW, Radford A, Sutskever I. Jukebox: a generative model for music. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.00341
Donahue C, McAuley J, Puckette M (2019b) Adversarial audio synthesis. arXiv:1802.04208 [cs]
Delgado M, Fajardo W, Molina-Solana M (2009) Inmamusys: Intelligent multiagent music system. Exp Syst Appl 36(3):4574–4580
Dong H-W, Hsiao W-Y, Yang L-C, Yang Y-H (2018) Musegan: Multi-track sequential generative adversarial networks for symbolic music generation and accompaniment. In: Thirty-second AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Dong H-W, Yang Y-H (2018) Convolutional generative adversarial networks with binary neurons for polyphonic music generation. arXiv:1804.09399 [cs, eess, stat]
Dong H-W, Yang Y-H (2019) Generating Music with GANs https://salu133445.github.io/ismir2019tutor ial/pdf/ismir2019-tutorial-slides.pdf. Accessed 11 Jan 2022
Engel J, Resnick C, Roberts A, Dieleman S, Norouzi M, Eck D, Simonyan K (20170) Neural audio synthesis of musical notes with waveNet autoencoders. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (pp. 1068-1077). PMLR
Engel J, Agrawal KK, Chen S, Gulrajani I, Donahue C, Roberts A (2019) Gansynth: Adversarial neural audio synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.08710
Farzaneh M, Toroghi RM. GGA-MG: Generative genetic algorithm for music generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.04687
Fux JJ, Edmunds J (1965) The study of counterpoint from Johann Joseph Fux’s Gradus ad parnassum. Number 277. WW. Norton & Company
Gillick J, Roberts A, Engel J, Eck D, Bamman D (2019) Learning to groove with inverse sequence transformations. In: International conference on machine learning (pp. 2269–2279). PMLR
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial nets. In: Adv Neural Inf Process Syst, 27
Guan F, Yu C, Yang S (2019) A GAN model with self-attention mechanism to generate multi-instruments symbolic music. In: 2019 International joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN)
Hadjeres G, Nielsen F (2017) Interactive music generation with positional constraints using anticipation-RNNs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1709.06404
Hadjeres G, Pachet F, Nielsen F (2017) DeepBach: a steerable model for bach chorales generation. In: International conference on machine learning, pp 119–127.PMLR
Han C, Murao K, Noguchi T, Kawata Y, Uchiyama F, Rundo L, Nakayama H, Satoh S (2019) Learning more with less: Conditional PGGAN-based data augmentation for brain metastases detection using highly-rough annotation on MR images. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International conference on information and knowledge management, pp 119–127
Herremans D, Chew E (2019) MorpheuS: generating structured music with constrained patterns and tension. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 10(4):510–523
Herremans D, Chuan C-H, Chew E (2017) A functional taxonomy of music generation systems. ACM Comput Surv 50(5):1–30
Hu X, Lee JH (2012, October) A cross-cultural study of music mood perception between american and chinese listeners. In: ISMIR (pp. 535–540)
Hu X, Yang Y-H (2017) The mood of Chinese Pop music: pepresentation and recognition. J Assoc Inf Sci Technol
Huang A, Wu R (2016) Deep learning for music. arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.04930
Huang C-F, Lian Y-S, Nien W-P, Chieng W-H (2016) Analyzing the perception of Chinese melodic imagery and its application to automated composition. Multimedia Tools Appl 75(13):7631–7654
Huang C-ZA, Cooijmans T, Roberts A, Courville A, Eck D (2019) Counterpoint by convolution. arXiv preprint arXiv:1903.07227
Huang C-Z A, Vaswani A, Uszkoreit J, Shazeer N, Simon I, Hawthorne C, Dai AM, Hoffman MD, Dinculescu M, Eck D (2018) Music transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.04281
Huang S, Li Q, Anil C, Oore S, Grosse RB (2019) Timbretron: A wavenet (cyclegan (cqt (audio))) pipeline for musical timbre transfer. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.09620
Jaques N, Gu S, Turner RE, Eck D (2017) Tuning recurrent neural networks with reinforcement learning
Jeong J, Kim Y, Ahn CW (2017) A multi-objective evolutionary approach to automatic melody generation. Exp Syst Appl 90:50–61 (Publisher: Elsevier)
Jhamtani H, Berg-Kirkpatrick T (2019) Modeling self-repetition in music generation using generative adversarial networks. In: Machine learning for music discovery workshop, ICML
Jiang J (2019) Stylistic melody generation with conditional variational auto-encoder
Jiang J, Xia GG, Carlton DB, Anderson CN, Miyakawa RH (2020) Transformer VAE: a hierarchical model for structure-aware and interpretable music representation learning. In: ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp 516–520. ISSN: 2379-190X
Jie CHEN (2015) Comparative study between Chinese and western music aesthetics and culture
Jin C, Tie Y, Bai Y, Lv X, Liu S (2020) A style-specific music composition neural network. Neural Process Lett 52(3):1893–1912
Kaliakatsos-Papakostas M, Floros A, Vrahatis MN (2020) Artificial intelligence methods for music generation: a review and future perspectives. Nat Inspired Comput Swarm Intell, pp 217–245. Publisher: Elsevier
Kaliakatsos-Papakostas MA, Floros A, Vrahatis MN (2016) Interactive music composition driven by feature evolution. SpringerPlus 5(1):1–38 (Publisher: Springer)
Keerti G, Vaishnavi A, Mukherjee P, Vidya AS, Sreenithya GS, Nayab D (2020) Attentional networks for music generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.03854
Kumar H, Ravindran B (2019) Polyphonic Music composition with LSTM neural networks and reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.01973
Leach J, Fitch J (1995) Nature, music, and algorithmic composition. Comput Music J 19(2):23–33 (Publisher: JSTOR)
Liang X, Wu J, Cao J (2019) MIDI-Sandwich2: RNN-based Hierarchical Multi-modal Fusion Generation VAE networks for multi-track symbolic music generation. arXiv:1909.03522 [cs, eess]. arXiv: 1909.03522
Lin P-C, Mettrick D, Hung PC, Iqbal F (2018) Towards a music visualization on robot (MVR) prototype. In: 2018 IEEE international conference on artificial intelligence and virtual reality (AIVR), pp 256–257. IEEE
Liu H-M, Yang Y-H (2018) Lead sheet generation and arrangement by conditional generative adversarial network. arXiv:1807.11161 [cs, eess]
Lopes HB, Martins FVC, Cardoso RT, dos Santos VF (2017) Combining rules and proportions: A multiobjective approach to algorithmic composition. In: 2017 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (CEC), pp 2282–2289. IEEE
Loughran R, O’Neill M (2020) Evolutionary music: applying evolutionary computation to the art of creating music. Genet Program Evol Mach 21(1):55–85 (Publisher: Springer)
Lousseief E, Sturm BLT, Sturm BL (2019) MahlerNet: Unbounded Orchestral Music with Neural Networks. In: the Nordic sound and music computing conference 2019 and the interactive sonification workshop (pp. 57–63)
Lu C-Y, Xue M-X, Chang C-C, Lee C-R, Su L (2019) Play as you like: timbre-enhanced multi-modal music style transfer. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell 33:1061–1068
Luo J, Yang X, Ji S, Li J (2019) MG-VAE: Deep Chinese folk songs generation with specific regional style. arXiv:1909.13287 [cs, eess]
Makris D, Kaliakatsos-Papakostas M, Karydis I, Kermanidis KL (2019) Conditional neural sequence learners for generating drums’ rhythms. Neural Comput Appl 31(6):1793–1804
Manzelli R, Thakkar V, Siahkamari A, Kulis B (2018) Conditioning deep generative raw audio models for structured automatic music. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.09905
Manzelli R, Thakkar V, Siahkamari A, Kulis B (2018) An end to end model for automatic music generation: Combining deep raw and symbolic audio networks. In: Proceedings of the musical metacreation workshop at 9th international conference on computational creativity, Salamanca, Spain
Medeot G, Cherla S, Kosta K, McVicar M, Abdallah S, Selvi M, Newton-Rex E, Webster K (2018) StructureNet: inducing structure in generated melodies. In: ISMIR, pp 725–731
Mogren O (2016) C-RNN-GAN: Continuous recurrent neural networks with adversarial training. arXiv:1611.09904 [cs]
Mura D, Barbarossa M, Dinuzzi G, Grioli G, Caiti A, Catalano MG (2018) A soft modular end effector for underwater manipulation.: a gentle, adaptable grasp for the ocean depths. IEEE Robot Autom Mag , 4:1–1
Muñoz E, Cadenas JM, Ong YS, Acampora G (2014) Memetic music composition. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 20(1):1–15 (Publisher: IEEE)
Olseng O, Gambäck B (2018) Co-evolving melodies and harmonization in evolutionary music composition. In: International conference on computational intelligence in music, sound, art and design, pp 239–255. Springer
Oord Avd, Dieleman S, Zen H, Simonyan K, Vinyals O, Graves A, Kalchbrenner N, Senior A, Kavukcuoglu K (2016) WaveNet: a generative model for raw audio. arXiv:1609.03499 [cs]
Oore S, Simon I, Dieleman S, Eck D, Simonyan K (2020) This time with feeling: learning expressive musical performance. Neural Comput Appl 32(4):955–967
Payne C (2019) MuseNet.OpenAI Blog. https://openai.com/blog/musenet/. Accessed 11 Jan 2022
Plut C, Pasquier P (2020) Generative music in video games: state of the art, challenges, and prospects. Entertain Comput 33:100337 (Publisher: Elsevier)
Ramanto AS, No JG, Maulidevi DNU. Markov chain based procedural music generator with user chosen mood compatibility. In: Int J Asia Digital Art Des Assoc, 21(1):19–24
Rivero D, Ramírez-Morales I, Fernandez-Blanco E, Ezquerra N, Pazos A (2020) Classical music prediction and composition by means of variational autoencoders. Appl Sci 10(9):3053
Roberts A, Engel J, Raffel C, Hawthorne C, Eck D (2018) A hierarchical latent vector model for learning long-term structure in music. In: International conference on machine learning (pp 4364–4373). PMLR
Scirea M, Togelius J, Eklund P, Risi S (2016) Metacompose: A compositional evolutionary music composer. In: International conference on computational intelligence in music, sound, art and design, pp 202–217. Springer
Sturm BL, Ben-Tal O, Monaghan Ú, Collins N, Herremans D, Chew E, Hadjeres G, Deruty E, Pachet F (2019) Machine learning research that matters for music creation: a case study. J New Music Res 48(1):36–55 (Publisher: Taylor & Francis)
Sturm BL, Santos JF, Ben-Tal O, Korshunova I (2016) Music transcription modelling and composition using deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1604.08723
Supper M (2001) A few remarks on algorithmic composition. Comput Music J 25(1):48–53
Tapus A (2009) The role of the physical embodiment of a music therapist robot for individuals with cognitive impairments: longitudinal study. In: 2009 Virtual rehabilitation international conference, pp 203–203. IEEE
Trieu N, Keller RM (2018) JazzGAN: Improvising with generative adversarial networks. In: MUME 2018: 6th international workshop on musical metacreation
Valenti A, Carta A, Bacciu D (2020) Learning style-aware symbolic music representations by adversarial autoencoders. arXiv:2001.05494 [cs, stat]
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. In: Adv Neural Inf Process Syst, pp 5998–6008
Veblen K, Olsson B (2002) Community music: toward an international overview. The new handbook of research on music teaching and learning, pp 730–753
Waite E, others (2016) Generating long-term structure in songs and stories. Web blog post. Magenta, 15(4)
Wang B, Yang Y-H (2019) PerformanceNet: score-to-audio music generation with multi-band convolutional residual network. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell 33:1174–1181
Williams D, Hodge VJ, Gega L, Murphy D, Cowling PI, Drachen A (2019) AI and automatic music generation for mindfulness, p 11
Wu C-W, Liu J-Y, Yang Y-H, Jang J-SR (2018) Singing style transfer using cycle-consistent boundary equilibrium generative adversarial networks. arXiv:1807.02254 [cs, eess]
Yang L-C, Chou S-Y, Yan Y-H (2017) Midinet: A convolutional generative adversarial network for symbolic-domain music generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.10847
Yu Y, Srivastava A, Canales S (2021) Conditional LSTM-GAN for melody generation from lyrics. ACM Trans Multimedia Comput Commun Appl 17(1):1–20 arXiv:1908.05551
Zhang N (2020) Learning adversarial transformer for symbolic music generation. IEEE, Publisher, IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems
Zhu H, Liu Q, Yuan NJ, Qin C, Li J, Zhang K, Zhou G, Wei F, Xu Y, Chen E (2018) XiaoIce Band: a melody and arrangement generation framework for pop music. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 2837–2846, London United Kingdom. ACM
Zhu J-Y, Park T, Isola P, Efros AA (2017) Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2223–2232
Zipf GK (2016) Human behavior and the principle of least effort: an introduction to human ecology. Ravenio Books
Hiller Jr LA, Isaacson LM (1957) Musical composition with a high speed digital computer. In: Audio engineering society convention 9. Audio Engineering Society
Cope D (1991) Recombinant music: using the computer to explore musical style. Computer 24(7):22–28
Miranda ER, Al Biles J (2007) Evolutionary computer music. Springer, Berlin
Wei S, Xia G (2022) Learning long-term music representations via hierarchical contextual constraints. arXiv:2202.06180 [cs, eess]
Guo R, Simpson I, Kiefer C, Magnusson T, Herremans D (2022) MusIAC: An extensible generative framework for music infilling applications with multi-level control. arXiv:2202.05528 [cs]
Dong H-W, Chen K, Dubnov S, McAuley J, Berg-Kirkpatrick T (2023) Multitrack music transformer. arXiv:2207.06983 [cs, eess]
Dubnov S, Chen K, Huang K. Deep musical information dynamics: novel framework for reduced neural-network music
Yu B, Lu P, Wang R, Hu W, Tan X, Ye W, Zhang S, Qin T, Liu T-Y (2022) Museformer: transformer with fine- and coarse-grained attention for music generation. arXiv:2210.10349 [cs, eess]
Zou Y, Zou P, Zhao Y, Zhang K, Zhang R, Wang X (2021) MELONS: generating melody with long-term structure using transformers and structure graph. arXiv:2110.05020 [cs, eess]
Schäfer T, Sedlmeier P, Städtler C, Huron D (2013) The psychological functions of music listening. Front Psychol 4:511
Ji S, Yang X, Luo J (2023) A survey on deep learning for symbolic music generation: representations, algorithms, evaluations, and challenges. ACM Comput Surv
Chrome Music Lab, Chrome’s Song Maker. Accessed 22 Oct 2023, from https://musiclab.chromeexperiments.com/Song-Makerx
Aiva Technologies SARL. (Copyright 2016-2023). AIVA. Accessed 22 Oct 2023, from https://www.aiva.ai/
Choi K, Park J, Heo W, Jeon S, Park J (2021) Chord conditioned melody generation with transformer based decoders. IEEE Access 9:42071–42080. Conference Name: IEEE Access
Lee S-g, Hwang U, Min S, Yoon S (2018) Polyphonic music generation with sequence generative adversarial networks. arXiv:1710.11418 [cs, eess]
Mangal S, Modak R, Joshi P (2019) LSTM based music generation system. IARJSET 6(5):47–54 arXiv:1908.01080 [cs, eess, stat]
Shin A, Crestel L, Kato H, Saito K, Ohnishi K, Yamaguchi M, Nakawaki M, Ushiku Y, Harada T (2017) Melody generation for pop music via word representation of musical properties. arXiv:1710.11549 [cs, eess]
Wada Y, Nishikimi R, Nakamura E, Itoyama K, Yoshii K (2018) Sequential generation of singing F0 contours from musical note sequences based on WaveNet. In: 2018 Asia-Pacific signal and information processing association annual summit and conference (APSIPA ASC), pp 983–989. ISSN: 2640-0103
Matsue J (2015) Focus: music in contemporary Japan. Routledge
Mok AO (2014) East meets west: Learning-practices and attitudes towards music-making of popular musicians. Br J Music Educ 31(2):179–194
Nooshin L, Widdess R (2006) Improvisation in Iranian and Indian music. J Indian Musicol Soc 36:104–119
Son JH (2015) Pagh-paan’s no-ul: Korean identity formation as synthesis of eastern and western music
Repetto RC, Pretto N, Chaachoo A, Bozkurt B, Serra X (2018) An open corpus for the computational research of arab-andalusian music. In: Proceedings of the 5th international conference on digital libraries for musicology, pp 78–86
Srinivasamurthy A, Gulati S, Repetto RC, Serra X (2021) Saraga: open datasets for research on indian art music. Emp Musicol Rev 16(1):85–98
Howard K (2016) Music as intangible cultural heritage: policy, ideology, and practice in the preservation of East Asian traditions. Routledge. Google-Books-ID: LYUWDAAAQBAJ
Carnovalini F, Rodà A (2020) Computational creativity and music generation systems: an introduction to the state of the art. Front Artif Intell, 3
Ji S, Luo J, Yang X (2020) A comprehensive survey on deep music generation: multi-level representations, algorithms, evaluations, and future directions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2011.06801
Donahue C, Mao HH, Li YE, Cottrell GW, McAuley J (2019) LakhNES: Improving multi-instrumental music generation with cross-domain pre-training. arXiv:1907.04868 [cs, eess, stat]
Simon I, Roberts A, Raffel C, Engel J, Hawthorne C, Eck D (2018) Learning a latent space of multitrack measures. arXiv:1806.00195 [cs, eess, stat]
Thickstun J, Harchaoui Z, Kakade S (2016) Learning features of music from scratch. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.09827
Acknowledgements
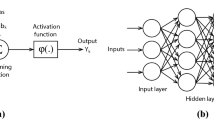
Figure 4-11 are cited from relevant paper on music generation, and we extend our sincere appreciation to the authors for their contribution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Methodology: LW; Formal analysis and investigation: ZZ; Writing—original draft preparation: ZZ, HL; Data curation: JP; Writing—review and editing: YQ, SL, ZZ; Supervision: QW, LW; Funding acquisition: LW.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Zhao, Z., Liu, H. et al. A review of intelligent music generation systems. Neural Comput & Applic 36, 6381–6401 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09418-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09418-2